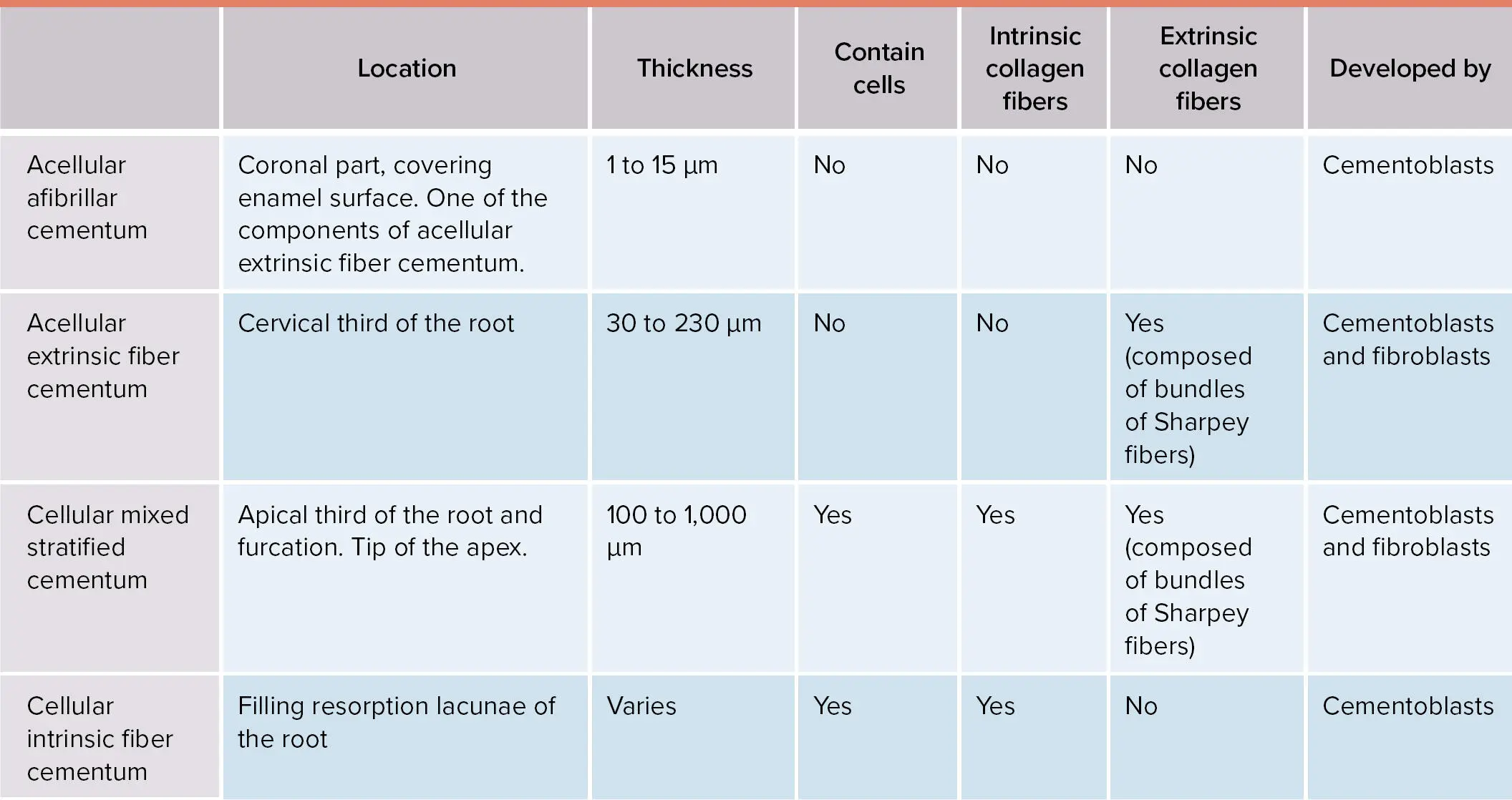
Based on the presence of cementocytes embedded in its extracellular matrix, the cementum can be classified as cellular or acellular. In addition, the fibers that form the cementum will contribute to the classification of the different types 5( Table 1-3).
TABLE 1-3 Features of the different types of cementum
As in the formation of the PDL, cementum starts developing in a prefunctional stage prior to the eruption of the tooth. After the crown is formed, the cells of the inner and outer enamel epithelium that constitute the cervical loop will proliferate deeper into the ectomesenchyme driving the development of the dental root. This structure is known as the Hertwig epithelial root sheath (HERS). The most apical portion of the HERS, which encloses the dental papilla, is known as the epithelial diaphragm. Cells from the HERS induce the differentiation of the dental papilla cells in a coronoapical direction to become odontoblasts that will form the dentin of the root. The number and morphology of the dental roots will be determined by the disposition of the HERS. The cementum, the mineral portion of the root facing the PDL, is formed by cementoblasts that are believed to originate from the ectomesenchymal cells of the dental follicle after the disintegration of the HERS. Cells from the HERS produce different proteins and mediators to induce the differentiation of the dental follicle cells into cementoblasts. Fibroblasts in the area produce bundles of collagen fibrils that form fringe fibers, and these are anchored to the tooth by the deposition of a mineral matrix by cementoblasts.
When the tooth is near to entering its functional stage, a shift in the formation of cementum can be seen from acellular extrinsic fibrillar cementum to mixed stratified cementum. The rate of growth of cementum is 1.5 to 3 µm per year. 12
Even though the previously described formation of cementum is the most accepted theory, an alternative hypothesis has been proposed. This theory suggests an enhanced role of the HERS in the formation of cementum through the differentiation of HERS cells to become cementoblasts. 13
The chemical composition of cementum is similar to bone with approximately one-third organic material, one-third mineral phase, and one-third water. The primary inorganic structure of cementum is also hydroxyapatite crystals. The organic material is composed of collagen, glycoproteins, and proteoglycans ( Box 1-1).
BOX 1-1 Organic chemical composition of cementum
| Collagenous proteins |
Collagen I (90%)Collagen III (5%) |
| Noncollagenous proteins |
Glycoproteins |
| Glycolipids |
| Proteoglycans |
| Enamel-related proteins |
The oral mucosa is composed of the mucosal tissues that cover the mouth, and it can be classified as masticatory mucosa (gingiva and hard palate), lining mucosa (alveolar mucosa, floor of the month, and internal surface of lips), and specialized mucosa (tongue). The lining or alveolar mucosa extends inside the cheeks, floor of the mouth, as well as soft palate, and it is characterized by the presence of a basal layer (which is positive to the expression of keratin 5, 14, and 19), an intermediate layer, and a superficial layer expressing keratin 13 and 4. 14
The gingiva (masticatory mucosa) is composed of free gingivaand attached gingiva, and it is characterized by the presence of keratin in the most superficial layer. Histologically, four layers of cells have been described (Fig 1-1):
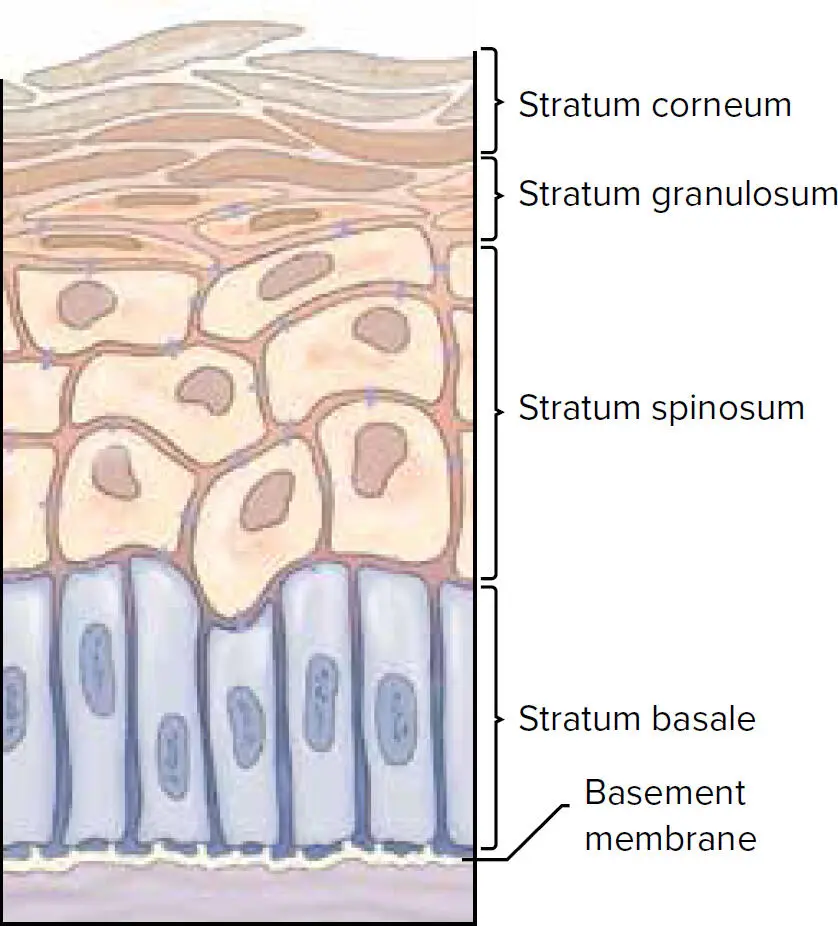
Fig 1-1 Layers of keratinized gingiva.
1 Stratum basale, which is characterized by the expression of keratin 5 and 14
2 Stratum spinous, named due to the spinous morphology of the cells in this layer
3 Stratum granulosum, characterized by the presence of round cytoplasmic granules
4 Stratum corneum with cornified cells
Gingiva has different names and presents with slight morphologic differences depending on the tissue that it covers (ie, free gingiva or attached gingiva; Fig 1-2).
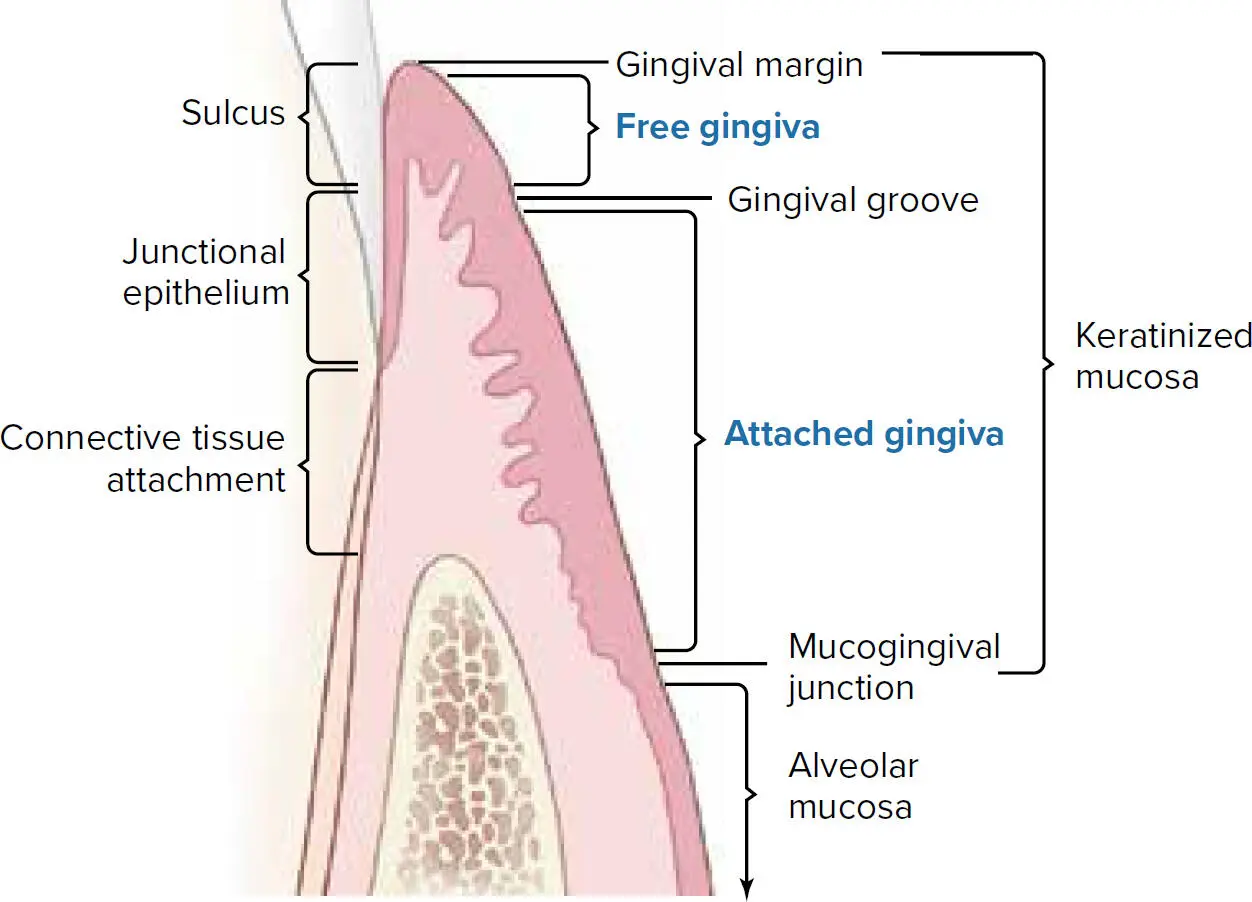
Fig 1-2 The gingiva.
Free gingiva is the portion of the gingival epithelium that extends from the free gingival margin to the gingival groove (see Fig 1-2). The gingival grooveis defined as the “shallow linear depression on the gingiva surface that demarcates the free gingiva and the attached gingiva.” 1The free gingiva covers the teeth at the vestibular and lingual sites following the contour of the tooth and the dental papilla. In normal conditions, the free gingiva presents as a coral pink color. The location of the gingival groove is determined by the position of the CEJ, and it is present in 4% to 54% of teeth with differences based on tooth type. 15,16
Attached to the tooth and/or alveolar bone, the attached gingiva is delimited by the gingival groove at the coronal end and the mucogingival junction at the apical end. In healthy conditions, it also presents with a coral pink color. A morphologic characteristic of the attached gingiva is the stippling or orange peel appearance. The stippling corresponds to small epithelial ridges and is developed in areas of high keratinization. When the attached gingiva is inflamed, it loses the superficial stippling, and the color turns to a darker red. 15,17,18
The mucogingival junction, which is the interphase between the attached gingiva and the oral mucosa, is located between 3 to 5 mm apical to the alveolar crest, and it has been shown to be stable over the years in reference to the base of the mandible or floor of the nose. Consequently, an increase in attached gingiva with age has been associated with the continuous eruption of the dentition. 19,20The dimensions of the attached gingiva have been investigated in classic studies by Bowers 21and Voigt et al. 22In the maxilla, the sites with the greatest width of attached gingiva are the central and lateral incisors. There is a decrease in canines and first premolars, and a slight increase over the second premolar and molar locations. In the mandible, the incisors also present with the greatest amount of attached gingiva with a sharp decrease around the canines and first premolars. At the second premolar site, the attached gingiva increases, and a decrease at the mandibular molar area is also observed. On the lingual aspect, the molar area presents with the greatest attached gingiva followed by premolars, incisors, and canines.
Based on the location and microscopic appearance, the gingival epithelium can be classified into three types: oral, sulcular, and junctional epithelium.
The oral epithelium is a keratinized stratified squamous epithelium that extends from the mucogingival junction to the free gingival margin. In some areas of the most superficial layer, the stratum corneum, the cells maintain their nuclei and are considered parakeratinized. If no nuclei are present in the stratum corneum, this epithelium is considered orthokeratinized. In addition to the keratinocytes, other cells can be found in the oral epithelium, such as melanocytes, which give pigmentation to the epithelium; Langerhans cells, which play a role in the immune response; and Merkel cells, which are important for sensory function.
Читать дальше