II. Northern shore of Hudson Strait:(5) Sikosuilarmiut (King Cape).(6) Akuliarmiut (North Bluff).(7) Qaumauangmiut (Middle Savage Islands).
III. Davis Strait:(8) Nugumiut (Frobisher Bay).(9) Oqomiut (Cumberland Sound):a. Talirpingmiut (west shore of Cumberland Sound and Nettilling).b. Qinguamiut (head of Cumberland Sound).c. Kingnaitmiut (Qeqerten and environs).d. Saumingmiut (southern part of Cumberland Peninsula).(10) Akudnirmiut (Davis Strait).a. Padlimiut (Padli Fjord).b. Akudnirmiut (Home Bay).
IV. Northern part of Baffin Land, North Devon, and Ellesmere Land:(11) Aggomiut.a. Tununirmiut (Eclipse Sound).b. Tununirusirmiut (Admiralty Inlet and North Devon).(12) Inhabitants of Umingman Nuna (Ellesmere Land).
V. Melville Peninsula, Wager River, and Southampton Island:(13) a. Iglulirmiut (Fury and Hecla Strait).b. Amitormiut (eastern coast of Melville Peninsula).(14) a. Pilingmiut (eastern coast of Fox Basin).b. Sagdlirmiut (islands of Fox Basin).(15) Aivillirmiut (Repulse Bay and Wager River).(16) Sagdlirmiut (Southampton Island):
VI. (17) Kinipetu (Chesterfield Inlet).
VII. Boothia Felix and King William Land:(18) Sinimiut (Pelly Bay).(19) Netchillirmiut (Boothia Felix and King William Land).(20) Ugjulirmiut (King William Land and Adelaide Peninsula).(21) Ukusiksalirmiut (estuary of Back River).
VIII. Qidnelik (coast west of Adelaide Peninsula).
IX. Inhabitants of North Greenland.
Table of Contents
Seal, Walrus, and Whale Hunting
Table of Contents
The staple food of the Central Eskimo is the seal, particularly Pagomys fœtidus . The methods of hunting this animal differ materially at different seasons, as its mode of life depends on the state of the ice.

Fig. 390. harpoon from Alaska.
(American Museum of Natural History,
New York.)
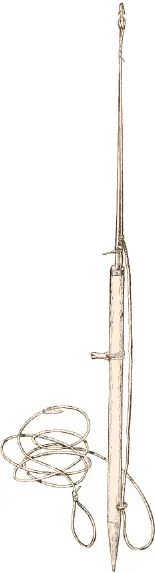
Fig. 391. Modern unang or sealing harpoon.
(Museum für Völkerkunde,
Berlin. IV A 6729.)
In the winter it takes to the smooth parts of the floe a few miles from the coast, where it scratches breathing holes through the ice, in which it rises to blow. It shuns hummocky ice and floes of more than one year’s age. Wherever the edge of the ice is at a great distance from the settlements, the only way of procuring seals is by watching for them at these holes. For the pursuit a light harpoon is used, called unang. The shape of this weapon has been somewhat changed since the introduction of rod iron. Formerly it consisted of a shaft having at one end an ivory point firmly attached by thongs and rivets, the point tapering toward the end. The point was slanting on one side so as to form almost an oblique cone. Thus it facilitated the separation of the harpoon head from the unang. On the opposite end of the shaft another piece of ivory was attached, generally forming a knob. The material used in making the shaft was wood, bone, or ivory, according to the region in which it was manufactured. In Iglulik and in Aggo the narwhal’s horn was the favorite material for the whole implement, a single horn being sufficient to make a whole shaft. Wherever wood could be procured small pieces were ingeniously lashed together. As the shaft is apt to be broken by the struggles of the animal when struck by the weapon, it was strengthened by a stout thong running along the whole length of the shaft. In all other respects the old design corresponds to the modern one. Unfortunately I have seen no specimen of this description, but a figure may be seen in Ross II, p. 272, in the hand of one of the natives. In Alaska a similar harpoon is in use, a specimen of which is represented in Fig. 390. It consists of a wooden shaft, with a stout ivory point at the lower end and another at the upper end. Both are fastened to the shaft by whalebone strings. In the upper end a slanting ivory point is inserted, which serves for attaching the harpoon head to it. The whole shaft is strengthened by a seal line, as shown in the figure.
The unang now in use in Baffin Land and on the western shore of Hudson Bay (Fig. 391) consists of a wooden shaft into which an iron rod (unartenga) is sunk. The latter is pointed at the end (see, also, Fig. 393) in about the same way as the old ivory implement. The socket is secured by a small ivory ring (unaqiuta) or a string wound around the end of the shaft. In the socket close to the iron rod a bent nail is inserted, forming a narrow eye (tagusiarbing). Near the center of the whole implement a small piece of ivory (tikagung; see, also, Fig. 418) is fastened to the shaft, forming a support for the hand when throwing the weapon. At the lower end of the shaft a string of deer sinews or a thong is fastened, forming a loop (nabiring) which passes through a hole drilled through the shaft. A stout iron point is also attached to the lower end of the shaft (tounga).

Fig. 392. Old style naulang or harpoon head. (Museum für Völkerkunde, Berlin. IV A 6692.) 1/1
The natives carry this implement on all their winter excursions, as it is serviceable for numerous purposes. It is always kept within reach on the sledge, as the strong iron point is useful for cutting down hummocks, should any obstruct the passage of the sledges, or for cutting holes through the ice, or it takes the place of a hatchet in breaking the frozen meat which is carried along for dogs’ food. The long iron rod is extremely useful in trying the strength of the ice or the depth of the snow. By taking precautionary measures of this kind the natives pass over extensive floes of weak ice.

Fig. 393. Modern naulang or harpoon head (Museum für Völkerkunde, Berlin. IV A 6729.) ½
The head belonging to the unang is called naulang. Since iron has been introduced in Baffin Land and Hudson Bay, the natives file their harpoon heads out of it, but adhere almost exactly to the old pattern. The old naulang was cut out of bone or more frequently out of ivory (Fig. 392). It was one inch to two inches long and had a piece of metal inserted into the slit at the top. Through the middle of the instrument a hole was drilled parallel to the plane of the blade. The harpoon line passed through the hole, and as soon as the point struck an animal and a strain was put upon the line it turned at a right angle to the latter, thus acting as a toggle. The effect was increased by two points at the lower end of the naulang, called uming (beard). These pressed into the flesh or the skin of the animal and prevented the harpoon head from slipping back.
The modern naulang (Fig. 393) is about the same length as the old one, but much more slender. While the back of the old pattern was straight, the points of the iron one are bent outward and backward in order to increase its effect.
The naulang is fastened to the harpoon line (iparang). This part of the instrument is much longer than the unang, as it must allow for the struggles of the diving seal. The end of the line passes through the hole of the naulang and a loop is formed and secured by deer sinew or arranged as may be seen in Fig. 393. At a distance equal to the length of the iron rod of the unang a small thong (taguta) is attached to the line and serves to fasten it to the shaft (see Fig. 391). It is drawn through the eye formed by the tagusiarbing. As soon as a strain is put upon the naulang the line parts from the shaft, as the taguta is only squeezed into the eye and is easily detached. The harpoon line passes through the nabiring or is fastened by a slipping hitch to the shaft of the unang.
Читать дальше
















