K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN)—For regression and classification problems, K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) algorithms are used. KNN approaches are using data and graded use similar steps to different data points. The information is reserved for the class with the closest neighbors. The value of k increases with the increase of the number of closest neighbors. KNN is not realistic on big data applications because of the high cost of calculation and memory.
Naive Bayes Classifier—For classification function Naive Bayes Classifier is commonly used. For any class or data point that belongs to a certain class, they define membership probabilities. The most probable class is the one with the highest likelihood. The efficiency of Naive Bayes is not possible in text classification tasks due to text redundant features and rough parameter estimation.
Neural Networks—A semi-supervised technique for classification and regression, the Neural networks. Neural Nets is a computing device consisting of highly interrelated processing elements that process data via their dynamic state response. Back Propagation is one of the best-known algorithms in the neural network. Neural networks have few challenges for big data with the growing scale of information. The huge quantity of information makes it difficult for the technique to maintain both reliability and efficiency and also increases the system operating load.
Over the last couple of decades, the concept of resilience has received increasing attention in several ways and is now viewed as a desirable feature of physical systems and communities. A popular feature in both meanings is that resilience “is the system’s capacity to tolerate external disturbance(s), adjust and rapidly return to the initial or a new stage,” and also offers a multi-disciplinary concept in resilience within the engineering sector [9 –15].
Resilience can be described as an ability to reach a desired level of reliability or provide a desired level of service or features in the physical systems, Q, immediately after a risk arises.
1.4.1 Sustainability and Resiliency Conditions
Most societies choose to be resilient and sustainable [50]. When priorities and plans are formulated separately in order to enhance resilience and sustainability, there are strong risks that the targets may overlap and may also clash. This chapter looks at the principles of safe and durable cities, how increasing environmental and constructed environments and stressors will need different approaches and resources to improve stability and longevity for the environment.
When their resilience and sustainable strategies align themselves, the best results for communities occur. However, sustainable and resilient advancement must be accomplished before promising future generations are delivered. Challenges include reduction of impacts on environmental systems, management and the time it takes to change current practices and replace existing infrastructure with standard renewal rates. Nevertheless, while the governance potential and sustainability and adaptation strategies are open, intergenerational wealth is undermined by expectations that natural environments (our atmosphere, habitats, and climate) are secure and healthy [16 –20]. Introduction to sustainability and the resilience of buildings, the dynamic nature of natural systems has not been fully understood through their intricate interrelationships across time and space and their preference for inclination points and threshold values. Many experts face the challenge of developing dangerous model infrastructure that does not involve potential improvements in risk magnitude or frequency, because scientific consensus is not yet formed on this topic. In fact, today’s construction methodology does not take into consideration the harm rates and related impacts on building operation recovery—a critical aspect of resilience.
1.4.2 Paradigm and Challenges of Sustainability and Resilience
A basic yet strong definition is sustainable development to ensuring that society “combines the present need without compromising potential generations’ capacity to fulfill their needs” (UN 1987). The groundbreaking Bruntland Commission study on sustainable growth presented this Sustainable development concept for the first time. With the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals in 2015, sustainable development remains an international initiative which has motivated policy and individuals worldwide to alleviate some of the more drastic consequences of mankind on the global operation of the environment.
The idea of cohesive societies emerged concurrently. Application and special concept of resilience to a variety of subjects and dimensions, include psychology, economics, public safety, protection, business continuity, disaster preparation and reaction, risk reduction and ability of the building system (i.e. design, transport, services and other infrastructure) to physically resist and rapidly recover. In terms of populations and dangerous incidents, “the capacity to adjust and withstand and recover rapidly from damage” is specified (PPD-21 2013). The idea of building resilience and infrastructure systems, in order to minimize damage to the environment, restore and reconstruct expenses as well as economic impacts, is to be avoided until a certain point, then improve or recover over a certain period of time [21, 22, 26 –28]. In reality there also are situations where the constructed system cannot avoid only threshold hazard in terms of the different facilities age and circumstances around a city. Throughout these situations, contingency preparation may be used to recognize performance gaps and transitional measures which would allow the society to continue to deliver services, if the building(s) or network system(s) impacted is not willing to do so. Such performance holes often present the possibility of beginning an innovative cycle to enhance construct environments efficiency.
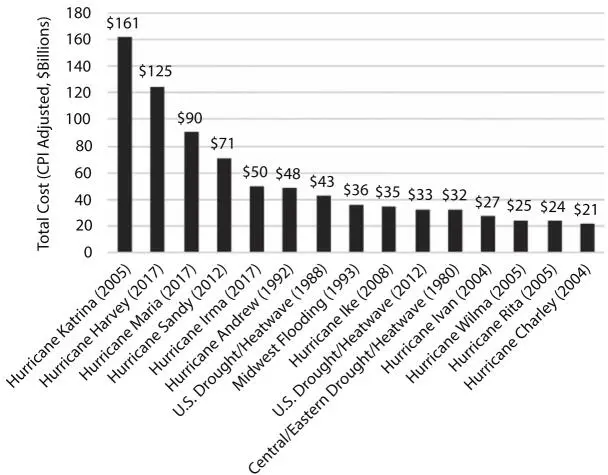
Figure 1.1Natural hazard year wise in US.
Natural disasters will affect societies by human loss, relocation, death, property harm and economic impacts. Such consequences and sluggish group rebounder may be amplificated by structural stressors like high unemployment, inadequate services or food shortages. The National Environmental Awareness Centers (NOAA, 2018a) report that 218 extreme weather events happened in the USA between 1980 and 2017 worth at least $1 billion. The degree to which societies have been affected and lost their work from natural disasters is seen in Figure 1.1. The enhancement of construction and infrastructure’s robust and sustainable efficiency will help cities escape major economic loss and long-term consequences.
1.4.3 Perspectives of Local Community
There are a number of communities in the United States which recover each year from a dangerous event. Over the last 50 years, an annual average of 40 declarations of presidential hazardous events has been issued (FEMA 2013). Hazardous results are first experienced and first handled in populations. While governments cannot eliminate natural threats, long-term planning and prioritized initiatives that are enforced over time will mitigate their effects. The level of recovery and the eventual outcome would rely on the scope and magnitude of the incident and on the action taken by government to mitigate harm, preserve properties, react in a timely and organized manner and restore government functionality within a given time period. Such activities collectively assess the strength of a group.
Читать дальше


![Чарльз Диккенс - A Tale of Two Cities [С англо-русским словарем]](/books/26616/charlz-dikkens-a-tale-of-two-cities-s-anglo-thumb.webp)










