1 1 Katz, E. (ed.) (2012). Molecular and Supramolecular Information Processing: From Molecular Switches to Logic Systems. Weinheim: Wiley‐VCH.
2 2 Katz, E. (ed.) (2012). Biomolecular Information Processing – From Logic Systems to Smart Sensors and Actuators. Weinheim: Wiley‐VCH.
3 3 Katz, E. (2019). Enzyme‐Based Computing Systems. Weinheim: Wiley‐VCH.

1 DNA Computing: Origination, Motivation, and Goals – Illustrated Introduction
Evgeny Katz
Clarkson University, Department of Chemistry and Biomolecular Science, Potsdam, NY, 13699, USA
1.1 Motivation and Applications
Exponential development of computing systems based on silicon materials and binary algorithms formulated as “Moore's law” [1] ( Figure 1.1) is coming to the end being limited by further component miniaturization and by the speed of operation. Conceptually novel ideas are needed to break through these limitations. The quest for novel ideas in the information processing has resulted in several exciting directions in the general area of unconventional computing [2–4], including research in quantum computing [5] and biologically inspired molecular computing [6–9]. Molecular computing systems, generally motivated by mimicking natural biological information processing [10,11], are not necessarily based on biomolecules and could be represented by synthetic molecules with signal‐controlled switchable properties. Synthetic molecular systems and nano‐species have been designed to mimic operation of Boolean logic gates and demonstrate basic arithmetic functions and memory units. However, despite progress achieved in assembling synthetic molecular systems performing basic Boolean operations and simple computations [6–9], these systems have limited complexity, and further increase of their complexity is very challenging. A new advance in the development of molecular information systems has been achieved with use of biomolecular species [12] ( Figure 1.2) such as deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) [13–16], oligopeptides [17], proteins [18], enzymes [2,19,20], antigens/antibodies [21], and even whole biological cells/organisms [22–24] capable of operating in a biological environment [25], borrowing some ideas from systems biology [26]. The advantage of the biomolecular computing systems is their ability to be integrated in artificially designed complex reacting processes mimicking multistep information processing networks. These systems are still far away from the natural information processing in cells but are already much more complex than pure synthetic molecular systems. In fact, biochemical reactions are at the core of the mechanism of life itself, and therefore one could set rather ambitious expectations for how far can (bio)chemical reaction systems be scaled up in complexity, if not speed, for information processing. While in a long perspective a “biocomputer” might become a reality [27], particularly for some special applications, e.g., for solving complex combinatorial problems [28], potentially promising to have an advantage over silicon‐based electronic computers due to parallel computing performed by numerous biomolecular units, the present level of technology does not allow any practical use of biomolecular systems for real computational applications. For achieving any practical result soon, some other applications, different from making a biocomputer, should be considered using the (bio)molecular systems with a limited complexity. One of the immediate possible applications for molecular logic systems is a special kind of biosensing [29–31] where the multiple input signals are logically processed through chemical reactions resulting in YES/NO decisions in the binary ( 0, 1) format. In this subarea of biomolecular logic systems, practical results are already possible at the present level of the system complexity, particularly for biomedical applications [32–35]. Overall, the research in molecular/biomolecular information processing, which has been motivated originally to progress unconventional computing applications, is broadly developing to areas not directly related to computing in its narrow definition. This research is bringing us to novel areas in sensing/biosensing [29–31], switchable “smart” materials controlled by logically processed signals [32–36], bioelectronic devices (e.g., biofuel cells) controlled by external signals [37,38], signal‐controlled release processes [39–43], etc.

Figure 1.1Moore's law – exponential increase of transistors on integrated circuit chips. (The plot shown in the figure is based on the data provided by Wikipedia: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Moore%27s_law.)
Source: From Katz [2]. Reprinted with the permission of John Wiley and Sons.
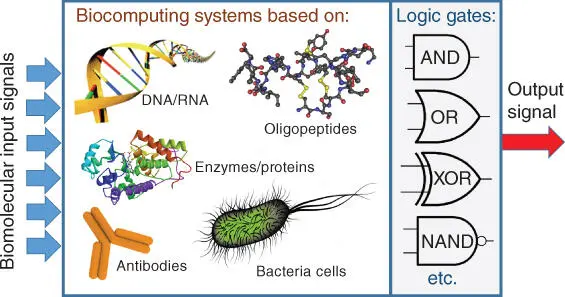
Figure 1.2Biomolecular computing systems mimicking operation of different Boolean logic gates and circuitries can be based on various species including oligopeptides, enzymes/proteins, DNA/RNA, antibodies, and even whole biological (e.g., microbial) cells.
Source: From Katz 2019 [2], Boolean Logic Gates Realized with Enzyme‐Catalyzed Reactions – Unusual Look at Usual Chemical Reactions. ChemPhysChem © 2018. Reproduced with the permission of John Wiley & Sons.
1.2 DNA‐ and RNA‐Based Biocomputing Systems in Progress
While the general topics of the biomolecular computing [12] and specifically the enzyme‐based computing [44] have been covered with recently published books, the present book is concentrated on the use of DNA and RNA molecules in computing systems, broadly defined as information processing systems. From the time (1953) when James D. Watson and Francis H.C. Crick ( Figure 1.3) discovered chemical structure of DNA ( Figure 1.4) [45], the progress in the DNA study resulted in many novel fundamental scientific concepts [46–48] and highly important practical applications [49]. Among many other, mostly biomedical applications, DNA molecules have been extensively studied over last two decades for unconventional biomolecular computing [13,15,50–55], following the pioneer work (1994) by Leonard M. Adleman [28,56] ( Figure 1.5). In his seminal work Adleman demonstrated for the first time computational use of DNA molecules for solving a “traveling salesman problem,” Hamiltonian path problem. Actually, this work initiated (bio)molecular computing research not necessary using DNA molecules.
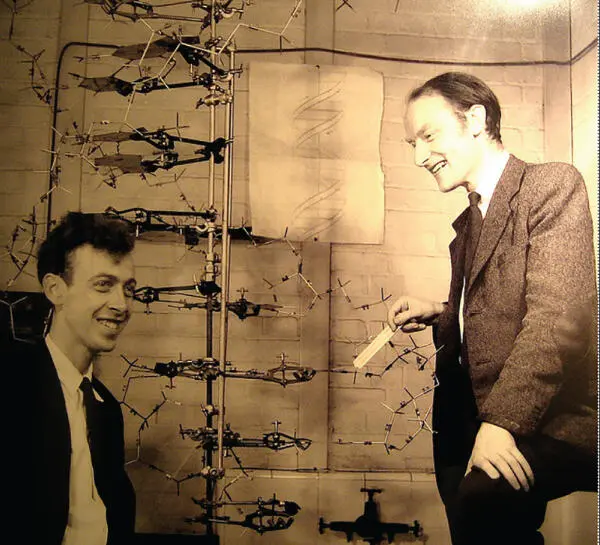

Figure 1.3The discoverers of the structure of DNA. James Watson (b.1928) at left and Francis Crick (1916–2004), with their model of part of a DNA molecule in 1953. Photographed in the Cavendish Laboratory, University of Cambridge, UK, in May 1953.
Source: From Watson and Crick [45]. https://cnx.org/contents/8M7b3dzJ@2/DNA-Structure. Licensed Under CC BY 4.0.
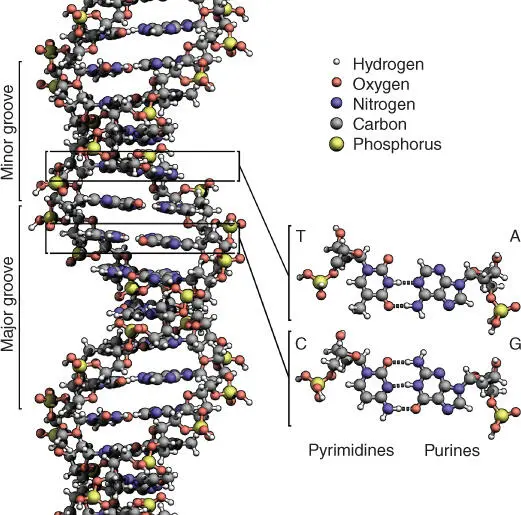
Figure 1.4The structure of the DNA double helix. The atoms in the structure are color‐coded by element, and the detailed structures of two base pairs are shown in the bottom right.
Читать дальше

















