Fig. 539. The man in the moon
whipping Qaudjaqdjuq.
Fig. 540. Qaudjaqdjuq
has become Qaudjuqdjuaq.
He returned to the moon, but Qaudjaqdjuq, who had now become Qaudjuqdjuaq (the big Qaudjaqdjuq), returned home tossing the stones with his feet and making them fly to the right and to the left. At night he lay down again among the dogs to sleep. Next morning he awaited the bears, and, indeed, three large animals soon made their appearance, frightening all the men, who did not dare to leave the huts.
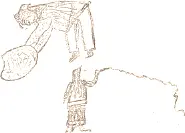
Then Qaudjuqdjuaq put on his boots and ran down to the ice. The men who looked out of the window hole said, “Look here, is not that Qaudjaqdjuq? The bears will soon make way with him.” But he seized the first by its hind legs and smashed its head on an iceberg, near which it happened to stand. The other one fared no better; the third, however, he carried up to the village and slew some of his persecutors with it. Others he pressed to death with his hands or tore off their heads (Fig. 541), crying: “That is for abusing me; that is for your maltreating me.” Those whom he did not kill ran away, never to return. Only a few who had been kind to him while he had been poor little Qaudjaqdjuq were spared, among them the girl who had given him the knife. Qaudjuqdjuaq lived to be a great hunter and traveled all over the country, accomplishing many exploits.

Fig. 541. Qaudjuqdjuaq killing his enemies.
Igimarasugdjuqdjuaq the Cannibal
Table of Contents
Igimarasugdjuqdjuaq was a very huge and bad man, who had committed many murders and eaten the victims after he had cut them up with his knife. Once upon a time his sister-in-law came to visit his wife, but scarcely had she entered the hut before Igimarasugdjuqdjuaq killed her and commanded his wife to cook her.
His wife was very much frightened, fearing that she herself would be the next victim, and resolved to make her escape. When Igimarasugdjuqdjuaq had left to go hunting she gathered heather, stuffed her jacket with it, and placed the figure in a sitting position upon the bed. Then she ran away as fast as she could and suc-ceeded in reaching a village. When her husband came home and saw the jacket he believed that it was a stranger who had come to visit him and stabbed him through the body. When he discovered, however, that his wife had deceived and left him, he fell into a passion and pursued her.
He came to the village and said: “Have you seen my wife? She has run away.” The Inuit did not tell him that she was staying with them, but concealed her from his wrath. At last Igimarasugdjuqdjuaq gave her up for lost and returned home.
The Inuit, however, resolved to revenge the many outrages which he had wrought upon them. They went to visit him and met him on the ice just below the hut. When he told them he was going bear hunting they said: “Let us see your spear.” This spear had a stout and sharp walrus tusk for a point. “Ah,” said they; “that is good for bear hunting; how sharp it is. You must hit him just this way.” And so saying they struck his brow, the point of the spear entering his brain, and then cut the body up with their knives.
Table of Contents
In olden times the Inuit were not the only inhabitants of the country in which they live at the present time. Another tribe similar to them shared their hunting ground. But they were on good terms, both tribes living in harmony in the villages. The Tornit were much taller than the Inuit and had very long legs and arms. Almost all of them were blear eyed. They were extremely strong and could lift large bowlders, which were by far too heavy for the Inuit. But even the Inuit of that time were much stronger than those of to-day, and some large stones are shown on the plain of Miliaqdjuin, in Cumberland Sound, with which the ancient Inuit used to play, throwing them great distances. Even the strongest men of the present generations are scarcely able to lift them, much less to swing them or throw them any distance.

Fig. 542. Tumiujang
or lamp of the Tornit.
(Museum für Volkerkunde,
Berlin IV, A 6848.)
The Tornit lived on walrus, seals, and deer, just as the Eskimo do nowadays, but their methods of hunting were different. The principal part of their winter dress was a long and wide coat of deerskins, similar to the jumper of the Eskimo, but reaching down to the knees and trimmed with leather straps. When sealing in winter they wore this garment, the lower edge of which was fastened on the snow by means of pegs. Under the jacket they carried a small lamp, called tumiujang (literally, resembling a footprint) or quming (Fig. 542), over which they melted snow in a small pot. Some Eskimo say that they opened the seals as soon as they were caught and cooked some meat over these lamps. When the seal blew in the hole they whispered, “Kapatipara” (I shall stab it) and, when they had hit it, “Igdluiliq.” Frequently they forgot about the lamp and in throwing the harpoon upset it and burned their skin.
All their weapons were made of stone. For the blades of their knives they used green slate (uluqsaq, literally material for women’s knives), which was fastened by ivory pins to a bone or ivory handle.
The points of their harpoons were made of bone, ivory, or slate; those of their lances, of flint or quartz, which was also used for drillheads; and they made neither kayaks nor bows.
Their method of hunting deer was remarkable. In a deer pass, where the game could not escape, they erected a file of cairns across the valley and connected them by ropes. Some of the hunters hid behind the cairns, while others drove the deer toward them. As the animals were unable to pass the rope they fled along it, looking for an exit, and while attempting to pass a cairn were lanced by the waiting hunter, who seized the body by the hind legs and drew it behind the line.
This tale is related as a proof of their enormous strength and it is said that they were able to hold a harpooned walrus as the Eskimo hold a seal.
The Tornit could not clean the sealskins so well as the Inuit, but worked them up with part of the blubber attached. Their way of preparing meat was disgusting, since they let it become putrid and placed it between the thigh and the belly to warm it.
The old stone houses of the Tornit can be seen everywhere. Generally they did not build snow houses, but lived the whole winter in stone buildings, the roofs of which were frequently supported by whale ribs. Though the Eskimo built similar structures they can be easily distinguished from one another, the bed of their huts being much larger than that of the Tornit.
Though both tribes lived on very good terms, the Inuit did not like to play at ball with the Tornit, as they were too strong and used large balls, with which they hurt their playfellows severely.
A remarkable tradition is told referring to the emigration of this people.
The Tornit did not build any kayaks, but as they were aware of the advantages afforded by their use in hunting they stole the boats from the Inuit, who did not dare to defend their property, the Tornit being by far their superiors in strength. Once upon a time a young Tuniq had taken the kayak of a young Inung without asking him and had injured it by knocking in the bottom. The Inung got very angry and ran a knife into the nape of the Tuniq’s neck while he was sleeping. (According to another tradition he drilled a hole into his head; this form is also recorded in Labrador.) The Tornit then became afraid that the Inuit would kill them all and preferred to leave the country for good. They assembled at Qernirtung (a place in Cumberland Sound), and in order to deceive any pursuers they cut off the tails of their jumpers and tied their hair into a bunch protruding from the crown of the head.
Читать дальше