Uses the skills of specialized employees who move from product to product, or customer to customer, as needed.
In practice, there can be many problems with a matrix structure. The disadvantages:
Lacks a control structure that allows staff to develop stable expectations of each other
Staff can be put off by the ambiguity and role conflict produced
Potential conflict between function s and product or customer teams over time.
6.1.6 Deciding on a structure
Notice how each phase influences the other over time. The sequences are not always inevitable or linear. Each phase is neither right nor wrong. They are signposts to guide the organization. By understanding the current state, senior executives are better able to decide in what direction, and how far, to move along the centralized-decentralized spectrum.
The key to applying service management organizational development is understanding the following:
Where the organization is in the sequence
The range of appropriate options
Each solution will bring new challenges.
6.1.7 Organizational change
No matter what type of change the organization decides on, there remains the problem of getting the organization to change. Implementing change can be thought of as a three-step process , as in Figure 6.9.
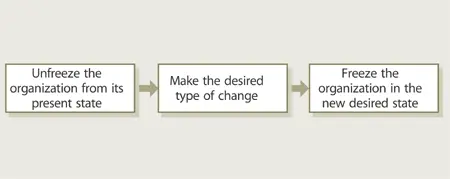
Figure 6.9 Three-step change process
Resistance to change will force the organization to revert to previous behaviours unless steps are taken to refreeze the new changes. Role and task changes are not enough. Managers must actively manage the process.
1. The first step to change is diagnosis . Namely, acknowledge the need for change and the factors prompting it. For example, complaints about service quality have increased or operating costs have escalated. Or morale is low while turnover is high. There is little point in focusing on improving costs if the customer is concerned about quality.
2. The second step is determining the desired state. While this can be a difficult planning process with alternative courses of action, it begins with the organization ’s strategy and desired structure. Is the strategy based on reducing costs or improving quality ? Should the organization adopt a product or geographic structure?
3. The third step is implementation. This three-step process begins with identifying possible impediments to change . What obstacles are anticipated? For example, functional managers may resist reductions in power or prestige. The more severe the change then the greater the difficulties encountered. Next, decide who will be responsible for implementing changes and controlling the change process. These change agents can be external, as in consultants, or internal, as in knowledgeable managers. External change agents tend to be more objective and less likely to be perceived to be influenced by internal politics, while internal agents tend to have greater local knowledge. Last, decide on which change strategy will most effectively unfreeze, change and refreeze the organization. These techniques fall into two categories: top-down and bottom-up. Top-down is a dramatic restructuring by senior managers while bottom-up is a gradual change by low-level employees. Example techniques include:
Education and communication
Participation and empowerment
Facilitation
Bargaining and negotiation
Process consultation
Team building and inter-group training.
6.2 Organizational departmentalization
It is common to think of organizational hierarchies in terms of function s. As the functional groups become larger, think of them in terms of departmentalization. A department can loosely be defined as an organizational activity involving over 20 people. When a functional group grows to departmental size, the organization can reorient the group to one of the following areas or a hybrid thereof:
Function – preferred for specialization, the pooling of resource s and reducing duplication
Product – preferred for servicing businesses with strategies of diverse and new products, usually manufacturing business es
Market space or customer – preferred for organizing around market structures. Provides differentiation in the form of increased knowledge of and response to customer preferences
Geography – the use of geography depends on the industry. By providing services in close geographical proximity, travel and distribution costs are minimized while local knowledge is leveraged
Process – preferred for an end-to-end coverage of a process.
Certain basic structures are preferred for certain service strategies, as shown in Table 6.1.
Basic structure
Strategic considerations
Functional
Specialization
Common standards
Small size
Product
Product focus
Strong product knowledge
Market space or customer
Service unique to segment
Customer service
Buyer strength
Rapid customer service
Geography
On-site services
Proximity to customer for delivery and support
Organization perceived as local
Process
Need to minimize process cycle times
Process excellence
Table 6.1 Basic organizational structures
6.3 Organizational design
The starting point for organizational design is strategy (Figure 6.10). It sets the direction and guides the criteria for each step of the design process.
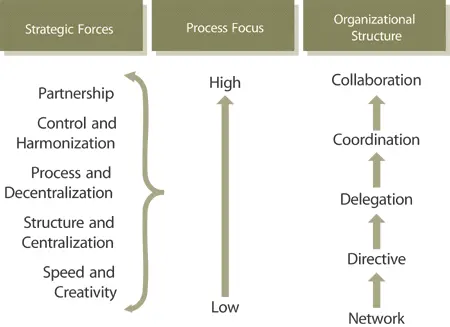
Figure 6.10 Matching strategic forces with organizational development
It is recommended to decide on a departmentalization structure prior to designing key processes. For example, if the provider’s organization will be structured by geography or aligned by customers, the process design will be guided by this criterion. Once key processes are understood, it is appropriate to begin organizational design (Figure 6.11).
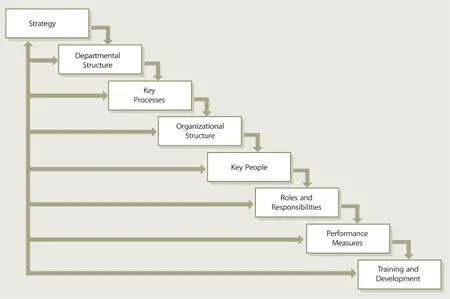
Figure 6.11 Organizational design steps
The flow depends on clearly articulated strategic criteria. Processes can be thought of as organizational software – configurable to the requirement s of a service strategy . Organizational designers should see each step as an iterative cycle: create basic processes and structures, learn about current and new conditions, and adjust as learning evolves.
6.4 Organizational culture
Organizational culture is the set of shared values and norms that control the IT organization’s interactions with each other and customers. Just as an organizational structure can improve performance , so, too, can an organization’s culture increase organizational effectiveness .
There are two types of organizational values: terminal and instrumental.
Terminal values are desired outcomes or end states. IT organizations can adopt any of the following as terminal values: quality , excellence, reliability , innovativeness or profitability. Terminal values are often reflected in the organization’s strategic perspective.
Instrumental values are desired modes of behaviour. IT organizations can adopt any of the following as instrumental values: high standards, respecting tradition and authority, acting cautiously and conservatively, or being frugal.
Читать дальше



