Figure 1.14. Tool string configurations.
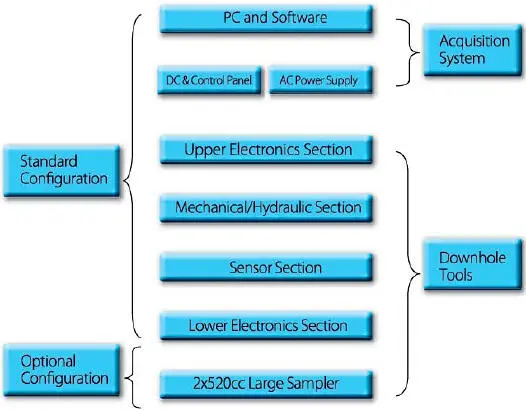
Figure 1.15. Tool architecture.
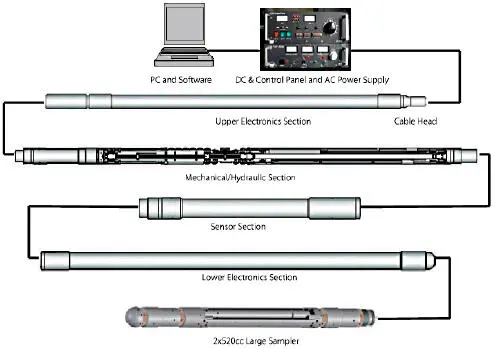
Figure 1.16. Tool and surface system.
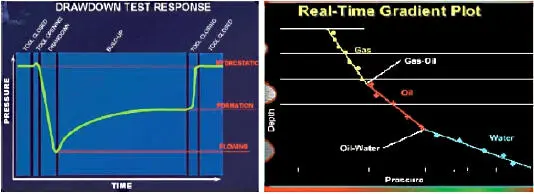
Figure 1.17.Pressure drawdown curve (left) and fluid contact curve (right).
1.2.3 Enhancing and enabling technologies.
While we principally focus on pressure transient analysis in this volume, a number of enabling technologies contribute to the operational success of formation testers in general, and in particular the robustness of the tools mentioned in Sections 1.2.1and 1.2.2. A critical problem is that associated with “stuck tools,” which results in expensive fishing jobs, lost tools and increased rig costs.
Stuck tool alleviation.Issues related to stuck pipe are as old as drilling itself. In “Development on Incongruous Pushing and Stuck Releasing Device of EFDT,” by Qin, X., Feng, Y., Song, W., Chu, X. and Wang, L. and appearing in Journal of China Offshore Oilfield Technology , Vol. 4, No. 1, April 2016, pp. 70-74, the authors analyze the causes of differential pressure sticking during openhole wireline logging. Their modular IPSRD releasing device, designed for EFDT formation tester applications, could be seamlessly assembled to the tool. “Stuck Release Arms” (SRA) are driven by hydraulic forces that free the dual probe tool from adhesive forces. In Chapters 4and 5, we show how mudcake thicknesses can be accurately modeled and predicted – small values to reduce chances for tool loss are needed, while larger thicknesses are required to seal tester pads to the sandface – at the same time, providing excellent descriptions for supercharge pressure effects.
The authors importantly point out that while measuring pressure and sampling, even at a single point in the well, duration times may last several hours or even tens of hours. In particular, for higher mud densities, the possibility of differential sticking – and the likelihood of expensive fishing jobs – is high. In extreme cases, loss of the tool downhole and well abandonment are possible. Figure 1.18explains the conceptual ideas behind IPSRD. The left diagram illustrates the differential sticking process, with the following nomenclature: 1-Wellbore fluid, 2-Backup, 3-EFDT, 4-Mudcake, 5-Probe, 6-Protector and 7-Formation. The right side outlines the tool architecture. Upper Stuck and Lower Stuck release modules USRM and LSRM are found at the top and bottom, with the Dual Probe Module (DPM) residing between the two. The “stuck release arms” (SRA) for each releasing module are designed in opposite directions for pushing separately. The paper describes several field applications and savings in logging costs.
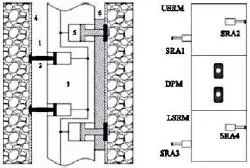
Figure 1.18. IPSRD stuck tool release mechanism.
Field facilities.Finally, we offer some snapshots of COSL logging trucks and rigsite facilities from which formation testing jobs are run. The photographs are self-explanatory.

Figure 1.19.Rigsite facilities.
1.3 Recent Formation Testing Developments.
Conventional formation tester tools with single and dual probes are shown in Figures 1.8and 1.9, noting that different testers may be outfitted with different pad designs depending on the application. For instance, small round nozzles may be used with firm matrix rock; in low permeability formations, larger nozzles may be preferable in order to prevent excessive pressure drawdowns that result in the undesired release of dissolved gas or increased mechanical demands. Larger slot nozzles are ideal when formations are lower in permeability or naturally fractured and higher pump rates are desired.
The right-side diagram in Figure 1.6shows an active pumping “sink probe” mounted on the mandrel, with a passive “horizontal” observation probe located 180° circumferentially away around the borehole. A “vertical probe” is also shown displaced axially from the sink probe and lying along the same azimuth. This conventional 1990s designed “triple probe” tool has seen wide application since its introduction. However, in low mobility formations, questions related to weak pressure signal detection and large diffusion arise.
These have motivated the design of a new and different type of “triple probe” tester, where three independently operated, closer probes are located about the borehole at 120° separations, all residing in the same axial plane and supporting pumping and pressure measurement. Axially displaced “vertical probes” also augment the new triple probe design. The new COSL tool offers advantages over conventional instruments and these are described in a companion 2021 book Formation Testing – Multiprobe Design and Pressure Analysis by Lu, Zhou, Feng, Yang and Chin (John Wiley & Sons). Because of the three-dimensional nature of the physics, the complementary volume develops new analysis and interpretation methods that account for borehole size and shape, and without invoking symmetry assumptions, since the probes may differ during any logging run and pump with different flow rate schedules. Figures 1.20– 1.22show example graphics from the book.

Figure 1.20. New triple probe formation tester. Pads with “small round nozzle and slot probe” (top) and “all long slot nozzles” (bottom).

Figure 1.21.New COSL triple probe tester, perspective view.
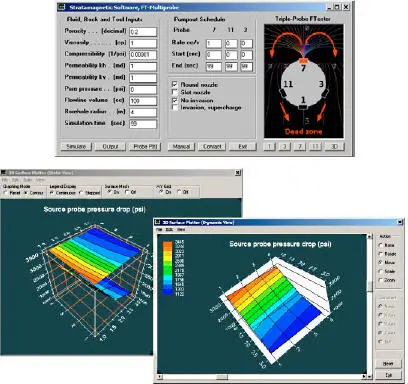
Figure 1.22. Simulator menu for Probes 3, 7 and 11 (top), sink Probe 7 pressure drop versus kh and kv at fixed rate (bottom).
• Chin, W.C., Formation Testing: Supercharge, Pressure Testing and Contamination Models , John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2019.
• Chin, W.C., Zhou, Y., Feng, Y. and Yu, Q., Formation Testing: Low Mobility Pressure Transient Analysis, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2015.
• Chin, W.C., Zhou, Y., Feng, Y., Yu, Q. and Zhao, L., Formation Testing: Pressure Transient and Contamination Analysis , John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2014.
• Lu, T., Qin, X., Feng, Y., Zhou, Y. and Chin, W.C., Supercharge, Invasion and Mudcake Growth in Downhole Applications , John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, 2021.
Читать дальше


















