Figure 5.4 Shared services
Utility-based Provisioningmaximizes the combination of services being provisioned over the same infrastructure so that even more services are provisioned utilizing the same resources found in the Shared Services model. This is accomplished by providing services on a utility basis, dependent on how much, how often, and at what times the customer needs them. (N.B. The term ‘utility’ is used here with a very specific meaning, different from the meaning used in the rest of the publication.) Examples of such services would include an accounting application with primary usage at the end of each month, a reporting service that receives heavy usage only around the 1st and 15th of each month, or a production-related service used only in every other production cycle as production line outputs are changed.
This service provisioning model is the most cost-effective and the most elusive in that it requires a level of knowledge and capability missing from many IT organizations today. These cost savings are achieved primarily through leveraging a deeper understanding of technology architecture s and customer needs in order to compile a service combination and architecture that enables maximum utilization of existing resources.
On-shore , Off-shore or Near-shore ?The advent of off-shore service provisioning and its related success is not new. However, companies are still finding that what represents an off-shore opportunity for one firm may not necessarily be an opportunity for another. Many service elements discussed in this publication (and others discussed in the Service design , Service Transition and Service Operation s publications) are combined in an analysis of what mix of on-shore, near-shore and off-shore service provisioning is right for a specific company at a specific time.
The Financial Management impact on this decision cannot be underestimated. If a company does not understand its core service cost components and variable cost dynamics , it will typically have a difficult time making logical and fact-based decisions regarding outsourcing models, and an equally difficult time asking the right questions of providers.
Service provisioning cost analysisis the activity of statistically ranking the various forms of provisioning (and often providers) to determine the most beneficial model. A simplified example of a comparative service provisioning cost analysis that accounts for the way provisioning models could impact the cost of a service is provided. Table 5.1 is a simplified example of service cost component s for the Service Desk function and how they come into play within the analysis of various provisioning models.
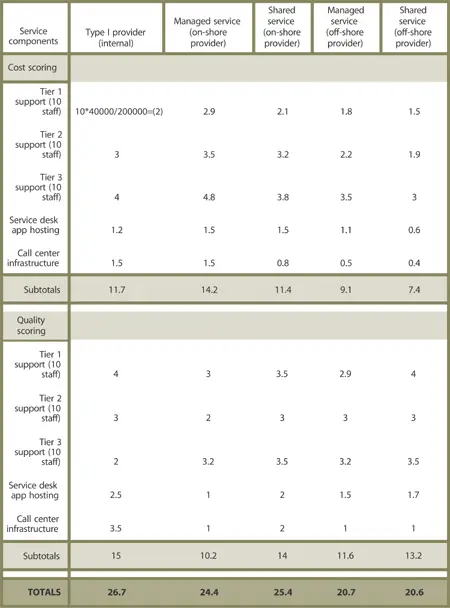
Click on image above to view a larger version in a new browser window
In this example, the scoring mechanism is normalized to a five-point scale where the lowest score is preferred. Notice that the company has ranked itself lower in some service components relative to the service quality and cost it has determined to be available in the market from alternative providers. If only the simplified overall scores for each provider are assessed, the off-shore shared services provider appears to offer the lowest cost and highest quality for the entire portfolio of services. On closer inspection, however, the same provider offers the same tiered support service quality as the company’s existing Type I provider in all areas except Tier 3 support, estimated to be inferior to the provider.
Given that existing internal Tier 1 support has been ranked among the bottom of all alternatives, and existing Tier 3 internal support is actually superior, this provider may not offer the correct combination of cost and quality. Similar deficiencies and strengths are evident throughout the provisioning scoring example above. What conclusions can you draw from the scoring? What are some possible causes for the scoring in the presented sections? What optimize d provisioning model would you conclude to be the most applicable for this company to adopt, given its current strengths and weaknesses?
5.1.3.3 Funding model alternatives
Funding addresses the financial impact s from changes to current and future demand for IT service s and the way in which IT will retain the funds to continue operations. This section offers a high-level discussion of various traditional models for the funding of IT Services. Since each model assumes a different perspective, yet rests on the same financial data, an increased ability to generate the requisite information translates to increased visibility into service costs and perceived value. The model chosen should always take into account and be appropriate for the current business culture and expectations.
Rolling Plan Funding– In a rolling plan , as one cycle completes another cycle of funding is added. This plan encourages a constant cycle of funding. However, it only addresses timing and does not necessarily increase accuracy. This type of model for funding would work well with a Service Lifecycle treatment where a commitment to fund a service is made at the beginning of the lifecycle and rolls until changes are made or the lifecycle has ended.
Trigger-Based Plans– Trigger-based funding occurs when identified critical triggers occur and set off planning for a particular event . For example, the Change Management process would be a trigger to the planning process for all approved changes that have financial impacts. Another trigger might be Capacity Planning where insight into capacity variance s would affect the financial translation of IT Services. This type of planning alleviates timing issues with accounting for past events, since the process requires future planning at the time of the change. It would be a good plan to use with portfolio service management since it deals with services on a lifecycle basis.
Zero-Based Funding– This funding refers to how funding of IT occurs. Funding is only enough to bring the balance of the IT financial centre back to zero or to bring the balance of the funding of a service back to zero until another funding cycle. This equates to funding only the actual costs to deliver the IT Service s.
5.1.3.4 Business Impact Analysis (BIA)
A BIA seeks to identify a company’s most critical business service s through analysis of outage severity translated into a financial value, coupled with operational risk . This information can help shape and enhance operational performance by enabling better decision making regarding prioritization of incident handling, problem management focus, change and release management operations, project priority , and so on. It is a beneficial tool for identifying the cost of service outage to a company, and the relative worth of a service. These two concepts are not identical.
The cost of service outage is a financial value placed on a specific service, and is meant to reflect the value of lost productivity and revenue over a specific period of time. The worth of a service relative to other services in a portfolio may not result exclusively from financial characteristics. Service Value, as discussed earlier, is derived from characteristics that may go beyond Financial Management , and represent aspects such as the ability to complete work or communicate with client s that may not be directly related to revenue generation. Both of these elements can be identified to a very adequate degree by the use of a BIA. While this section will discuss and illustrate the output of, and approach to creating a BIA, the reader should realize that the examples of BIA format and output represented here are not the only options, and alternative formats are visible throughout industry.
Читать дальше


