Dr. Pass - Economics
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Dr. Pass - Economics» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Economics
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Economics: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Economics»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Economics — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Economics», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Asymmetry of information is likely to lead to ADVERSE SELECTION or to MORAL HAZARD in transactions. Asymmetric information also applies to the principal-agent relationship (see AGENCY COST) where the principal cannot observe the agent’s level of effort. See PRINCIPAL-AGENT THEORY.
ATMsee AUTOMATIC TELLER MACHINE.
atomistic competitionsee PERFECT COMPETITION.
attributes modelsee PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS/ATTRIBUTES MODEL.
auctiona means of selling goods and services to the highest bidder among a number of potential customers. Auctions can take several forms. One form is an open auction, increasing bid, competition in which the bids of all parties are observable and bidders drop out as the price increases until only the highest bidder remains. Another form is an open auction, decreasing price, auction in which the auctioneer starts off from a very high price that is then slowly decreased until one bidder agrees to buy at the last announced price. This form of auction is often called a ‘Dutch auction’. Yet another form is a sealed-bid, closed auction in which all bidders have to submit their bids in sealed envelopes at the same time. In open auctions, bidders can gain some information about the private valuations that other bidders place upon the goods to be sold, while in sealed-bid auctions the private valuations of bidders remain unobservable. The principles of auctions apply to situations where firms seek tenders to supply products.
auditthe legal requirement for a JOINT-STOCK COMPANY to have its BALANCE SHEET and PROFIT-AND-LOSS ACCOUNT (the financial statements) and underlying accounting system and records examined by a qualified auditor, so as to enable an opinion to be formed as to whether such financial statements show a true and fair view and that they comply with the relevant statutes. See also ENVIRONMENTAL AUDIT, VALUE FOR MONEY AUDIT.
Austrian schoola group of late 19th-century economists at the University of Vienna who established and developed a particular line of theoretical reasoning. The tradition originated with Professor Carl Menger who argued against the classical theories of value, which emphasized PRODUCTION and SUPPLY. Instead, he initiated the ‘subjectivist revolution’, reasoning that the value of a good was not derived from its cost but from the pleasure, or UTILITY, that the CONSUMER can derive from it. This type of reasoning led to the MARGINAL UTILITY theory of value whereby successive increments of a commodity yield DIMINISHING MARGINAL UTILITY.
Friedrich von Wieser developed the tradition further, being credited with introducing the economic concept of OPPORTUNITY COST. Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk helped to develop the theory of INTEREST and CAPITAL, arguing that the price paid for the use of capital is dependent upon consumers’ demand for present CONSUMPTION relative to future consumption. Ludwig von Mises and Friedrich von Hayek subsequently continued the tradition established by Carl Menger et al. See also CLASSICAL ECONOMICS.
authorized or registered or nominal share capitalthe maximum amount of SHARE CAPITAL that a JOINT-STOCK COMPANY can issue at any time. This amount is disclosed in the BALANCE SHEET and may be altered by SHAREHOLDERS at the company ANNUAL GENERAL MEETING. See also ISSUED SHARE CAPITAL.
automatic (built-in) stabilizerselements in FISCAL POLICY that serve to automatically reduce the impact of fluctuations in economic activity. A fall in NATIONAL INCOME and output reduces government TAXATION receipts and increases its unemployment and social security payments. Lower taxation receipts and higher payments increase the government’s BUDGET DEFICIT and restore some of the lost income (see CIRCULAR FLOW OF NATIONAL INCOME MODEL). See FISCAL DRAG.
automatic teller machine (ATM)a cash point (‘hole in the wall’) facility in which a banker’s card can be used by a customer of a COMMERCIAL BANK or BUILDING SOCIETY to withdraw cash both inside and outside banking hours. The ‘Link’ network enables customers to use their cards in the ATMs of other banks as well as their own.
automatic vendinga means of retailing products to consumers via vending machines. Automatic vending has been employed extensively in selling, for instance, food, beverages and cigarettes. The use of vending machines has also become prominent in the banking/building society sector as a means of dispensing cash.
automationthe use of mechanical or electrical machines, such as robots, to undertake frequently repeated production processes to make them self-regulating, thus minimizing or eliminating the use of labour in these processes. Automation often involves high initial capital investment but, by reducing labour costs, cuts VARIABLE COST per unit. See FLEXIBLE MANUFACTURING SYSTEM, PRODUCTIVITY, TECHNOLOGICAL PROGRESSIVENESS, CAPITAL-LABOUR RATIO, MASS PRODUCTION, COMPUTER.
autonomous consumptionthat part of total CONSUMPTION expenditure that does not vary with changes in NATIONAL INCOME or DISPOSABLE INCOME. In the short term, consumption expenditure consists of INDUCED CONSUMPTION (consumption expenditure that varies directly with income) and autonomous consumption. Autonomous consumption represents some minimum level of consumption expenditure that is necessary to sustain a basic standard of living and which consumers would therefore need to undertake even at zero income. See CONSUMPTION SCHEDULE.
autonomous investmentthat part of real INVESTMENT that is independent of the level of, and changes in, NATIONAL INCOME. Autonomous investment is mainly dependent on competitive factors such as plant modernization by businesses in order to cut costs or to take advantages of a new invention. See INDUCED INVESTMENT, INVESTMENT SCHEDULE.
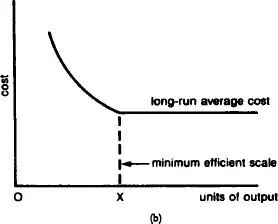
Fig. 10 Average cost (long-run).(a) The characteristic U-shape of the long-run average cost curve. (b)The characteristic L-shaped curve that in practice normally results from expansion.
average cost (long-run)the unit cost (TOTAL COST divided by number of units produced) of producing outputs for plants of different sizes. The position of the SHORT-RUN average total cost (ATC) curve depends on its existing size of plant. In the long run, a firm can alter the size of its plant. Each plant size corresponds to a different U-shaped short-run ATC curve. As the firm expands its scale of operation, it moves from one curve to another. The path along which the firm expands – the LONG-RUN ATC curve – is thus the envelope curve of all the possible short-run ATC curves. See Fig. 10 (a).
It will be noted that the long-run ATC curve is typically assumed to be a shallow U-shape, with a least-cost point indicated by output level OX. To begin with, average cost falls (reflecting ECONOMIES OF SCALE); eventually, however, the firm may experience DISECONOMIES OF SCALE and average cost begins to rise.
Empirical studies of companies’ long-run average-cost curves, however, suggest that diseconomies of scale are rarely encountered within the typical output ranges over which companies operate, so that most companies’ average cost curves are L-shaped, as in Fig. 10 (b). In cases where diseconomies of scale are encountered, the MINIMUM EFFICIENT SCALE at which a company will operate corresponds to the minimum point of the long-run average cost curve (Fig. 10 (a)). Where diseconomies of scale are not encountered within the typical output range, minimum efficient scale corresponds with the output at which economies of scale are exhausted and constant returns to scale begin (Fig. 10 (b)). Compare AVERAGE COST (SHORT-RUN).
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Economics»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Economics» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Economics» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












