Example 4.2 (Operating context for a passenger ship)
For a passenger ship, the operating context is continuously changing with the operation and the location of the ship. The environmental conditions, such as wind, visibility, waves, and current will change frequently. Depending on where the ship is traveling, more or less extreme environmental conditions may occur. It may also be exposed to subzero temperatures, causing icing, and may meet icebergs or icefloes. Further, when navigating close to shore, the ship has to avoid shallow waters where it can ground. A completely different operating context is when the ship is in port, loading and unloading passengers and cargo. When designing the ship, all the extremes of the operating context have to be considered, but in operation, the context will vary from hour to hour (or even more quickly) and operation has to continuously adapt to these variations.
In military applications, the concept of operations (CONOPS) document describes the operating context of the item.
4.4 System Modeling and Analysis
A system analysis is always based on a model, which is a simplification of the system or of one or more properties of the system. Many types of models are available. Among these are system structure models, also called architecture models, functional models, state transition models, and so on. System modeling helps the analyst to understand the structure and functionality of the system. Models may further be used to communicate with other stakeholders to the risk assessment. The IEV defines a model as follows:
Mathematical or physical representation of a system or a process, based with sufficient precision upon known laws, identification, or specified suppositions (IEV 351‐42‐26).
An example of a model is a map of a terrain. The model (the map) provides a lot of information about the system, but it will always be a simplification compared to the real world. The information that is included is still useful for navigating.
Models can be established for elements at all levels of systems. Models for the lowest level, the components, are usually black box models. In a black box model, the component is not decomposed to any lower‐level parts and only the inputs and possible outputs for each component function are considered, as shown in Figure 4.3.
 Figure 4.3Black box model for a component function.
Figure 4.3Black box model for a component function.
The system modeling process is shown in Figure 4.4. The modeling process is, in this book, started by studying a technical or sociotechnical system, sometimes based on an existing system, but most often based on drawings and system information/data. A number of regular and potential dynamic processes take place in the system (represented by the curved arrow in Figure 4.4). These processes include failures and hazardous events.
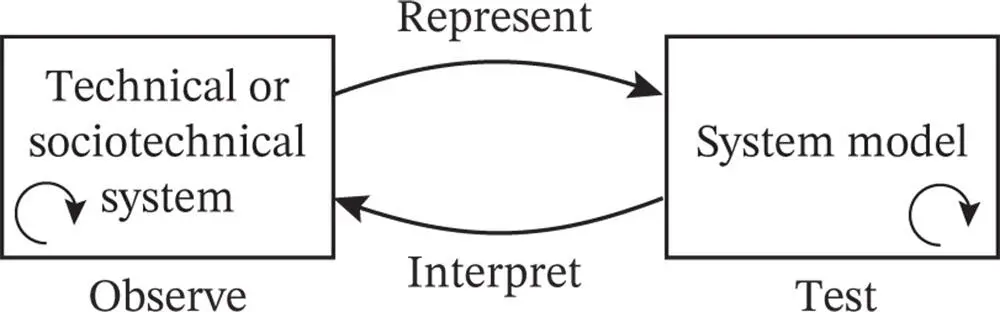 Figure 4.4The system modeling and analysis process.
Figure 4.4The system modeling and analysis process.
To be able to do a careful study, we need to establish a system model that simplifies the actual processes, such that we can use mathematical methods to deduce results. The system model is a representation of the actual system. All the methods and tools we use in risk analysis are applicable only in the framework of the model, and the results are correct only to the extent that the model reflects the properties and weaknesses of the actual system. What we study in the model depends on the objectives of the study and the characteristics of the model. When a result is obtained, we have to interpret this result in the actual system and argue its relevance.
4.4.2.1 The Newtonian–Cartesian Paradigm
A paradigm is a world view underlying the theories and methods of any scientific subject. For traditional sciences, the Newtonian–Cartesian paradigm has been, and still is, the most essential and all the systems discussed in this book are rooted in this paradigm. The basis for this paradigm was made by the French philosopher Réne Déscartes (1596–1650) and the English scientist Sir Isaac Newton (1642–1726). The main building blocks of the Newtonian–Cartesian paradigm are:
Déscartes' theory on reductionism, which says that all systems (and problems) can be fully understood by decomposing the system into its constituent elements and by separately studying each element (see Figure 4.1).
Newton's three laws of forces and motion, his theories on universal gravitation, and the unifying theory known as Newtonian mechanics.
Déscartes's fundamental division between mind and matter, implying that mental processes do not interfere with the physical world, and vice versa. He considered the physical world as a machine, where its behavior is governed by the laws of mechanics, which in the paradigm are Newton's laws.
The assumption of a universal time that “flows” as a constant and unchangeable process, and is the same for everyone.
The assumption of a constant and universal space. Déscartes developed the Cartesian coordinate system such that the location and movement of an element in the space can be uniquely specified.
The space between physical objects can be considered as empty.
The Newtonian–Cartesian paradigm is mechanistic and sees the world as a set of isolated items that interact in a linear, cause and effect way. The Newtonian–Cartesian paradigm has had an enormous success and most of our current knowledge about physical systems (from atoms to the outer space) are based on this paradigm. The Newtonian–Cartesian paradigm may be summed up by the metaphor:
The whole is no more or no less than the sum of the parts.
For a long time, the Newtonian–Cartesian paradigm was considered to be of totally general applicability, but more recent insights have shown that this is not the case. The first stumbling block for the paradigm was the development and acceptance of quantum mechanics and its probabilistic focus. The second and more definitive stumbling block was Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity where it was shown that time and space are dependent on gravitation fields and velocity. A high number of detailed experiments have proved the correctness of Einstein's theories.
Almost all our education has been based on the Newtonian–Cartesian paradigm and all assumptions and rules therefore seem obvious. Most of us struggle to imagine that they are not totally general.
4.4.3 System Analysis and Synthesis
The word analysis comes from Ancient Greek and means “breaking up.” We define system analysis as follows:
Definition 4.9 (System analysis)
The process of studying a system by decomposing the system into elements (functions or components) to gain a better understanding of the system and to realize how the elements relate to each other.
System analysis implies that all adequate knowledge about a system can be obtained by breaking the system down – or decomposing it – into its constituent elements and by carefully and individually studying each of the constituent elements and the interfaces and connections between these. A system can only be analyzed adequately when the system complies with the Newtonian–Cartesian paradigm.
In the context of risk assessment, analysis is used to identify weak points and to determine the risk associated with a system. The system may be an existing system or a proposed system concept. The analysis is always performed based on a system model. Several types of models and analyses are described in detail later in the book.
Читать дальше

 Figure 4.3Black box model for a component function.
Figure 4.3Black box model for a component function. Figure 4.4The system modeling and analysis process.
Figure 4.4The system modeling and analysis process.










