Warranties in general are part of the value proposition that influences customers to buy. For customers to realize the expected benefits of manufactured goods utility is necessary but not sufficient. Defects and malfunctions make a product either unavailable for use or diminish its functional capacity. Warranties assure the products will retain form and function for a specified period under certain specified conditions of use and maintenance. Warranties are void outside such conditions. Normal wear and tear is not covered. Most importantly, customers are owners and operators of purchased goods.
In the case of services, the customers are neither the owners nor the operators of service asset s that provide utility. That responsibility is with service providers along with maintenance and improvements. Customers simply utilize the service. There is no wear and tear, misuse, neglect, and damage of service assets limiting the validity of warranty.
Service providers communicate the value of warranty in terms of levels of certainty. Their ability to manage service assets instils confidence in the customer about the support for business outcomes. Warranty is stated in terms of the availability , capacity , continuity and security of the utilization of services.
3.1.5.1 Availability
Availability is the most elementary aspect of assuring value to customers. It assures the customer that services will be available for use under agreed terms and conditions. The availability of a service is its most readily perceived attribute from a user ’s perspective. A service is available only if users can access it in an agreed manner. Perceptions and preferences vary by customer and by business context. The customer is responsible for managing the expectations and needs of its users. Within specified conditions, such as area of coverage, periods, and delivery channels, services are expected to be available to users that the customer authorizes.
Availability of a service is more subtle than a binary evaluation of available and unavailable. The customer’s tolerance for graceful degradation of availability should be determined and factored into service design . For example, if a subset of user s is responsible for a vital business function , service instances for these users can be hosted on dedicated resource s with fault tolerance so that the customer retains some critical capability to operate .
3.1.5.2 Capacity
Capacity is an assurance that the service will support a specified level of business activity or demand at a specified level of quality . Customer s drive business activity with the assurance of adequate capacity. Variations in demand are accommodated within an agreed range. Service provider s undertake to maintain resources to give customers freedom from capacity shortfalls and underutilized asset s. Capacity is of particular importance where the utility of the service arises from access to shared resources. Service providers help customers with shortages during periods of peak-demand.
Guaranteed capacity during particular periods or at particular locations is also valuable to customers who need to start up new or expanded operations with time-to-market as a critical success factor . Such business plan s require low set-up costs and lead times. Additionally, due to the high-risks of new or expanded operations, customers may prefer not to make the investments required to own and operate business assets. Business es that face highly uncertain demand from their own customers also find value in services on demand with little or no latency. Opportunity cost s are high in terms of lost customers.
Without effective management of capacity, service providers will not be able to deliver the utility of most services. Capacity Management is a critical aspect of service management because it has a direct impact on the availability of services. The capacity available to support services also has an impact on the level of service continuity committed or delivered. Effective management of service capacity can therefore have first-order and second-order effects on service warranty .
3.1.5.3 Continuity
Continuity assures the service will continue to support the business through major failure s or disruptive event s. The service provider undertakes to maintain service asset s that will provide a sufficient level of contingency and recovery . Specialized systems and processes will kick in to ensure that the service level s received by the customer’s assets do not fall below a predefined level. Assurance also includes the restoration or normalcy in a predefined time to limit the overall impact of a failure or event. Continuity is assured primarily through redundancy and dedicated resources isolated from ripple effects.
3.1.5.4 Security
Security assures that the utilization of services by customers will be secure. This means that customer assets within the scope of service delivery and support will not be exposed to certain risk s. Service providers undertake to implement general and service-level controls that will ensure that the value provided to customers is complete and not eroded by any avoidable costs and risks. Service security covers the following aspects of reducing risks:
Authorized and accountable usage of services as specified by customer
Protection of customers’ asset s from unauthorized or malicious access
Security zones between customer assets and service assets.
Service security plays a supporting role to the other three aspects of service warranty. Effectiveness in security has a positive impact on those aspects.
Service security inherits all the general properties of the security of physical and human assets, and intangibles such as data, information, coordination, and communication. Service security has challenges imposed by the following characteristics of service management:
Service asset s are typically shared by more than one customer entity
Value is delivered just-in-time through the orchestration of several service assets
Customer action or inaction is a source of security risk s.
3.1.6 Combined effect of utility and warranty
Value creation is the combined effect of utility and warranty . Value for customers can be increased by either of the two factors. Both are necessary: neither is sufficient by itself. Each should be considered a separate factor of value creation (Figure 3.7).
The ability to deliver a certain level of warranty to customers by itself is a basis of competitive advantage for service provider s. This is particularly true where services are commoditized or standardized. In such cases, it is hard to differentiate value largely in terms of utility for customers. When customers have a choice between service providers whose services provide more or less the same utility but different levels of warranty, then they prefer the greater certainty in the support of business outcomes.
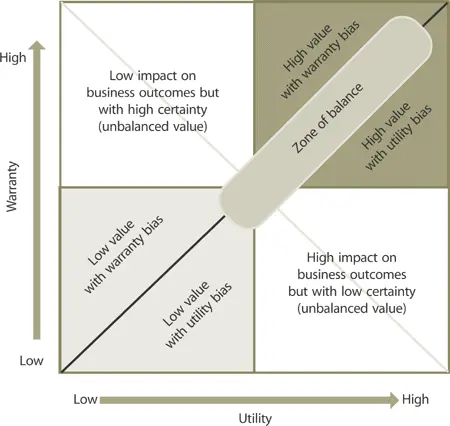
Figure 3.7 Combined effects of utility and warranty on customer assets
‘Fewest calls dropped on average’ is the value proposition of one major provider of mobile communication services expressed in its advertisements. An equally large competitor counteracts with the value proposition of best available coverage in the majority of urban areas. The other perpetual basis of differentiation is the number of calls made for a flat fee within peak hours of usage. This is an indirect measure of the capacity of over-subscribed service assets that service providers are assuring for the exclusive use of their customers. Of course, when competitive action leads to reduced differentiation based on warranty, service providers respond with service package s that offer additional utility , such the GPS navigation or wireless email on mobile phones.
Читать дальше

