Definition 2.6 (Operating context)
The environmental and operating conditions under which the item is (or is expected to be) operating.
In some applications, the concept of operations (CONOPS) document describes the operating context of the item.
2.5 Functions and Performance Requirements
To be able to identify all potential item failures, the reliability engineer needs to have a thorough understanding of the various functions of the item and the performance criteria related to each function.
A function is a duty or an action the item has been designed to perform. A function requires one or more inputs to provide an output. The function is performed by technical and other resources and will usually also require some control (e.g. start signals). A function and its inputs and outputs are shown in Figure 2.3. The function and its elements are illustrated in Example 2.1.
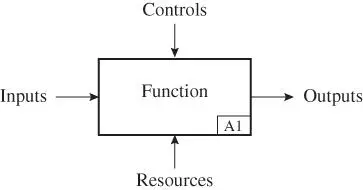
Figure 2.3A function illustrated as a functional block.
Consider a simple flashlight. The main function of the flashlight is to produce light. The required input is electric power coming from a battery. The resource is the flashlight with battery. The function is controlled by switching on/off the flashlight.
A function may be defined as follows:
Definition 2.7 (Function)
An activity, process, or transformation stated by a verb and a noun that describes what must be accomplished.
A function is an intended effect of an item and should be described such that each function has a single definite purpose. It is recommended to give the functions names that have a declarative structure, and say “what” is to be done rather than “how.” The functions should preferably be expressed as a statement comprising a verb plus a noun; for example, provide light, close flow, contain fluid, pump fluid, and transmit signal. In practice, it is often difficult to specify a function with only two words, and additional words may need to be added.
2.5.2 Performance Requirements
New products and systems are developed to fulfill a set of requirements . These requirements are usually written into a requirement document . The requirements may be based on (i) identified customer needs, (ii) manufacturer's ideas to make the product more competitive, and (iii) requirements in standards, laws, and regulations. The IEV defines the term “requirement” as follows:
Definition 2.8 (Requirement)
Need or expectation that is stated, generally implied or obligatory (IEV 192‐01‐13).
A performance requirement is a specification of the performance criteria related to a function. If, for example, the function is “pump water,” a performance requirement may be that the output of water must be between 100 and 110 l/min. Some functions may have several performance requirements. Performance requirements are also referred to as functional requirements or performance standards .
2.5.3 Classification of Functions
A complicated item may have a high number of required functions. All functions are not equally important, and a classification may therefore be an aid for identification and analysis purposes. One way of classifying functions is as follows:
Essential functions. These are the functions required to fulfill the intended purpose of the item. The essential functions are simply the reasons for installing or using the item. The essential function is sometimes reflected in the name of the item. An essential function of a pump is, for example, to “pump fluid.”
Auxiliary functions. These are the functions that are required to support the essential functions. The auxiliary functions are usually less obvious than the essential functions, but may in many cases be as important as the essential functions. Failure of an auxiliary function may in many cases be more safety‐critical than a failure of an essential function. An auxiliary function of a pump is, for example, to “contain fluid.”
Protective functions. These functions are intended to protect people, equipment, and the environment from damage and injury. The protective functions may be classified as follows:Safety functions (i.e. to prevent hazardous events and/or to reduce consequences to people, material assets, and the environment)Security functions (i.e. to prevent vulnerabilities, physical attacks, and cyberattacks)Environment functions (e.g. anti‐pollution functions)Hygiene functions (e.g. for items used in food production or in hospitals).
Information functions. These functions cover condition monitoring, various gauges and alarms, communication monitoring, and so forth.
Interface functions. These functions apply to the interfaces between the item in question and other items. The interfaces may be active or passive. A passive interface is, for example, present when the item is a support or a base for another item.
Superfluous functions. These functions are never used and are often found in electronic equipment that have a wide range of “nice to have” functions that are not really necessary. Superfluous functions may further be found in systems that have been modified several times. Superfluous functions may also be present when the item has been designed for an operating context that is different from the actual operating context. In some cases, failure of a superfluous function may cause failure of other functions.
Some functions may belong to more than one class. For some applications, it may further be relevant to classify functions as follows:
1 Online functions. These functions are operated either continuously or so often that the user has current knowledge about their status. The termination of an online function is called an evident or detected failure.
2 Off‐line functions. These functions are used intermittently or so infrequently that their availability is not known by the user without some special check or test. Some offline functions are not possible to test without damaging the item. An example of an offline function is the essential function of the airbag system of a car. Many protective functions are offline functions. The termination of the ability to perform an offline function is called a hidden or undetected failure.
2.5.4 Functional Modeling and Analysis
The objectives of a functional analysis are to
1 Identify all the functions of the item.
2 Identify the functions required in the various operating modes of the item.
3 Provide a hierarchical decomposition of the item functions (see Section 2.5.5).
4 Describe how each function is realized and provide the associated performance requirements.
5 Identify the interrelationships between the functions.
6 Identify interfaces with other systems and with the environment.
Functional analysis is an important step in systems engineering (Blanchard and Fabrycky 2011), and several analytical techniques have been developed. We briefly mention two of these techniques: Function trees and SADT / IDEF 0.
For complicated systems, it is sometimes beneficial to illustrate the various functions as a tree structure called a function tree . A function tree is a hierarchical functional breakdown structure starting with a system function or a system mission and illustrating the corresponding necessary functions on lower levels of indenture. The function tree is created by asking how an already established function is accomplished. This is repeated until functions on the lowest level are reached. The diagram may also be developed in the opposite direction by asking why a function is necessary. This is repeated until functions on the system level are reached. Function trees may be represented in many different ways. An example is shown in Figure 2.4.
Читать дальше













