If you’re using a computer with Windows 10: You can type system on the search bar at the bottom of the Windows desktop. Then click the System Information app when it appears. If you have a File Explorer window open, you can also right-click directly on the This PC link in the navigation pane on the left (see the sidebar “A quickie on right-clicking,” later in this chapter) and then choose Properties from the menu that appears. This takes you to a screen that summarizes the computer’s operating system version, processor speed, and memory amount. (See Figure 3-1.) Note that other versions of the Windows operating system may require different steps to find the same information. FIGURE 3-1:A summary of the physical makeup of a computer with Windows Vista.
Mac users: You can click on the apple (top left of the menu bar) and then choose the About This Mac option from the menu that appears, to see a similar summary. (See Figure 3-2.)
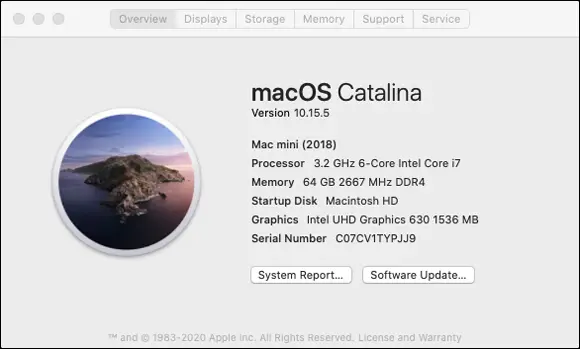
FIGURE 3-2:A summary of the physical makeup of a computer with Mac OS X.
The role of computer memory is to assist the processor by temporarily storing instructions and other information for faster processing. Computer programs, also known as applications — Microsoft Word, for example — require computers to have a specific amount of memory available for their use. Memory is measured in gigabytes (GB).
Your computer’s current memory capacity can be found on the same page as its processor speed. (See the preceding section and Figures 3-1 and 3-2.) Most newer computers come with plenty of memory, right off the shelf. However, if your computer is a few years older, it may not meet the minimum requirements for taking an online course. If this is the case, talk to either the institution’s technical support team or a computer retailer about increasing your computer’s memory. Depending on how old your computer is, increasing its memory may be all you need to do.
Your computer’s hard drive is where all your files are stored. This includes the files required to run the computer’s operating system and your installed applications. Think of the hard drive as a digital filing cabinet. How much information can be stored on your computer’s hard drive depends on its size. Newer hard drives are measured in gigabytes or terabytes (TB). Older hard drives were measured using megabytes (MB).
Institutions may require that you have a hard drive with enough space to install additional programs and store your documents, such as homework assignments.
The monitor is the device that displays your computer’s output. A monitor’s display is based on two components: size and resolution. Monitors come in a variety of sizes based on their diagonal measurements in inches. For example, a 20-inch monitor measures 20 inches from the top left corner to the bottom right corner. However, a 20-inch monitor has only an 18.8-inch viewable display. This disparity matters because the picture is developed using pixels, and the number of pixels that can fit in a given space is measured in terms of width by height. For example, on a monitor with a 640 x 480 resolution, there are 640 pixels across the screen and 480 pixels from top to bottom. The larger the monitor size, the bigger the pixels need to be to fill the space. Most institutions require you to have a monitor with a minimum resolution of 1024 x 768. A 17-inch monitor is best; however, monitors between 15 and 21 inches should also be suitable. Even the 13.3-inch monitors on our laptops display 1024 x 768 pixels just fine.
Many online courses use audio and video files to support the curriculum. To hear the speech portion of each of these files, you need a good pair of speakers or a headset. Most computers come with speakers upon purchase. The speakers should work fine. However, your family and other housemates may prefer that you use a headset, to reduce distractions. Don’t rush out and buy anything expensive. The headset you use to listen to your music player will work just fine. Your computer should have a built-in sound card and a round headphone jack for plugging in. The headphone jack may be located on the front or back of your computer. Or, if you use a laptop, the jack may be on one side. Most headphone jacks have a small Headset icon either above the jack or directly next to it.
Some instructors also may ask you to participate in a web-based conference using Internet applications. These applications allow instructors and students to communicate in a variety of ways, including via voice over the Internet. To do this, you need to have a microphone. Many computers, especially laptops, have built-in microphones. These can work, but we recommend that you purchase an inexpensive headset that incorporates a microphone. Look to spend about $50 for the basic set.
Some programs or courses may require you to have a webcam, which is a camera for your computer. When you turn it on, the members of your audience see you sitting in front of the computer, as if they were looking through your screen. A webcam may be required for a couple of reasons:
First, you may be required to give synchronous presentations, and you may be asked to share an image of yourself during the presentation.
Second, an institution may require a webcam if a proctoring service is used for testing. Some proctoring services have you log in to a site and share your webcam so that they can confirm your identity and monitor your environment during a test. Most laptops and Chromebooks come with a webcam built in. If you have a desktop machine, you may need to purchase a separate camera.
A laptop is a full computer system that is compact and easy to take on the go. You can buy laptops with either the Windows or Mac operating system on it that either meets or exceeds the minimum requirements we mention in the previous section. The Chromebook is a type of laptop that uses the Google Chrome operating system. It is specifically designed to run cloud-based applications, much like smartphones and tablets. Due to the limitation of relying solely on cloud-based applications, a Chromebook is often dramatically cheaper than a laptop. For the most part, you can accomplish much of your coursework on a Chromebook, though we recommend that you check the minimum requirements of your institution before making the investment. Many specialty programs cannot be installed on a Chromebook. Most Chromebooks and laptops come with a webcam built in.
Believe it or not, most mobile devices meet the minimum requirements needed to accomplish a lot of online learning tasks, including participating in synchronous sessions. For example, many institutions deliver their online courses using a specific learning management system application, where students log in to their virtual classroom and access course content. Most learning management systems — Canvas, for example — have a student mobile app that can be used on a smartphone or tablet to access the course. The same goes for synchronous communication tools such as Zoom. Students can use a mobile application to log in to a live session with their instructor and peers and participate in real time directly from their phone or tablet. This can be convenient for those on the move who want to watch a video on their bus commute to work or read a required article under a tree at lunch. Though these devices bring a lot of convenience and access to the learning experience, they aren’t always the best tool for the job; therefore, we recommend that they not be used as the primary device for participating in your online course. For example, mobile devices often have problems when it comes to creating content such as essays, taking quizzes and exams, and participating in online discussions.
Читать дальше













