Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие
(зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Power Electronics-Enabled Autonomous Power Systems»).
Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге —
напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Power systems worldwide are going through a paradigm shift from centralized generation to distributed generation. This book presents the SYNDEM (i.e., synchronized and democratized) grid architecture and its technical routes to harmonize the integration of renewable energy sources, electric vehicles, storage systems, and flexible loads, with the synchronization mechanism of synchronous machines, to enable autonomous operation of power systems, and to promote energy freedom. This is <i>a game changer for the grid. It is the sort of breakthrough – like the touch screen in smart phones – that helps to push an industry from one era to the next,</i> as reported by Keith Schneider, a New York Times correspondent since 1982. This book contains an introductory chapter and additional 24 chapters in five parts: Theoretical Framework, First-Generation VSM (virtual synchronous machines), Second-Generation VSM, Third-Generation VSM, and Case Studies. Most of the chapters include experimental results. <br /><br />As the first book of its kind for power electronics-enabled autonomous power systems, it <br /><br />• introduces a holistic architecture applicable to both large and small power systems, including aircraft power systems, ship power systems, microgrids, and supergrids <br />• provides latest research to address the unprecedented challenges faced by power systems and to enhance grid stability, reliability, security, resiliency, and sustainability <br />• demonstrates how future power systems achieve harmonious interaction, prevent local faults from cascading into wide-area blackouts, and operate autonomously with minimized cyber-attacks <br />• highlights the significance of the SYNDEM concept for power systems and beyond <br /><br /><i>Power Electronics-Enabled Autonomous Power Systems</i> is an excellent book for researchers, engineers, and students involved in energy and power systems, electrical and control engineering, and power electronics. The SYNDEM theoretical framework chapter is also suitable for policy makers, legislators, entrepreneurs, commissioners of utility commissions, energy and environmental agency staff, utility personnel, investors, consultants, and attorneys.

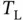 and
and 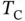 . (a)
. (a) 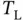 . (b)
. (b) 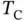 ....Figure 17.4 Interpretation of the universal transformation matrix
....Figure 17.4 Interpretation of the universal transformation matrix 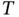 .Figure 17.5 Universal droop controller.Figure 17.6 Rel‐time simulation results of three inverters with different ty...Figure 17.7 Experimental set‐up consisting of an L‐inverter, an R‐inverter, ...Figure 17.8 Experimental results with the universal droop controller. (a)
.Figure 17.5 Universal droop controller.Figure 17.6 Rel‐time simulation results of three inverters with different ty...Figure 17.7 Experimental set‐up consisting of an L‐inverter, an R‐inverter, ...Figure 17.8 Experimental results with the universal droop controller. (a) 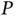 ...
...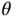 ‐converter.Figure 19.7 Control structure for the droop‐controlled rectifier. (a) Contro...Figure 19.8 Experimental results in the GS mode. (a) Real power
‐converter.Figure 19.7 Control structure for the droop‐controlled rectifier. (a) Contro...Figure 19.8 Experimental results in the GS mode. (a) Real power 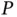 , grid volt...Figure 19.9 Experimental results in the NS‐H mode. (a) Real power
, grid volt...Figure 19.9 Experimental results in the NS‐H mode. (a) Real power 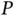 , grid vo...Figure 19.10 Experimental results in the NS‐L mode. (a) Real power
, grid vo...Figure 19.10 Experimental results in the NS‐L mode. (a) Real power 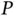 , grid v...Figure 19.11 Transient response when the system starts up. (a) Real power
, grid v...Figure 19.11 Transient response when the system starts up. (a) Real power 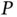 ,...Figure 19.12 Transient response when a load is connected to the system. (a) ...Figure 19.13 Experimental results showing the capacity potential of the rect...Figure 19.14 Controller for the conversion leg.Figure 19.15 Comparative experimental results with a conventional controller...
,...Figure 19.12 Transient response when a load is connected to the system. (a) ...Figure 19.13 Experimental results showing the capacity potential of the rect...Figure 19.14 Controller for the conversion leg.Figure 19.15 Comparative experimental results with a conventional controller...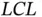 filter.Figure 20.2 The equivalent circuit diagram of the controller.Figure 20.3 The overall control system.Figure 20.4 Controller states. (a)
filter.Figure 20.2 The equivalent circuit diagram of the controller.Figure 20.3 The overall control system.Figure 20.4 Controller states. (a) 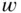 and
and 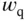 . (b)
. (b) 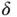 and
and 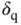 .Figure 20.5 Implementation of the current‐limiting universal droop controlle...Figure 20.6 Operation with a normal grid. (a) Real and reactive power, RMS c...Figure 20.7 Transient response of the controller states with a normal grid. ...Figure 20.8 Operation under a grid voltage sag
.Figure 20.5 Implementation of the current‐limiting universal droop controlle...Figure 20.6 Operation with a normal grid. (a) Real and reactive power, RMS c...Figure 20.7 Transient response of the controller states with a normal grid. ...Figure 20.8 Operation under a grid voltage sag 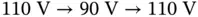 for 9 s. (a) Real and react...Figure 20.9 Controller states under the grid voltage sag
for 9 s. (a) Real and react...Figure 20.9 Controller states under the grid voltage sag 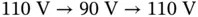 for 9 s. (a)
for 9 s. (a)  an...Figure 20.10 Operation under a grid voltage sag
an...Figure 20.10 Operation under a grid voltage sag 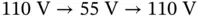 for 9 s. (a) Real and reac...Figure 20.11 Controller states under the grid voltage sag
for 9 s. (a) Real and reac...Figure 20.11 Controller states under the grid voltage sag 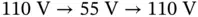 for 9 s. (a)
for 9 s. (a)  a...
a... .Figure 21.2 Two systems with disturbances and external ports interconnected ...Figure 21.3 Three‐phase grid‐connected converter with a local load.Figure 21.4 The controller for a cybersync machine with
.Figure 21.2 Two systems with disturbances and external ports interconnected ...Figure 21.3 Three‐phase grid‐connected converter with a local load.Figure 21.4 The controller for a cybersync machine with  to be supplied as Figure 21.5 The mathematical structure of the system constructed to facilita...Figure 21.6 Blocks
to be supplied as Figure 21.5 The mathematical structure of the system constructed to facilita...Figure 21.6 Blocks 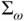 and
and 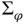 implemented with the integral controller. (a)
implemented with the integral controller. (a) 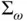 . ...Figure 21.7 A cybersync machine equipped with regulation and self‐synchroniz...Figure 21.8 Simulation results from a cybersync machine, where the detailed ...Figure 21.9 Experimental results from a cybersync machine. (a) Around synchr...
. ...Figure 21.7 A cybersync machine equipped with regulation and self‐synchroniz...Figure 21.8 Simulation results from a cybersync machine, where the detailed ...Figure 21.9 Experimental results from a cybersync machine. (a) Around synchr...










