1 ...8 9 10 12 13 14 ...20 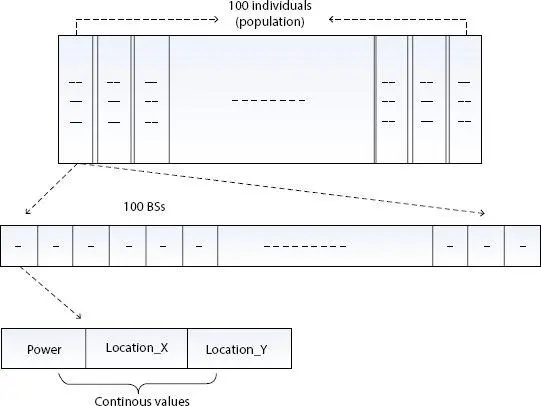
Figure 1.13Illustrative example ofthe proposed algorithm [41].

Figure 1.14The algorithm for the transmission [41].
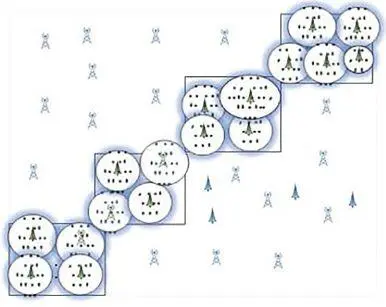
Figure 1.15An illustrative example of the working of the transmission algorithm [41].
1.6 Conclusion & Future Work
In today’s era, almost everything is connected through the Internet. IoT devices network is a prominent example of it, and it leads to the requirement of faster communication network such as 5G. With faster communication, we can yield full capabilities of IoT devices in the various application domains such as healthcare, I-IoT, agriculture, etc. Presently some issues exist such as transmission efficiency and cell power utilization with limited solutions for these issues. In future more efficient algorithms, protocols and viable solution are required and will be developed to get the maximum potential of IoT devices with the 5G network.
1. Gubbi, J., Buyya, R., Marusic, S., Palaniswami, M., Internet of Things (IoT): A vision, architectural elements, and future directions.
2. Ermolov, V. et al ., Significance of Nanotechnology for future wireless devices and Communications. The 18th Annual IEEE International Symposium on PIMRC’07 .
3. Salahuddin, M. A., Al-Fuqaha, A., & Guizani, M., Exploiting context severity to achieve opportunistic service differentiation in vehicular Ad Hoc networks. IEEE transactions on vehicular technology , 63, 6, 2901–2915, 2013.
4. Yu, Z., Liang, Y., Xu, B. et al ., Towards a smart campus with mobile social networking, in: Proceedings of the 4th IEEE Int’l Conference on Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom) , IEEE, Dalian, China, 2011.
5. Pearl, D. Journal of Higher Education Outreach and Engagement, 17, 3, 1–157, 2013.
6. Minoli, D., and Occhiogrosso, B., Practical aspects for the integration of 5G networks and IoT applications in smart cities environments. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing , 2019, 2019.
7. Painter, S., Fournier, J., Grape, C., Grummon, P., Morelli, J., Whitmer, S., & Cevetello, J., Research on learning space design: Present state, future directions. Society of College and University Planning, 2013.
8. Kyriazis, D., Varvarigou, T., White, D. et al ., Sustainable smart city IoT applications: heat and electricity management & ecoconscious cruise control for public transportation, in: Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Symposium on “A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks” (WoWMoM) , IEEE, Madrid, Spain, 2013.
9. Minoli, D., What is the internet of things?. Building the Internet of Things with IPv6 and MIPv6: The Evolving World of M2M Communications, 1–27, 2013.
10. Grodi, R., Rawat, D.B., Rios-Gutierrez, F., Smart parking: Parking occupancy monitoring and visualization system for 28 Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing smart cities, in: Proceedings of the Southeast Con , IEEE, Norfolk, VA, USA, 2016.
11. Soudani, A., Marrón, P., & Shih, C. Y. Wireless Ad Hoc Sensor Networks.
12. Shuja, J., Gani, A., Shamshirband, S., Ahmad, R. W., & Bilal, K., Sustainable cloud data centers: A survey of enabling techniques and technologies. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews , 62, 195–214, 2016.
13. Liu, X. F., Zhan, Z. H., Deng, J. D., Li, Y., Gu, T., & Zhang, J. An energy efficient ant colony system for virtual machine placement in cloud computing. IEEE transactions on evolutionary computation , 22, 1, 113–128, 2016.
14. Juels, A., RFID security and privacy: A research survey. IEEE journal on selected areas in communications, 24, 2, 381–394, 2006.
15. Ly, F., Carrier Network Virtualization 2016: The Future of 5G and System Integrators. Radisy, 2016.
16. Mahmoud, M. S., & Mohamad, A. A., A study of efficient power consumption wireless communication techniques/modules for internet of things (IoT) applications, 2016.
17. Lee, J.-S., Su, Y.-W., Shen, C.-C., A Comparative Study of Wireless Protocols: Bluetooth, UWB, ZigBee, and Wi-Fi. 33rd Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society (IECON) , Taipei, 5–8 November 2007, pp. 46–51, http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/iecon.2007.4460126.
18. Tozlu, S., Senel, M., Mao, W., Keshavarzain, A., Wi-Fi Enabled Sensors for Internet of Things: A Practical Approach. IEEE Commun. Mag ., 50, 134–143, http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/MCOM.2012.6211498, 2012.
19. Burchfield, T.R., Venkatesan, S., Weiner, D., Maximizing Throughput in ZigBee Wireless Networks through Analysis, Simulations and Implementations. Proceedings of the International Workshop on Localized Algorithms and Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks , Santa Fe, 18–20, 18–20 June 2007.
20. Alliance, L., LPWA technologies unlock new IoT market potential. White Paper. LoRa, 2015.
21. Nguyen, D. D., Nguyen, H. X., & White, L. B., Reinforcement learning with network-assisted feedback for heterogeneous RAT selection. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications , 16, 9, 6062–6076, 2017.
22. Le, Q. V., Jaitly, N., & Hinton, G. E., A simple way to initialize recurrent networks of rectified linear units. arXiv preprint arXiv:1504.00941, 2015.
23. Alnwaimi, G., Vahid, S., & Moessner, K., Dynamic heterogeneous learning games for opportunistic access in LTE-based macro/femtocell deployments. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications , 14, 4, 2294–2308, 2014.
24. Wang, L. C., & Cheng, S. H. Data-driven resource management for ultra-dense small cells: An affinity propagation clustering approach. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering , 6, 3, 267–279, 2018.
25. Parwez, M. S., Rawat, D. B., & Garuba, M., Big data analytics for user-activity analysis and user-anomaly detection in mobile wireless network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics , 13, 4, 2058–2065, 2017.
26. Li, R., Zhao, Z., Zhou, X., Ding, G., Chen, Y., Wang, Z., & Zhang, H., Intelligent 5G: When cellular networks meet artificial intelligence. IEEE Wireless communications , 24, 5, 175–183, 2017.
27. Jiang, C., Zhang, H., Ren, Y., Han, Z., Chen, K. C., & Hanzo, L., Machine learning paradigms for next-generation wireless networks. IEEE Wireless Communications , 24, 2, 98–105, 2016.
28. Han, S. Y., Abu-Ghazaleh, N. B., & Lee, D. Efficient and consistent path loss model for mobile network simulation. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking , 24, 3, 1774–1786, 2015.
29. Liu, J., Deng, R., Zhou, S., & Niu, Z., Seeing the unobservable: Channel learning for wireless communication networks. In 2015 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) , (pp. 1–6), IEEE, 2015.
30. Minoli, D., & Occhiogrosso, B., Practical aspects for the integration of 5G networks and IoT applications in smart cities environments. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing , 2019.
31. Osseiran, A., Braun, V., Hidekazu, T., Marsch, P., Schotten, H., Tullberg, H., ... & Schellman, M., The foundation of the mobile and wireless communications system for 2020 and beyond: Challenges, enablers and technology solutions. In 2013 IEEE 77th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring) , (pp. 1–5), IEEE, 2013.
Читать дальше















