The routing unit protocol is distinguished based on their characteristics are Table-Driven Routing Protocol (TDRP), On-Demand Routing Protocol (ODRP), and Hybrid Routing Protocol (HRP) [30]. The definition of routing unit protocols based on their characteristics is as follows:
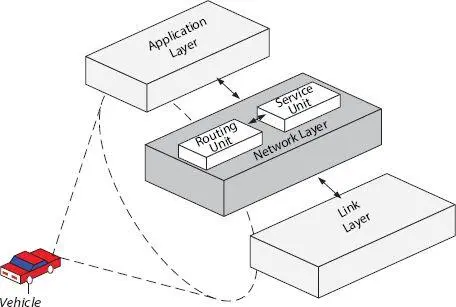
Figure 2.2A framework of service discovery.
Table 2.2Comparison of routing unit and service unit.
| Characteristics |
Routing unit |
Service unit |
| Protocols |
Routing protocols |
Service protocols |
| Leaned on |
Process-Oriented |
Resource-Oriented |
| Discover |
Finds the superlative path |
Finds the superlative services |
| Parameter for Discovery |
Distance, energy, cost, and so on. |
Accuracy and efficiency. |
| Mechanism |
Route discovery mechanism |
Service discovery mechanism |
| Information |
Routing information |
Service information |
| Layer |
Network layer |
Network layer |
| Protocols |
PUSD, PLSD, and HSD [13–27]. |
TDRP, ODRP, and HRP [28]. |
| Reliability |
Yes |
Yes |
TDRP: This protocol reads the topological information continuously and updates it in the routing table.
ODRP: This protocol reads the topological information when it requires.
HRP: Hybrid uses the features of both TDRP and ODRP.
2.5 Service Discovery Architecture for 5G-VANET Milieu
The few important network characteristics to be considered while designing the service discovery architecture for 5G-VANET are dense, mobility, scalability, collision, failure, congestion, reliability, service availability, and latency. The services provided by the service discovery mechanism are classified into two types such as fixed services and moving services. The definitions of fixed and moving services are as follows:
Fixed Services: The fixed services are the services stored by the service provider in the repository.
Moving services: The moving services are dynamic service. The few examples of moving services are real-time gaming, music sharing, file sharing between two vehicles, and so on.
The service discovery mechanism can be divided into vehicle user side discovery and service provider side discovery. The definition is stated as follows:
2.5.1 Vehicle User Side Discovery
The vehicle user application program does easier as it did not work with the discovery part. Rather, it transmits a request packet to the router. From the router forwards the request to the SP.
2.5.2 Service Provider Side Discovery
The service provider stores the resources (service instances) in the Service Registry (SR). SP checks for the required services in the SR.
The service instances are stored/registered based on two options such as self-pattern and third-party pattern. The self-pattern stores the services by itself. In a third-party pattern the third party stores the services. The service instance changes periodically. For each vehicle user request, the discovery mechanism has to be taken place.
The service registry is a vital component of the service discovery process. It consists of a collection database that stores the service instances.
Figure 2.3 depicts the architecture of service discovery processes for fixed services in the 5G-VANET milieu. The architecture of service discovery processes consists of five components such as human–machine interface display, functional module, context module, non-functional module, and composer. The VANET user enters the request in the human–machine interface display, it’s the functional requirement. The context module gathers the context information from the GPS sensors. The non-functional requirements such as scalability, integrity, cost of service, capacity, security, robustness, and performance are specified by the developers. The composer combines the context information, functional information, and non-functional information and transmits it to the Service Provider (SP). The SP searches for the required resources in the registry and retrieves the optimal services to the VANET users.
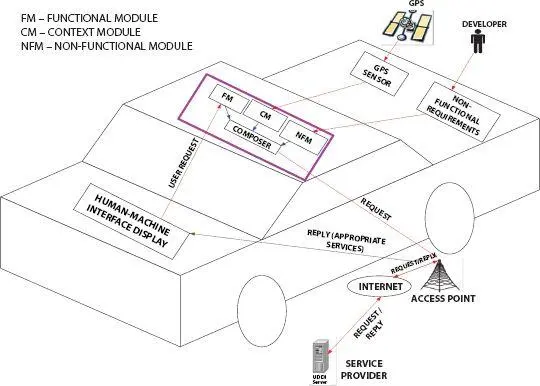
Figure 2.3Service discovery Architecture for 5G-VANET milieu.
2.6 Performance Evaluation Metrics for Service
Discovery Mechanism in the 5G-VANET Milieu
The petty important performance evaluation metrics which are used to measure the performances of the service discovery mechanism in the 5G-VANET milieu are vehicle user to target delay, success rate, response time, average bandwidth consumption, delivery ratio, packet order ratio, collision ratio, and duplicate packets ratio. The performance evaluation metrics are stated in the definition:
Vehicle User-To-Target Delay: The vehicle user-to-target delay determines the delay in terms of milliseconds from sender to receiver. It includes the queuing delay, processing time, and retransmission delay.
Success Rate (SR): SR determines the failed and successful transactions. Response Time: A response time determines the average time consumption between the response and request.
Average Bandwidth Consumption: It calculates the average bandwidth consumption for a single transaction.
Delivery Ratio: Delivery ratio is calculated by packets delivered to the packet sent, in terms of numbers. It determines the number of successful delivery of packets.
Packet Order Ratio: The packet order ratio determines the received packet order.
Collision Ratio: The collision ratio is calculated by packets collided to the packets sent in numbers.
Duplicate Packets Ratio : The duplicate packets ratio is calculated by determining the duplicate packets at the destination, estimated in numbers.
2.7 The Advantage of Service Discovery in the 5G-VANET Milieu
By integrating the 5G with VANET will not only affords the vehicle users with seamless connectivity but also endorse a glut of a new application.
The 5G-VANET users can enjoy the high data rate with low latency.
The 5G-VANET users can enjoy the voice streaming video and interactive multimedia without any intermittent.
5G enhances the discovery procedures in a VANET milieu by affording high reliability and low latency.
2.8 The Disadvantage of Service Discovery in the 5G-VANET Milieu
5G-VANET milieu technology is still in research and development.
The 5G-VANET milieu infrastructure is a high cost.
The affording the security and privacy in the 5G-VANET milieus is a major task.
Protecting the service consumers and providers from security attacks is another major issue in the discovery procedures.
2.9 Future Enhancement and Research Directions
The technological infrastructure such as vehicles to everything and vehicle to infrastructure communications modes can be enhanced.
The Intelligent Transportation System (ITS) performance can be enhanced.
Читать дальше














