12 Chapter 13Figure 13.1 Toehold‐mediated strand displacement reactions. (a) A DNA duplex...Figure 13.2 Toehold switch riboregulators [18] and input logic [20]. (a) Toe...Figure 13.3 Switching guide RNAs using toehold‐mediated strand displacement....Figure 13.4 Activation of RNA interference via toehold‐mediated strand displ...
13 Chapter 14Figure 14.1 A prototypical DNA strand displacement reaction showing one of t...Figure 14.2 Allosteric toehold mechanism. A first input invades the target d...Figure 14.3 (a) Cooperative hybridization of the inputs induces the displace...Figure 14.4 Associative toehold mechanism. The helper strand (orange) facili...Figure 14.5 Remote toehold mechanism. A spacer separates the toehold and the...Figure 14.6 The toehold exchange reaction. The process is fully reversible v...Figure 14.7 Programmed reconfiguration of DNA assemblies using the strand di...Figure 14.8 Programmed reconfiguration of DNA assemblies using the strand di...Figure 14.9 Dynamic reconfiguration of DNA‐based interlocked catenanes using...Figure 14.10 Programmed motion of a bipedal DNA walker. An attaching strand ...Figure 14.11 Autonomous directional motion of a DNA bipedal walking device. ...Figure 14.12 A DNA‐based transporter. (a) Details of the movement of the wal...Figure 14.13 Directed graph G representing Adleman's Hamiltonian path proble...Figure 14.14 Adleman's DNA solution to the Hamiltonian path problem.Figure 14.15 Graphical representation of a 2‐SAT problem.Figure 14.16 The Boolean logic operators NOT (a), AND (b), and OR (b). The d...Figure 14.17 (a) Deoxyribozyme‐based AND logic gate design with hairpins pre...Figure 14.18 Strand displacement cascade illustrating a toehold exchange str...Figure 14.19 The DNA seesaw architecture. (a) Abstract seesaw gate formalism...Figure 14.20 Operation of logic gates immobilized on a solid‐phase support. ...Figure 14.21 Early developments in DNA catalytic systems. (a) Kinetic contro...Figure 14.22 Entropy‐driven catalytic DNA system. The catalyst first interac...
14 Chapter 15Figure 15.1 Basic molecular logic units and their activation during training...Figure 15.2 The molecular assembly line and its operation. (a) The basic com...Figure 15.3 Scheme of a walking DNAzyme and its track. (a) The walking princ...Figure 15.4 Domain‐level (a) and schematic (b) representations of the miRNA‐...Figure 15.5 Mean squared displacement, 〈 x 2( t )〉.Figure 15.6 The irreversible catalysis of substrates to products leads to th...Figure 15.7 (a) Implementation of a state transition through DNAzymes. (b) 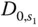
15 Chapter 16Figure 16.1 Conjectured self‐assembly of DNA origami. (a) Phase 1: Synthesis...Figure 16.2 Simplistic illustration of primitives: a conceptual illustration...Figure 16.3 Strand displacement reaction. (a) Before strand displacement. (b...Figure 16.4 Zip transformation. (a) Before zip. (b) After zip. Strands s1, …...Figure 16.5 Unzip transformation. (a) Before unzip. (b) After unzip. Strands...Figure 16.6 Zip and unzip by DNA hairpins. (a) A pair of adjacent hairpins. ...Figure 16.7 Zip and unzip by strand‐displacing polymerase. (a) Unhybridized ...Figure 16.8 AFM characterization. (a) M1 before zip. (b) M1 after zip. (c) M...Figure 16.9 Dynamic devices created from a single DNA origami. (a) Examples ...Figure 16.10 Dynamic network of nanocontainers using DNA origami transformer...Figure 16.11 Initiated transformations: repeated units of these consolidated...
16 Chapter 17Figure 17.1 Conventional DNA computing and its decoding. (A) Adleman [1] des...Figure 17.2 Applications of nanopore technology. (a) Schematic illustration ...Figure 17.3 Nanopore decoder methodology. NAND operation in a droplet system...Figure 17.4 DNA relay mechanism. (a–f) Conceptual diagrams of the DNA relay ...Figure 17.5 Nanopore decoder applications. (a) Four individual operations as...Figure 17.6 Nanopore detection of miRNAs. (a) MiRNA detection using DNA prob...
17 Chapter 18Figure 18.1 Pipeline of a typical DNA‐based digital storage system.
18 Chapter 19Figure 19.1 General scheme of the system operation: the enzyme computing sys...Figure 19.2 Two enzyme systems used in this study and their corresponding lo...Figure 19.3 (a) Potential measurements on the sensing electrode – general sc...Figure 19.4 (a) Optical analysis of the DNA released (note that the DNA was ...Figure 19.5 The general scheme illustrating the DNA‐based 3‐AND logic gate o...Figure 19.6 Principal scheme of a three‐input deoxyribozyme AND gate. Strand...Figure 19.7 Digital performance of the DNA logic gate. (a) General scheme. (...Figure 19.8 The truth table (a), block diagram (b), and equivalent electroni...Figure 19.9 Experimental realization of the biocatalytic Fredkin gate in the...Figure 19.10 Experimental realization of the Fredkin gate (photo of the flow...Figure 19.11 The block scheme of the entire system including (A) the enzyme‐...Figure 19.12 Operation of the electrochemical interface between the enzyme a...Figure 19.13 (A) Logic scheme (including the ID and XOR gates operating in ...Figure 19.14 Schematic representation of the DNA reactions mimicking XOR fun...Figure 19.15 (a) Nerve cells deposited on a microelectrode array. (b) Beyond...
1 Cover Page
2 Title Page
3 DNA‐ and RNA‐Based Computing Systems
4 Preface
5 Table of Contents
6 Begin Reading
7 Index
8 WILEY END USER LICENSE AGREEMENT
1 iii
2 iv
3 xiii
4 xiv
5 1
6 2
7 3
8 4
9 5
10 6
11 7
12 8
13 9
14 10
15 11
16 12
17 13
18 14
19 15
20 16
21 17
22 18
23 19
24 20
25 21
26 22
27 23
28 24
29 25
30 26
31 27
32 28
33 29
34 31
35 32
36 33
37 34
38 35
39 36
40 37
41 38
42 39
43 40
44 41
45 42
46 43
47 45
48 46
49 47
50 48
51 49
52 50
53 51
54 52
55 53
56 54
57 55
58 57
59 58
60 59
61 60
62 61
63 62
64 63
65 64
66 65
67 66
68 67
69 68
70 69
71 70
72 71
73 72
74 73
75 74
76 75
77 76
78 77
79 78
80 79
81 80
82 81
83 82
84 83
85 84
86 85
87 86
88 87
89 88
90 89
91 90
92 91
93 92
94 93
95 94
96 95
97 96
98 97
99 98
100 99
101 100
102 101
103 102
104 103
105 105
106 106
107 107
108 108
109 109
110 110
111 111
112 112
113 113
114 114
115 115
116 116
117 117
118 118
119 119
120 120
121 121
122 122
123 123
124 124
125 125
126 126
127 127
128 128
129 129
130 130
131 131
132 132
133 133
134 134
135 135
136 136
137 137
138 138
139 139
140 140
141 141
142 142
143 143
144 144
145 145
146 146
147 147
148 148
149 149
150 150
151 151
152 152
153 153
154 154
155 155
156 156
157 157
158 158
159 159
160 160
161 161
162 162
163 163
164 164
165 165
166 166
167 167
168 168
169 169
170 170
171 171
172 172
173 173
174 174
175 175
176 176
177 177
Читать дальше