David Clinton - AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «David Clinton - AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
and efficiently prepare for the SAA-C02 Exam with this comprehensive study guide
AWS Certified Solutions Study Guide: Associate (SAA-C02) Exam, Third Edition In this study guide, accomplished and experienced authors Ben Piper and David Clinton show you how to:
Design resilient architectures Create high-performing architectures Craft secure applications and architectures Design cost-optimized architectures Perfect for anyone who hopes to begin a new career as an Amazon Web Services cloud professional, the study guide also belongs on the bookshelf of any existing AWS professional who wants to brush up on the fundamentals of their profession.
AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
A cloud computing platform offers on‐demand, self‐service access to pooled compute resources where your usage is metered and billed according to the volume you consume. Cloud computing systems allow for precise billing models, sometimes involving fractions of a penny for an hour of consumption.
Cloud Computing Optimization
The cloud is a great choice for so many serious workloads because it's scalable, elastic, and, often, a lot cheaper than traditional alternatives. Effective deployment provisioning will require some insight into those three features.
Scalability
A scalable infrastructure can efficiently meet unexpected increases in demand for your application by automatically adding resources. As Figure 1.2shows, this most often means dynamically increasing the number of virtual machines (or instances as AWS calls them) you've got running.
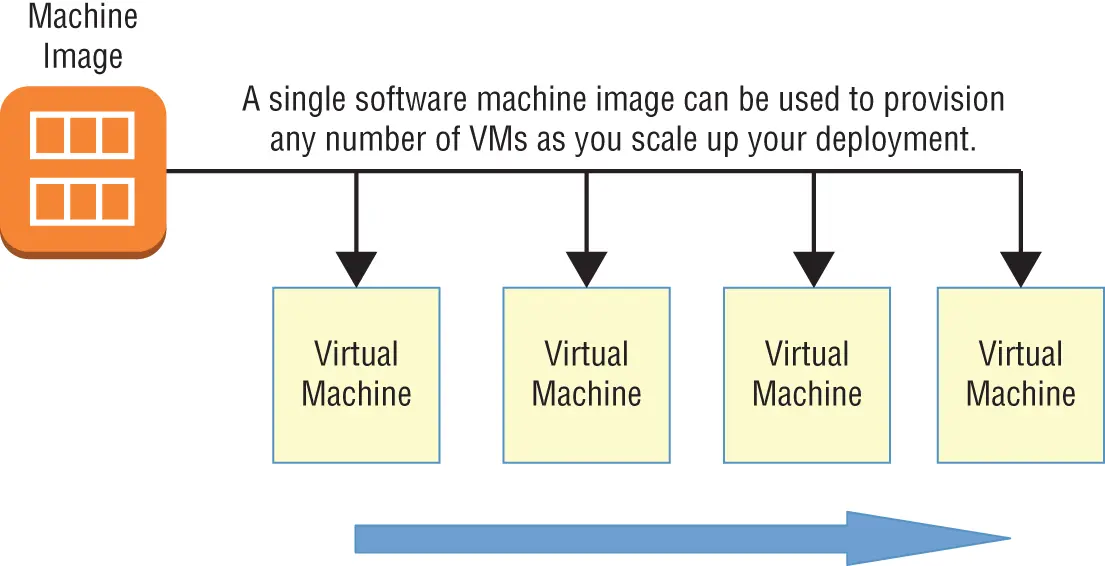
FIGURE 1.2 Copies of a machine image are added to new VMs as they're launched.
AWS offers its autoscaling service through which you define a machine image that can be instantly and automatically replicated and launched into multiple instances to meet demand.
Elasticity
The principle of elasticity covers some of the same ground as scalability—both address how the system manages changing demand. However, though the images used in a scalable environment let you ramp up capacity to meet rising demand, an elastic infrastructure will automatically reduce capacity when demand drops. This makes it possible to control costs, since you'll run resources only when they're needed.
Cost Management
Besides the ability to control expenses by closely managing the resources you use, cloud computing transitions your IT spending from a capital expenditure (capex) framework into something closer to operational expenditure (opex).
In practical terms, this means you no longer have to spend $10,000 up front for every new server you deploy—along with associated electricity, cooling, security, and rack space costs. Instead, you're billed much smaller incremental amounts for as long as your application runs.
That doesn't necessarily mean your long‐term cloud‐based opex costs will always be less than you'd pay over the lifetime of a comparable data center deployment. But it does mean you won't have to expose yourself to risky speculation about your long‐term needs. If, sometime in the future, changing demand calls for new hardware, AWS will be able to deliver it within a minute or two.
To help you understand the full implications of cloud compute spending, AWS provides a free Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Calculator at aws.amazon.com/tco-calculator. This calculator helps you perform proper “apples‐to‐apples” comparisons between your current data center costs and what an identical operation would cost you on AWS.
The AWS Cloud
Keeping up with the steady stream of new services showing up on the AWS Console can be frustrating. But as a solutions architect, your main focus should be on the core service categories. This section briefly summarizes each of the core categories (as shown in Table 1.1) and then does the same for key individual services. You'll learn much more about all of these (and more) services through the rest of the book, but it's worth focusing on these short definitions, because they lie at the foundation of everything else you're going to learn.
TABLE 1.1 AWS service categories
| Category | Function |
|---|---|
| Compute | Services replicating the traditional role of local physical servers for the cloud, offering advanced configurations including autoscaling, load balancing, and even serverless architectures (a method for delivering server functionality with a very small footprint) |
| Networking | Application connectivity, access control, and enhanced remote connections |
| Storage | Various kinds of storage platforms designed to fit a range of both immediate accessibility and long‐term backup needs |
| Database | Managed data solutions for use cases requiring multiple data formats: relational, NoSQL, or caching |
| Application management | Monitoring, auditing, and configuring AWS account services and running resources |
| Security and identity | Services for managing authentication and authorization, data and connection encryption, and integration with third‐party authentication management systems |
Table 1.2describes the functions of some core AWS services, organized by category.
TABLE 1.2 Core AWS services (by category)
| Category | Service | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Compute | Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) | EC2 server instances provide virtual versions of the servers you would run in your local data center. EC2 instances can be provisioned with the CPU, memory, storage, and network interface profile to meet any application need, from a simple web server to one part of a cluster of instances providing an integrated multi‐tiered fleet architecture. Since EC2 instances are virtual, they're resource‐efficient and deploy nearly instantly. |
| Lambda | Serverless application architectures like the one provided by Amazon's Lambda service allow you to provide responsive public‐facing services without the need for a server that's actually running 24/7. Instead, network events (like consumer requests) can trigger the execution of a predefined code‐based operation. When the operation (which can currently run for as long as 15 minutes) is complete, the Lambda event ends, and all resources automatically shut down. | |
| Auto Scaling | Copies of running EC2 instances can be defined as image templates and automatically launched (or scaled up ) when client demand can't be met by existing instances. As demand drops, unused instances can be terminated (or scaled down ). | |
| Elastic Load Balancing | Incoming network traffic can be directed between multiple web servers to ensure that a single web server isn't overwhelmed while other servers are underused or that traffic isn't directed to failed servers. | |
| Elastic Beanstalk | Beanstalk is a managed service that abstracts the provisioning of AWS compute and networking infrastructure. You are required to do nothing more than push your application code, and Beanstalk automatically launches and manages all the necessary services in the background. | |
| Networking | Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) | VPCs are highly configurable networking environments designed to host your EC2 (and RDS) instances. You use VPC‐based tools to secure and, if desired, isolate your instances by closely controlling inbound and outbound network access. |
| Direct Connect | By purchasing fast and secure network connections to AWS through a third‐party provider, you can use Direct Connect to establish an enhanced direct tunnel between your local data center or office and your AWS‐based VPCs. | |
| Route 53 | Route 53 is the AWS DNS service that lets you manage domain registration, record administration, routing protocols, and health checks, which are all fully integrated with the rest of your AWS resources | |
| CloudFront | CloudFront is Amazon's distributed global content delivery network (CDN). When properly configured, a CloudFront distribution can store cached versions of your site's content at edge locations around the world so that they can be delivered to customers on request with the greatest efficiency and lowest latency. | |
| Storage | Simple Storage Service (S3) | S3 offers highly versatile, reliable, and inexpensive object storage that's great for data storage and backups. It's also commonly used as part of larger AWS production processes, including through the storage of script, template, and log files. |
| S3 Glacier | A good choice for when you need large data archives stored cheaply over the long term and can live with retrieval delays measuring in the hours. Glacier's lifecycle management is closely integrated with S3. | |
| Elastic Block Store (EBS) | EBS provides the persistent virtual storage drives that host the operating systems and working data of an EC2 instance. They're meant to mimic the function of the storage drives and partitions attached to physical servers. | |
| Storage Gateway | Storage Gateway is a hybrid storage system that exposes AWS cloud storage as a local, on‐premises appliance. Storage Gateway can be a great tool for migration and data backup and as part of disaster recovery operations. | |
| Database | Relational Database Service (RDS) | RDS is a managed service that builds you a stable, secure, and reliable database instance. You can run a variety of SQL database engines on RDS, including MySQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, and Amazon's own Aurora. |
| DynamoDB | DynamoDB can be used for fast, flexible, highly scalable, and managed nonrelational (NoSQL) database workloads. | |
| Application management | CloudWatch | CloudWatch can be set to monitor process performance and resource utilization and, when preset thresholds are met, either send you a message or trigger an automated response. |
| CloudFormation | This service enables you to use template files to define full and complex AWS deployments. The ability to script your use of any AWS resources makes it easier to automate, standardizing and speeding up the application launch process. | |
| CloudTrail | CloudTrail collects records of all your account's API events. This history is useful for account auditing and troubleshooting purposes. | |
| Config | The Config service is designed to help you with change management and compliance for your AWS account. You first define a desired configuration state, and Config evaluates any future states against that ideal. When a configuration change pushes too far from the ideal baseline, you'll be notified. | |
| Security and identity | Identity and Access Management (IAM) | You use IAM to administrate user and programmatic access and authentication to your AWS account. Through the use of users, groups, roles, and policies, you can control exactly who and what can access and/or work with any of your AWS resources. |
| Key Management Service (KMS) | KMS is a managed service that allows you to administrate the creation and use of encryption keys to secure data used by and for any of your AWS resources. | |
| Directory Service | For AWS environments that need to manage identities and relationships, Directory Service can integrate AWS resources with identity providers like Amazon Cognito and Microsoft AD domains. | |
| Application integration | Simple Notification Service (SNS) | SNS is a notification tool that can automate the publishing of alert topics to other services (to an SQS Queue or to trigger a Lambda function, for instance), to mobile devices, or to recipients using email or SMS. |
| Simple Workflow (SWF) | SWF lets you coordinate a series of tasks that must be performed using a range of AWS services or even nondigital (meaning, human) events. | |
| Simple Queue Service (SQS) | SQS allows for event‐driven messaging within distributed systems that can decouple while coordinating the discrete steps of a larger process. The data contained in your SQS messages will be reliably delivered, adding to the fault‐tolerant qualities of an application. | |
| API Gateway | This service enables you to create and manage secure and reliable APIs for your AWS‐based applications. |
AWS Platform Architecture
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












