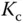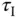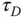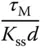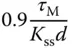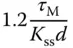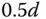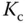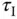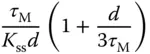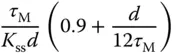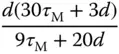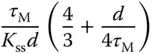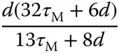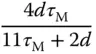Liuping Wang - PID Control System Design and Automatic Tuning using MATLAB/Simulink
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Liuping Wang - PID Control System Design and Automatic Tuning using MATLAB/Simulink» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:PID Control System Design and Automatic Tuning using MATLAB/Simulink
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
PID Control System Design and Automatic Tuning using MATLAB/Simulink: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «PID Control System Design and Automatic Tuning using MATLAB/Simulink»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
PID Control System Design and Automatic Tuning using MATLAB Provides unique coverage of PID Control of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), including mathematical models of multi-rotor UAVs, control strategies of UAVs, and automatic tuning of PID controllers for UAVs
Provides detailed descriptions of automatic tuning of PID control systems, including relay feedback control systems, frequency response estimation, Monte-Carlo simulation studies, PID controller design using frequency domain information, and MATLAB/Simulink simulation and implementation programs for automatic tuning Includes 15 MATLAB/Simulink tutorials, in a step-by-step manner, to illustrate the design, simulation, implementation and automatic tuning of PID control systems Assists lecturers, teaching assistants, students, and other readers to learn PID control with constraints and apply the control theory to various areas. Accompanying website includes lecture slides and MATLAB/ Simulink programs
is intended for undergraduate electrical, chemical, mechanical, and aerospace engineering students, and will greatly benefit postgraduate students, researchers, and industrial personnel who work with control systems and their applications.

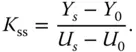
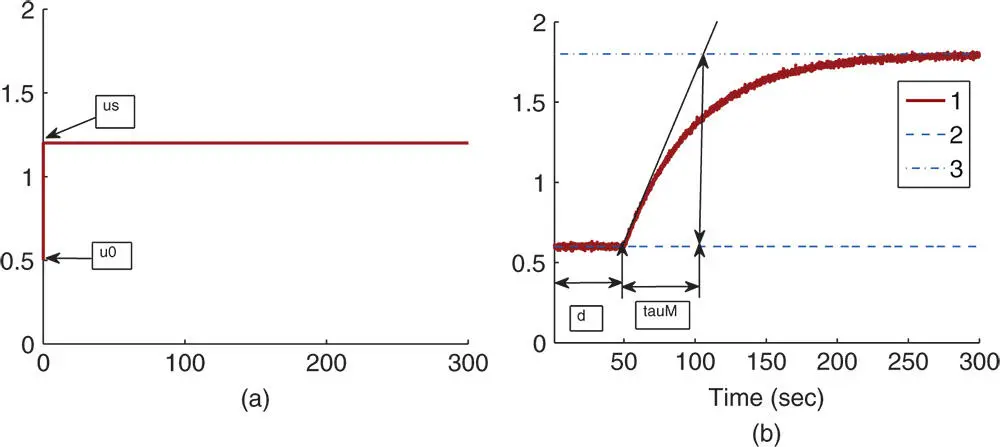
 ); line (3) steady-state output position in completion of the response (
); line (3) steady-state output position in completion of the response ( 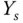 ).
).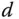 is shown in the figure, which is the delayed time when the output responds to the change in the input signal. The parameter time delay
is shown in the figure, which is the delayed time when the output responds to the change in the input signal. The parameter time delay 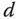 reflects the situation that the output response remains unchanged despite the step input signal being injected. Thus, it is estimated using the time difference between when the step reference change occurred (
reflects the situation that the output response remains unchanged despite the step input signal being injected. Thus, it is estimated using the time difference between when the step reference change occurred ( 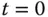 for this figure) and when the output response moved away from its steady-state value (see the time interval in Figure 1.14(b) marked with the first set of arrows). A line with maximum slope is drawn on Figure 1.14(b), which is intersected with the line corresponding to the indicator of
for this figure) and when the output response moved away from its steady-state value (see the time interval in Figure 1.14(b) marked with the first set of arrows). A line with maximum slope is drawn on Figure 1.14(b), which is intersected with the line corresponding to the indicator of 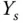 . The intersecting point shown in Figure 1.14(b) determines the value of
. The intersecting point shown in Figure 1.14(b) determines the value of 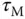 that is a measurement of the dynamic response time.
that is a measurement of the dynamic response time.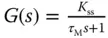 ) to a unit step input signal can be expressed as
) to a unit step input signal can be expressed as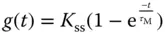
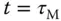 ,
,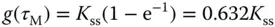
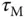 using 63.2% of the rising time in the step response. This estimation of time constant gives a different value from the case when using the maximum slope approach. For the majority of the applications, this will result in a smaller time constant
using 63.2% of the rising time in the step response. This estimation of time constant gives a different value from the case when using the maximum slope approach. For the majority of the applications, this will result in a smaller time constant 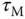 , and from the empirical tuning rules stated in the later part of the section, a smaller proportional gain
, and from the empirical tuning rules stated in the later part of the section, a smaller proportional gain 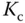 will follow. One can evaluate this approach as an exercise using Problem 1.2.
will follow. One can evaluate this approach as an exercise using Problem 1.2.