The track below the GENCODE track is the RefSeq gene predictions from NCBI track. This is a composite track showing human protein-coding and non-protein-coding genes taken from the NCBI RNA reference sequences collection (RefSeq; Box 1.2). By default, the RefSeq track is shown in dense mode, with the exons of the individual transcripts condensed into a single line ( Figure 4.2). Note that, in this dense mode, the exons are displayed as blocks, as in the GENCODE track, but there are no arrowheads on the gene model to show the direction of transcription. To change the display of the RefSeq track to view individual transcripts, open the Track Settings page for the NCBI RefSeq track by clicking on the track name in the first row of the Genes and Gene Predictions section (below the graphical view shown in Figure 4.2). The resulting Track Settings page ( Figure 4.4) allows the user to choose which type of RefSeqs to display (e.g. all, curated only, or predicted only). In this example, we change the mode of the RefSeq Curated track from dense to full , and the resulting graphical view ( Figure 4.5) displays each curated RefSeq as a separate transcript. In contrast to the GENCODE track, there are only three RefSeq transcripts for the HIF1A gene, and the HIF1A-AS2 RefSeq transcript is much shorter than the GENCODE transcript with the same name. These discrepancies are due to differences in how the RefSeq and GENCODE transcript sets are assembled ( Boxes 1.2and 4.2).

Figure 4.3 The genomic context of the human HIF1A gene, after clicking on zoom out 3× . The genes immediately upstream ( FLJ22447 ) and downstream ( SNAPC1 ) of HIF1A are now visible.
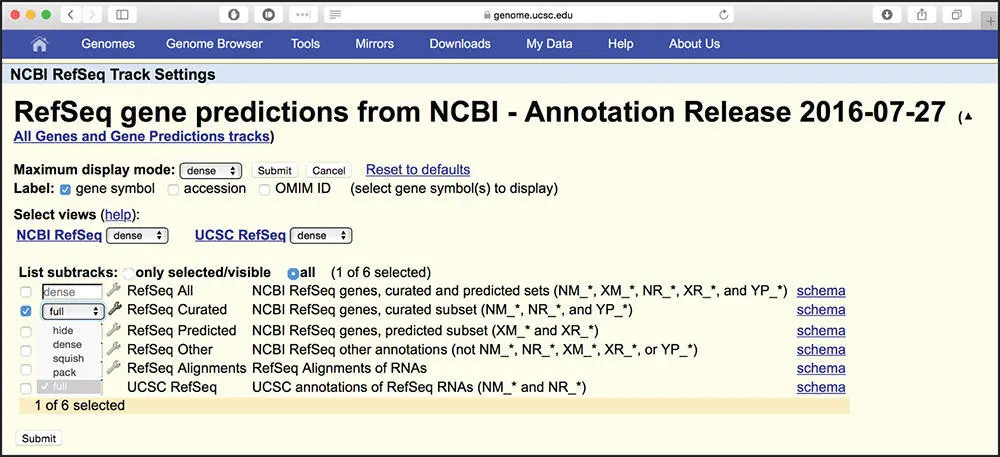
Figure 4.4 The RefSeq Track Settings page. The track settings pages are used to configure the display of annotation tracks. By default, all of the RefSeq tracks are set to display in dense mode, with all features condensed into a single line. In this example, the Curated RefSeqs are being set to display in full mode, in which each RefSeq transcript will be labeled and displayed on a separate line. The remainder of the RefSeqs will be displayed in dense mode. The types of RefSeqs, curated and predicted, are described in Box 1.2. After changing the settings, press the submit button to apply them.
Additional information about each transcript in the GENCODE and RefSeq tracks is available by clicking on the gene symbol ( HIF1A , in this case); as the original search was for HIF1A , the gene name is highlighted in inverse type. For GENCODE genes, UCSC has collected information from a variety of public sources and includes a text description, accession numbers, expression data, protein structure, Gene Ontology terms, and more. For RefSeq transcripts, UCSC provides links to NCBI resources. Both GENCODE and RefSeq details pages provide a link to Genomic Sequence in the Sequence and Links section, allowing users to retrieve genomic sequences connected to an individual transcript. From the selection menu ( Figure 4.6), users can choose whether to download the sequence upstream or downstream of the gene, as well as the exon or intron sequence. The sequence is returned in FASTA format.
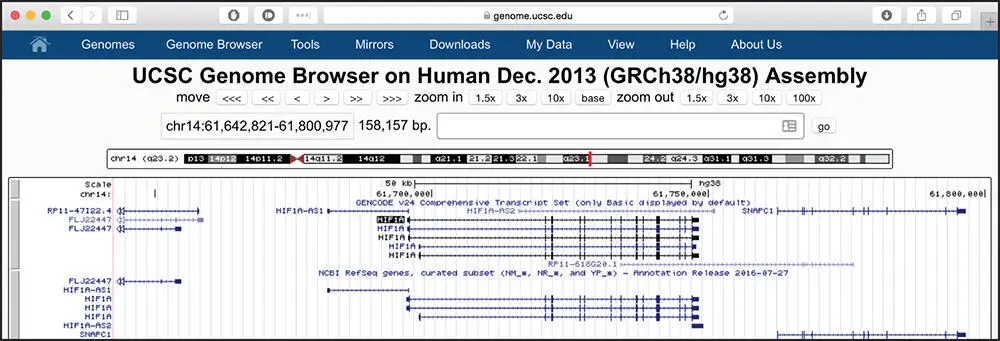
Figure 4.5 The genomic context of the human HIF1A gene, after displaying RefSeq Curated genes in full mode. Each RefSeq transcript is now drawn on a separate line, so that individual exons, as well as the direction of transcription, are visible. Compare this rendition with Figure 4.2, where all RefSeq transcripts are condensed on a single line.
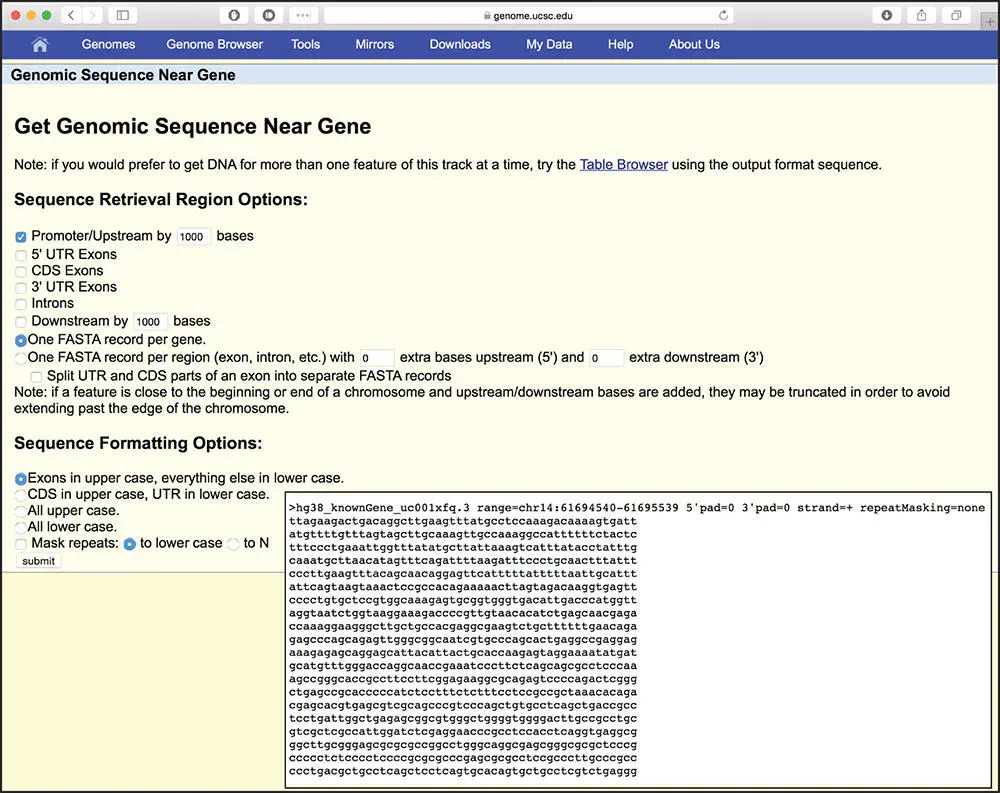
Figure 4.6 The Get Genomic Sequence page that provides an interface for users to retrieve the sequence for a feature of interest. Click on an individual transcript in the GENCODE or RefSeq track to open a page with additional details for that transcript. On either of those details pages, click the link for Genomic Sequence to open the page displayed here, which provides choices for retrieving sequences upstream or downstream of the transcript, as well as intron or exon sequences. In this example, retrieve the sequence 1000 nt upstream of the annotated transcription start site. Shown in the inset is the result of retrieving the FASTA-formatted sequence 1000 nt upstream of the HIF1A transcript.
Further down on the graphical view shown in Figure 4.3are tracks from the ENCODE Regulation super-track: Layered H3K27Ac and DNase Clusters . These data were generated by the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) Consortium between 2003 and 2012 (ENCODE Project Consortium 2012). The ENCODE Consortium has developed reagents and tools to identify all functional elements in the human genome sequence. The Layered H3K27Ac track indicates regions where there are modified histones that may indicate active enhancers ( Box 4.3).
Histone proteins package DNA into chromosomes. Post-translational modifications of these histones can affect gene expression, as well as DNA replication and repair, by changing chromatin structure or recruiting histone modifiers (Lawrence et al. 2016). The post-translational modifications include methylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, ubiquitylation, and sumoylation. Histone H3 is primarily acetylated on lysine residues, methylated at arginine or lysine, or phosphorylated on serine or threonine. Histone H4 is primarily acetylated on lysine, methylated at arginine or lysine, or phosphorylated on serine.
Histone modification (or “marking”) is identified by the name of the histone, the residue on which it is marked, and the type of mark. Thus, H3K27Ac is histone H3 that is acetylated on lysine 27, while H3K79me2 is histone H3 that is dimethylated on lysine 79. Different histone marks are associated with different types of chromatin structure. Some are more likely found near enhancers and others near promoters and, while some cause an increase of expression from nearby genes, others cause less. For example, H3K4me3 is associated with active promoters, and H3K27me3 is associated with developmentally controlled repressive chromatin states.
The DNase Clusters track depicts regions where chromatin is hypersensitive to cutting by the DNaseI enzyme. In these hypersensitive regions, the nucleosome structure is less compacted, meaning that the DNA is available to bind transcription factors. Thus, regulatory regions, especially promoters, tend to be DNase sensitive. The track settings for the ENCODE Regulation super-track allows other ENCODE tracks to be added to the browser window, including additional histone modification and DNaseI hypersensitivity data. Changing the display of the H3K4Me3 peaks from hide to full highlights the peaks in the H3K4Me3 track near the 5′ ends of the HIF1A and SNAPC1 transcripts that overlap with DNase hypersensitive sites ( Figure 4.7, blue highlights). These peaks may represent promoter elements that regulate the start of transcription.
Читать дальше








