While narrating the importance of selecting the components of emulsion like oil, emulsifying agents, tonicity‐adjusting agent, etc., the emulsion formulator should also consider the application of Design Expert ®software to optimize a formula for making the final emulsion. The non‐exhaustive and selected list of excipients used to make emulsions suitable for regulatory approval is briefly discussed in this chapter in conjunction with a case study of how to optimize a formula by applying the ICH Q8(R2), Q9, and Q10 guidelines. The QbD approach using the Design Expert ®software could also further be substantiated via artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) as proposed recently by Ghate et al. (2019). The AI and ML approach applied on the optimization and selection of emulsion formula is considered to reduce the amount of excipients, formulation preparation time, and thus the possible toxicity reduction due to high excipient concentration. Hence, the AI and ML approach is one of the welcome additions in the emulsion‐making technology to get cleared rapidly the regulatory hurdles.
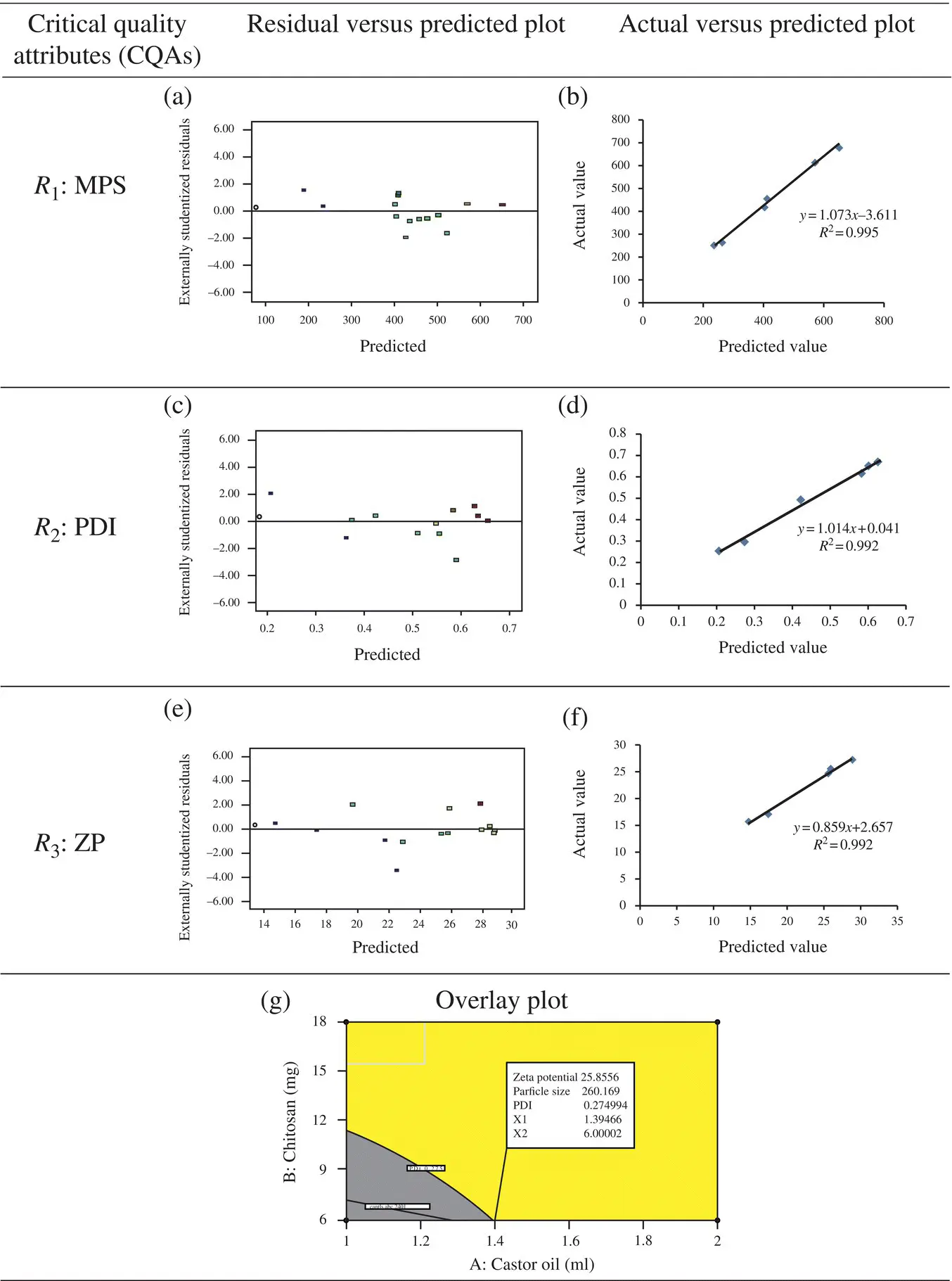
Figure 2.7. Derived plots obtained from 3D‐response surface model: residual versus predicted plot (a, c, e), actual versus predicted plot (b, d, f), and overlay plot (g).
1 Abele, S., Sjöberg, M., Hamaide, T. et al. (1997), Reactive surfactants in heterophase polymerization. 10. Characterization of the surface activity of new polymerizable surfactants derived from maleic anhydride, Langmuir, 13, 176–181. doi: 10.1021/la960577n
2 Akkar, A. and Müller, R.H. (2003a), Formulation of intravenous carbamazepine emulsions by SolEmuls® technology, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 55, 305–312. doi:10.1016/s0939‐6411(03)00028‐6
3 Akkar, A. and Müller, R.H. (2003b), Intravenous itraconazole emulsions produced by SolEmuls technology, Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 56, 29–36. doi:10.1016/s0939‐6411(03)00063‐8
4 Aveyard, R., Binks, B.P., and Clint, J.H. (2003), Emulsions stabilized solely by colloidal particles, Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci., 100 (102), 503–546. doi:10.1016/S0001‐8686(02)00069‐6
5 Badawy, S.I., Narang, A.S., LaMarche, K.R. et al. (2016), Integrated application of quality‐by‐design principles to drug product development: a case study of brivanib alaninate film‐coated tablets, J. Pharm. Sci., 105 (1), 168–181. doi:10.1016/j.xphs.2015.11.023
6 Benichou, A., Aserin, A., and Garti, N. (2004), Double emulsions stabilized with hybrids of natural polymers for entrapment and slow release of active matters, Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci., 108 (109), 29–41. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2003.10.013
7 Binks, B.P. and Catherine, P. (2005), Nanoparticle silica‐stabilised oil‐in‐water emulsions: improving emulsion stability, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 253, 105–115. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2004.10.116
8 Binks, B.P., Desforges, A., and Duff, D.G. (2007b), Synergistic stabilization of emulsions by a mixture of surface‐active nanoparticles and surfactant, Langmuir, 23, 1098–1106. doi:10.1021/la062510y
9 Binks, B.P. and Lumsdon, S.O. (2000), Influence of particle wettability on the type and stability of surfactant‐free emulsions, Langmuir, 16, 8622–8631. doi:10.1021/la000189s
10 Binks, B.P., Rodrigues, J.A., and Frith, W.J. (2007a), Synergistic interaction in emulsions stabilized by a mixture of silica nanoparticles and cationic surfactant, Langmuir, 23, 3626–3636. doi:10.1021/la0634600
11 Buttle, S., Schmidt, R.H., and Müller, R.H. (2002), Production of amphotericin B emulsions based on SolEmuls technology, in: Fourth World Meeting on Pharmaceutics, Biopharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology, Florence, pp. 1535–1536.
12 Capek, I. (2004), Degradation of kinetically‐stable o/w emulsions, Adv. Colloid Interf. Sci., 107, 125–155. doi:10.1016/S0001‐8686(03)00115‐5
13 Cegnar, M., Kos, J., and Kristl, J. (2004), Cystatin incorporated in poly(lactide‐co‐glycolide) nanoparticles: development and fundamental studies on preservation of its activity, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci., 22, 357–364. doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2004.04.003
14 Cohen, T., Sauvageon‐Martre, H., Brossard, D. et al. (1996), Amphotericin B eye drops as a lipidic emulsion, Int. J. Pharm., 137, 249–254. doi:10.1016/0378‐5173(96)04473‐0
15 Constantinides, P.P., Han, J., and Davis, S.S. (2006), Advances in the use of tocols as drug delivery vehicles, Pharm. Res., 23, 243–255. doi:10.1007/s11095‐005‐9262‐9
16 Constantinides, P.P., Tustian, A., and Kessler, D.R. (2004), Tocol emulsions for drug solubilization and parenteral delivery, Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 56, 1243–1255. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2003.12.005
17 Cotlier, E., Baskin, M., and Kresca, L. (1975), Effects of lysophosphatidyl choline and phospholipase A on the lens, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 14, 697–701.
18 Cui, F., Wang, Y., Wang, J. et al. (2007), Preparation of redispersible dry emulsion using Eudragit E100 as both solid carrier and unique emulsifier, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 307, 137–141. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2007.05.013.
19 Calvo, P., Remuñá‐López, C., Vila‐Jato, J.L. et al. (1997), Development of positively charged colloidal drug carriers: chitosan‐coated polyester nanocapsules and submicro‐emulsions, Colloid Polym. Sci., 275, 46–53. doi:10.1007/s003960050050
20 Davis, S.S. and Washington, C. (1988), Drug emulsion, European Patent 0,296, 845, A1.
21 Dale, P.J., Kijlstra, J., and Vincent, B. (2006), The temperature stability of single and mixed emulsions stabilized by nonionic surfactants, Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 291, 85–92. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.06.016
22 Debevec, V., Srčič, S., and Horvat, M. (2018), Scientific, statistical, practical, and regulatory considerations in design space development, Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm., 44 (3), 349–364. doi:10.1080/03639045.2017.1409755
23 EMA (2014), Questions and answers on level of detail in the regulatory submissions, EMA/59240/December 10, 2014.
24 EMA (2017), Report from the EMA‐FDA QbD pilot program, EMA/213746/April 19, 2017.
25 Eskandar, N.G., Simovic, S., and Clive, A. (2009), Nanoparticle coated submicron emulsions: sustained in‐vitro release and improved dermal delivery of all‐trans‐retinol, Pharm. Res., 26, 1764–1775. doi:10.1007/s11095‐009‐9888‐0
26 Fahmy, R. Kona, R. Dandu, R. et al. (2012), Quality by design I: application of failure mode effect analysis (FMEA) and Plackett‐Burman design of experiments in the identification of “main factors” in the formulation and process design space for roller‐compacted ciprofloxacin hydrochloride immediate‐release tablets, AAPS PharmSciTech., 13 (4), 1243–1254. doi: 10.1208/s12249‐012‐9844‐x
27 FDA Guidance for Industry (2004) PAT‐a framework for innovative pharmaceutical development, manufacturing, and quality assurance, ( https://www.fda.gov/media/71012/download, Accessed on June 16, 2019).
28 FDA Guidance for Industry (2006), Q8 pharmaceutical development, ( https://www.fda.gov/media/71524/download, Accessed on June 16, 2019).
29 Ghate, V.M., Kodoth, A.K., Raja, S. et al. (2019), Development of MART for the rapid production of nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with all‐trans retinoic acid for dermal delivery, AAPS PharmSciTech., 20, 162. doi:10.1208/s12249‐019‐1307‐1
30 Goldstein, D., Gofrit, O., Nyska, A. et al. (2007a), Anti‐HER2 cationic immunoemulsion as a potential targeted drug delivery system for the treatment of prostate cancer, Cancer Res., 67, 269–275. doi:10.1158/0008‐5472.CAN‐06‐2731
Читать дальше













