The pricing of a service is the cost-to-value translation necessary to achieve clarity and influence the demand and consumption of services. The activity involves identifying the cost baseline for services and then quantifying the perceived value added by a provider’s service asset s in order to conclude a final service value. The primary goal of Service Valuation is to produce a value for services that the business perceives as fair, and fulfils the needs of the provider in terms of supporting it as an ongoing concern. A secondary objective is the improved management of demand and consumption behaviour. It is helpful to restate what constitutes service value so that the translation to price can be more easily dissected:
‘Value is created when service providers are able to deploy their capabilities and resource s (i.e. service assets), and with a certain level of assurance, deliver to the customer a greater utility of their services. As established earlier, this utility is in the form of enhancing or enabling the performance of customer assets, and contributing to the realization of business outcomes.’
Within this definition, the service value elements of warranty and utility require translation of their value to an actual monetary figure. Therefore service valuation focuses primarily on two key valuation concepts:
Provisioning Valueis the actual underlying cost to IT related to provisioning a service, including all fulfilment elements, both tangible and intangible. Input comes from financial system s, and consists of payment for actual resource s consumed by IT in the provisioning of a service. These cost element s include items such as:
Hardware and software licence costs
Annual maintenance fees for hardware and software
Personnel resources used in the support or maintenance of a service
Utilities, data centre or other facilities charges
Taxes, capital or interest charges
Compliance costs.
The sum of these actual service costs typically represents the baseline from which the minimum value of a service is calculated since providers are seldom willing to offer a service where they are unable to recover the provisioning cost. Of course there are exceptions to this, especially related to Type I providers in situations where alternatives for provisioning of a specific service are limited or non-existent.
Service Value Potentialis the value-added component based on the customer’s perception of value from the service or expected marginal utility and warranty from using the service, in comparison with what is possible using the customer’s own assets (Figure 5.2). Provisioning Value elements add up first to establish a baseline. The value-added components of the service are then monetized individually according to their perceived value to estimate the true value of the service package . All of these components would then be summed along with the baseline costs to determine the ultimate value of the service. The interrelated concepts of provisioning value and perceived service value potential are illustrated in Figure 5.2.
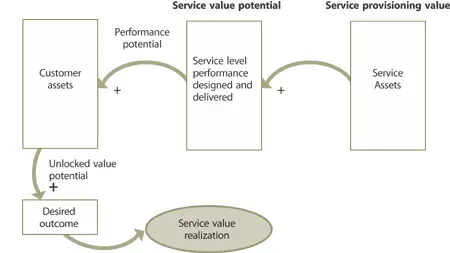
Figure 5.2 Customer assets are the basis for defining value
Provisioning Value elements are typically easier to quantify due to availability of purchasing and human resources (HR) information. However, a number of techniques are available to assist with the identification of service value potential, and are addressed elsewhere in this publication and the Service Design publication. The evolution of traditional accounting methods toward a service-oriented approach that supports the decomposition and valuation of value potential component s is discussed later in this section.
5.1.2.2 Demand modelling
Poorly managed service demand is a source of cost and risk . The tight coupling of service demand and capacity (consumption and production) requires Financial Management to quantify funding variations resulting from changes in service demand. Financial demand modelling focuses on identifying the total cost of utilization (TCU) to the customer , and predicting the financial implications of future service demand. The Service Catalogue provides critical information on service demand for modelling, decision making, and control .
Demand modelling uses service-oriented financial information with factors of demand and supply in order to model anticipated usage by the business , and provisioning requirement s by IT. This is for identifying funding requirements, variations and driver s of those variations, and to assist in the management of service demand. In this context, inputs for managing service demand include pricing and incentive adjustments that are intended to alter customer consumption patterns. Without critical demand data from Capacity Management and the Service Catalogue , translated into financial requirements, this is not possible.
Mature service organizations are able to apply the practice of Service valuation to their Service Catalogue to establish a value for each service , service component, and service level package . This enables the capability to generate demand plan s and related financial requirement s for expected service consumption. This service demand planning is translated to financial funding requirements for the entire enterprise at a business unit level or lower, and consumption of both services and budget s can be viewed in real time through an extension of the Service Catalogue.
Through the application of Financial Management, the Service Catalogue is able to provide customers with the capability to regulate their demand and prepare budgets. This partly addresses the problem of over-consumption by business and subsequent dissonance with the value of the service. Capacity Planning also provides important information related to service demand by providing usage data and trend reporting largely from a technical component perspective (think bandwidth, resource s, processing capacity etc. that carry a financial impact ), and by tracking significant expected variance s in demand related to strategic event s such as product launches, entry into new markets, and acquisitions or divestitures. Demand modelling can leverage data from capacity management because of the tight coupling.
5.1.2.3 Service Portfolio Management
Financial Management is a key input to Service portfolio management . By understanding cost structures applied in the provisioning of a service, a company can benchmark that service cost against other providers. In this way, companies can use IT financial information, together with service demand and internal capability information, discussed previously, to make beneficial decisions regarding whether a certain service should be provisioned internally. For instance, if a company identifies its internal cost of providing ‘Service A’ to be £50 per month per user , and then finds a provider with the economics of scale and the focused skill set required to offer the identical service for £33 per month, the company may decide that it would rather focus its resources on other services where it possesses a greater ability to offer lower cost and/or higher quality , and to outsource Service A to the other provider.
Читать дальше

