Biological abnormalities refer to either genetic disorders, which may cause secondary problems, or infectious, bacterial, and immunodeficiency diseases. Tuberculosis, cholera, malaria, and AIDS as one of the deadliest one caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are some examples of biological diseases.
Genetic disorders are caused by point mutation or gene damage due to insertion or deletion of a gene bond, deletion of a gene or genes, missing chromosomes, or trinucleotide repeat disorder. There are many types of such disorders, including colour blindness, cystic fibrosis, Down syndrome, haemophilia, neurofibromatosis, polycystic kidney disease, and spinal muscular atrophy.
Monitoring the human body for diseases often starts from noninvasive examinations and data recordings followed by taking and testing blood or urine samples. In the later stages, however, invasive tissue sampling by means of biopsy or various imaging modalities may become necessary. As an example, for monitoring a tumour in the body, the examination may be extended to biopsy operation and radiography to enable accurate diagnosis.
A class of biological diseases called autoimmune diseases are among the top mortality causes according to the American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA). These diseases are the result of an abnormal immune response of the body against substances and tissues normally present in the body [15]. To diagnose autoimmune diseases, high resolution imaging of the affected organ through indirect immunofluorescence (IIF) is needed. IIF is an imaging technique that captures images of human epithelial type-2 (HEp-2) cells [16]. Using this imaging technique, antinuclear antibody (ANA), a type of autoantibody binding to the contents of the cell nucleus, is considered a hallmark of autoimmune diseases.
In the IIF test, antibodies are first stained in HEp-2 tissue and then bound to a fluorescent chemical compound. In the cells containing ANAs, the antibodies bound to the nucleus demonstrate different patterns that can be captured and seen via microscope imaging. Categorising the patterns in the HEp-2 cell images can be used to distinguish the phase and severity of autoimmune diseases [17]. The IIF imaging test consists of five different stages [18] where the first stage is autofocus image acquisition to reduce photobleaching effects [19]. The second stage is automatic segmentation of the cells using methods such as the similarity-based watershed and adaptive edge-based segmentation [20, 21]. This is followed by the mitotic cell segmentation using morphological and textural features and local binary patterns (LBPs) [22]. In the fourth stage, the intensity level images are classified into three classes of negative, intermediate, and positive intensities [23]. Finally, the cell staining patterns are classified into centromere (Ce), coarse-speckled (Cs), cytoplasmatic (Cy), fine-speckled (Fs), homogeneous (H), nucleolar (N), and Golgi (G), corresponding to different types of autoimmune diseases.
Computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems, developed by engineers and computer scientists for automatic classification of HEp-2 cells, have attracted much interest in the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases. The systems reduce the cost and time of the diagnosis process and provide repeatability of the test for different physicians.
2.5 Psychological and Behavioural State of the Human Body
Body functions under brain control, thus any factor affecting the human brain, consequently influence the behavioural and physical states of the body. The new technology, the tremendous research, and the conceptual advances in the behavioural, biological, and medical sciences can certainly aid recognition of bidirectional and multilevel relationships between behaviour and health. Psychological, neurological, and anatomical diagnoses often involve different screening and testing procedures. For example, epileptic seizure has different symptoms including whole body movement, heart rate variation, and most importantly changes in the EEG dynamics and waveforms. On the other hand, an anatomical problem, often caused by a brain tumour, should be diagnosed through medical imaging followed by pathological tests.
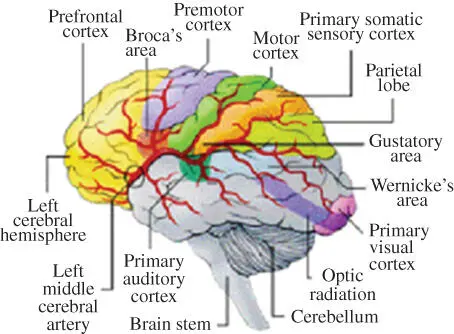
Figure 2.2 Different brain sensory zones. ( See color plate section for color representation of this figure )
Although the brain's action is unpredictable during wakefulness and is influenced by internal, such as emotions, and external, such as event and movement-related stimuli, during sleep the brain follows a number of well-defined states, generating predictable continuous or intermittent rhythms.
The abnormality in the brain may originate from different brain zones ( Figure 2.2). Hence, the assessment of the human brain through various screening and imaging modalities during different behavioural states promotes our understanding of the links between human behaviour and basic neurological and neurochemical processes or specific neuroanatomic pathways.
The number of diseases and disorders in the brain is probably more than that of any other organ in the body. Most brain abnormalities manifest themselves in well-defined patterns in multichannel EEG recordings. However, not all these abnormalities have been studied through EEG analysis. The most important and popular brain abnormalities and diseases are listed alphabetically:
Amnesia (amnestic syndrome): the loss of memories, such as facts, information, and experiences. Though it generally doesn't cause a loss of self-identity and those with amnesia are usually lucid and know who they are, they may have trouble learning new information and forming new memories. Amnesia can be caused by damage to areas of the brain that are vital for memory processing. Unlike a temporary episode of memory loss, amnesia can be permanent. There's no specific treatment for amnesia,
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS): a motor neuron disease and a rare group of neurological diseases that mainly involve the nerve cells (neurons) responsible for controlling voluntary muscle movement such as for chewing, walking, breathing, and talking. The disease is progressive and therefore the symptoms become worse over time. Currently, there is no cure for ALS and no effective treatment to halt or reverse its progression. ALS belongs to a wider group of disorders known as motor neuron diseases caused by the gradual deterioration (degeneration) and death of motor neurons. Motor neurons are nerve cells that extend from the brain to the spinal cord and to muscles throughout the body. These motor neurons initiate and provide vital communication links between the brain and the voluntary muscles. Early symptoms of ALS usually include muscle weakness or stiffness. All muscles under voluntary control are gradually affected, and individuals lose their strength and the ability to speak, eat, move, and even breathe and mostly die from respiratory failure, usually within three to five years from when the symptoms first appear.
Ataxia: neurological symptoms (rather than disorders) related to the movement and control of posture and balance, resulting in poor coordination. Ataxia can be due to many different causes. Cerebellar ataxia means unsteadiness due to pathology in the cerebellum, which is a leaf-like structure in the back part of the brain.
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): a brain disorder diagnosed by an ongoing pattern of severe inattention or hyperactivity impulsivity which affects the functioning or development of humans often from childhood and the impulsivity in action and behaviour continues into old age.
Autism or autism spectrum disorder (ASD): a neurodevelopmental disorder characterised by deficits in communication, social interaction, and the presence of restricted, repetitive behaviours. Social communication deficits include impairments in aspects of joint attention and social reciprocity, as well as difficulties in the use of verbal and nonverbal communicative behaviours for social interaction.
Читать дальше













