Radioactive ionizers use a radioactive source to ionize the air by impact of radioactive particles with molecules in the air. Exactly balanced ion streams are produced by this means, as the molecule splits into two ions, one positive and one negative ion. The rate of production of ions is small and limited by the level of radioactivity of the ionizing material.
2.8.4 Rate of Charge Neutralization
Each ion that reaches a charged surface will add its charge to the surface. As this is usually the opposite polarity to the surface charge, the arriving ion will normally neutralize an equal and opposite polarity surface charge. The rate at which ions arrive at the surface depends on the electrostatic field strength, the concentration of ions in the air, and the mobility of the ions (Jonassen 2016b). This can be thought of as an ion current flow. Different air ions can have different mobility depending on the size, polarity, and charge of the ions.
As the charged surface neutralization process continues, surface voltages and field strength reduce, and the drift of ions to the surface reduces with the reducing field strength. The neutralization process continues ever more slowly until the electrostatic fields and thus forces on the ions are insufficient to attract further charge from the air.
If the surface voltage is monitored, the voltage is seen to reduce at a reducing quasi‐exponentially decaying rate. This is used in a charge plate monitor (CPM) instrument to measure the effectiveness of ionizers in neutralizing charges on surfaces. A typical voltage decay curve obtained is shown in Figure 2.25.
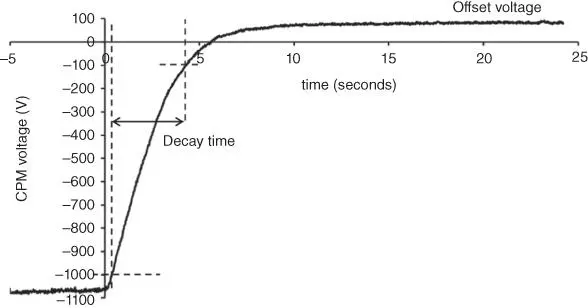
Figure 2.25Electrostatic voltage on a CPM plate reducing during charge neutralization showing decay time and offset.
Charge neutralization by ionizers is typically quite a slow process and can take tens of seconds or longer, depending on the electrostatic field strength and ion density in the region surrounding the charged surface. This charge density, and the speed of charge neutralization, can be affected by many factors.
2.8.5 The Region of Effective Charge Neutralization Around an Ionizer
The ion density in the air typically reduces with the distance from the ionizer. This is in part because the ion cloud tends to spread out due to repulsion forces between like polarity ions. In addition, attraction between positive and negative charges in the cloud causes them to move toward each other and recombine to neutralize each other (Jonassen 2016a).
As the ion cloud is drifting in air, movement of the air can have a significant effect on the location of the cloud and the local ion concentration. Ions can be blown toward or away from the region where they are wanted (e.g. by drafts from a fan or open window). Conversely, in many situations a fan can be used to blow ions to the location they are needed to improve charge neutralization effectiveness.
2.8.6 Ionizer Balance and Charging of a Surface by an Unbalanced Ionizer
An ion cloud is rarely accurately balanced in terms of ion charge polarity density. One consequence of this is that any surface within the ion cloud tends to reach a state of excess charge reflecting the ion density balance in the ion cloud. If, for example, the ion cloud has excess positive ions, then surfaces within the ion cloud will tend to become positively charged until electrostatic fields are sufficient to prevent further ion deposition. This effect will create residual voltages on insulating surfaces and isolated conductors within the ion cloud. With a well‐balanced ionizer, this effect will be small, and the excess voltage achieved may be only a few volts or tens of volts. This “offset voltage” is an important parameter of an ionizer specification ( Figure 2.25).
A poorly maintained ionizer can become seriously out of balance. This can happen in service due to erosion or contamination of the ionizer needles. If this occurs, then surfaces within the ion cloud may become charged to hundreds or even thousands of volts. Monitoring this effect over time and performing appropriate maintenance of an ionizer to prevent the imbalance from reaching an excessive level is an important aspect of ionizer maintenance (Simco Ion TN‐003 2019).
2.9 Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
ESDs can give waveforms that have very fast (nanosecond or subnanosecond) rise times, high peak current levels of tens of amps, and oscillatory waveforms. Discharge current rise rates can be of the order of 10 9A s −1, and electrostatic fields may collapse with rates of the order of 10 12V s −1. The ESD source may radiate or conduct strong transient electromagnetic fields over a wide frequency band up to GHz frequencies.
These induce transients in nearby conductors, especially tracks or wires of significant length that can act as efficient antennas at the frequencies radiated in the discharge. This radiated or conducted interference can cause upset or malfunction to nearby equipment such as test equipment. Giant magnetoresistive (GMR) heads have been demonstrated to be damaged by this type of ESD transient (Wallash and Smith 1998).
EMI can also be an issue in highly automated facilities where automated test equipment (ATE) can test large numbers of production items. EMI may cause the ATE to register a product fail or to otherwise malfunction (Tamminen et al. 2015). This can represent a loss of production or output.
2.10 How to Avoid ESD Damage of Components
2.10.1 The Circumstances Leading to ESD Damage of a Component
ESD damage does not occur unless there is ESD. The circumstances leading to ESD are as follows:
A conductor attains a high voltage through induction or triboelectrification. The conductor may be○ A person○ A metal or other conductive item such as a tool, machine part, or cable○ An ESDS component
The conductor touches, or comes sufficiently near to another conductor or ESDS device, for ESD to occur.
The ESD current passes through a part of the ESDS device that may be damaged by ESD.
The discharge current, charge, energy, or voltages developed on the ESDS device must exceed a threshold at which damage is likely to occur.
Most ESDS devices are not directly damaged by exposure to electrostatic fields. The risk is usually due to induced voltages on the device or a nearby conductor causing ESD when the ESDS device touches the conductor. For some high‐impedance, voltage‐sensitive devices, induced voltages can cause a risk of breakdown within the device.
2.10.2 Risk of ESD Damage
The occurrence of ESD to a susceptible component does not necessarily cause a failure. Indeed, it is likely that ESD happens before detectable damage occurs. So, ESD damage is perhaps best thought of as a risk with a probability that may depend on many factors.
The likelihood that ESD occurs to an ESDS device.
Most devices have many possible ESD entry points. Each of these will typically have a different ESD susceptibility.
The likelihood that the ESD strength will exceed the ESD damage threshold of the device at the point of discharge.
Considering these conditions shows why ESD damage is a probabilistic phenomenon. Only a small fraction of ESD events may cause ESD damage, because
The capacity of the ESD source to produce damage varies with the characteristics of the source.
The magnitude of the source voltage and energy will vary tremendously with the conditions that cause it.
The variation in discharge paths will cause great variation in characteristics of the discharge such as peak current, waveform, rise and fall times and duration, and power and energy deposited in the ESDS device.
Читать дальше













