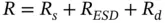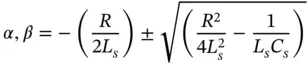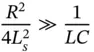Jeremy M. Smallwood - The ESD Control Program Handbook
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Jeremy M. Smallwood - The ESD Control Program Handbook» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:The ESD Control Program Handbook
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
The ESD Control Program Handbook: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «The ESD Control Program Handbook»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
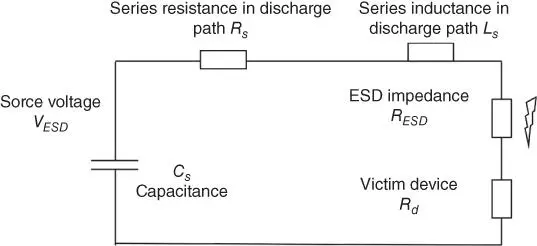
The ESD Control Program Handbook Chapter 6 deals with requirements for compliance given by the IEC 61340-5-1 and ANSI/ESD S20.20 ESD control standards.
Chapter 7 gives an overview of the selection, use, care and maintenance of equipment and furniture commonly used to control ESD risks. The chapter explains how these often work together as part of a system and must be specified with that in mind.
ESD protective packaging is available in an extraordinary range of forms from bags, boxes and bubble wrap to tape and reel packaging for automated processes. The principles and practice of this widely misunderstood area of ESD control are introduced in Chapter 8. The thorny question of how to evaluate an ESD control program is addressed in Chapter 9 with a goal of compliance with a standard as well as effective control of ESD risks and possible customer perceptions.
Whilst evaluating an existing ESD control program provides challenges, developing an ESD control program from scratch provides others. Chapter 10 gives an approach to this.
Standard test methods used in compliance with ESD control standards are explained and simple test procedures given in Chapter 11.
ESD Training has long been recognised as essential in maintaining effective ESD control. Chapter 12 discusses ways of covering essential topics and how to demonstrate static electricity in action. The book ends with a look at where ESD control may go in the near future.
The ESD Control Program Handbook Gives readers a sound understanding of the subject to analyze the ESD control requirements of manufacturing processes, and develop an effective ESD control program Provides practical knowledge, as well as sufficient theory and background to understand the principles of ESD control Teaches how to track and identify how ESD risks arise, and how to identify fitting means for minimizing or eliminating them Emphasizes working with modern ESD control program standards IEC 61340-5-1 and ESD S20:20
is an invaluable reference for anyone tasked with setting up, evaluating, or maintaining an effective ESD control program, training personnel, or making ESD control related measurements. It would form an excellent basis for a University course on the subject as well as a guide and resource for industry professionals.