Pressures obtained in PTA logging are used for multiple applications. For example, depending on the tool, permeability, anisotropy, compressibility and pore pressure are all possible (the term “mobility,” defined as the ratio of permeability to viscosity, is often interchangeably used, assuming that the viscosity is known). The pore pressure itself is used to identify fluids by their vertical hydrostatic gradients; this is possible because changes in pressure are affected by changes in fluid density. Sudden changes in pressure, for instance, may indicate the presence of barriers. However, the raw measured pressure, unless corrected for the “cushioning” effects associated with flowline volume, will not reflect pore pressures accurately. The correction depends, in turn, on the line volume as well as the compressibility and the mobility of the formation fluid. All said, the physics and math can be challenging, but solutions and analytical highlights are presented in the next chapter for a wide variety of tools and applications. Chapter 2provides a broad state-of-the-art review for source and sink models.
1.2.1 Enhanced Formation Dynamic Tester (EFDT ®).
The “Enhanced Formation Dynamic Tester” is an advanced wireline formation testing system that delivers: (1) Multiple, large-volume high-purity formation fluid samples with downhole fluid characterization, (2) Reliable formation pressure testing, and (3) Real-time downhole fluid analyze, and more. Typical tool string configurations and architectures are shown in Figures 1.10and 1.11. For detailed specifications, the reader is referred to the latest updated manufacturer’s literature.

Figure 1.10. Tool string configurations.
COSL’s EFDT is designed to obtain formation pressures and formation fluid samples at discrete depths within a reservoir. Analyzing pressure buildup profile and the properties of fluid samples helps provide a more complete description of reservoir fluids and behavior. The EFDT service provides key petrophysical information to determine the reservoir volume, producibility of a formation, type and composition of the movable fluids, and to predict reservoir behavior during production.
THE EFDT is a modular formation testing system. It can be customized for the specialized applications. The modularity of EFDT ensures its ability to test and sample fluids in a wide range of geological environments and borehole conditions. For its basic configuration, the string includes a fully controllable Dual Probe Module for fluid in-taking, a Flow Pump Module for variable-volume drawdown and pump out of contaminated fluids, a Fluid Sensor Module for dynamic properties of fluids, a PVT Carrier Module for monophase sampling, and a Large Sample Carrier Module for large-volume normal sampling. It can also be configured with a Straddle Packer Module, an Optical Analysis Module, a Focused Probe Module and a Multi-PVT Tank Module to meet the requirements of complex reservoir formation tests, such as low permeability rock or natural fractures.
The EFDT enables up to five properties of fluid and formation to be monitored during testing: fluid conductivity or capacitivity, fluid density, fluid dynamic pressure, fluid optical analysis and formation permeability and anisotropy. The EFDT provides up to four MonoPhase Sampling Tanks (MPST) for one run, which recovers high-quality pressure-compensated reservoir fluid samples during borehole formation testing operations. The new Multi-PVT Module can take up to 24-48 PVT samples in one run (6 X 350 ml per module). The EFDT uses standard EDIB telemetry protocol, is combinable with other EDIB logging tools, and requires the company’s ELIS surface acquisition system. Surface control interfaces and user output displays are given in Figures 1.12and 1.13. Applications, benefits and features are summarized below.
Applications
Formation pressure measurements and fluid contact identification
Repeatable formation fluid sampling
Measurement of formation permeability and anisotropy
Vertical interference testing
ln-situ downhole fluid analysis
Benefits
Fast, high-accuracy pressure measurement using Quartz Pressure Gauges (QPG) with temperature compensation
Conductivity/capacitivity, density, fluid dynamic pressure, NIR optical analysis and formation permeability anisotropy for real-time reservoir evaluation
Savings of 50% sampling time using focus probe
Multiple samples in one run, providing high quality PVT samples
Features
Modularity, offering expanded testing versatility
Accurate pressure measurement using QPG
Real time downhole fluid assessment
PVT quality formation fluid samples
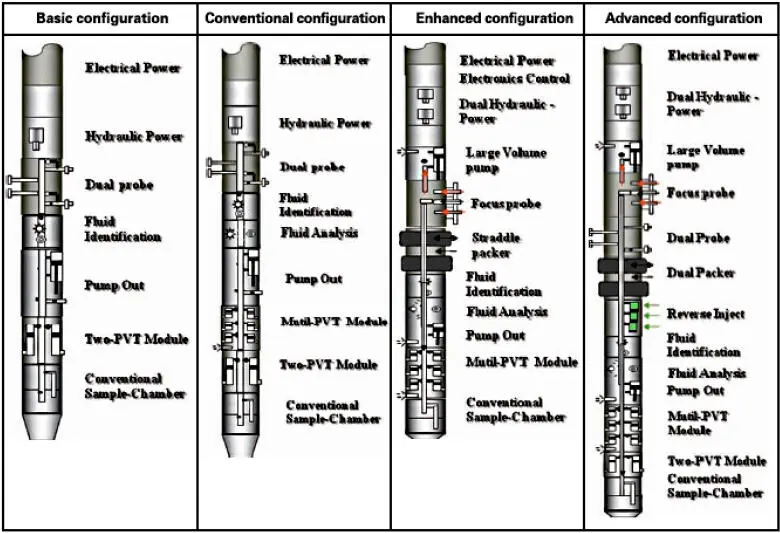
Figure 1.11. Tool architectures.
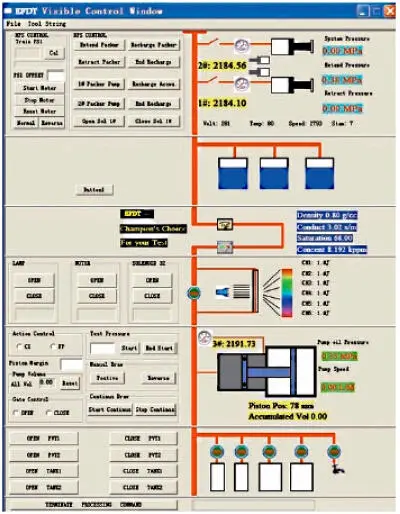
Figure 1.12. Surface control interface.
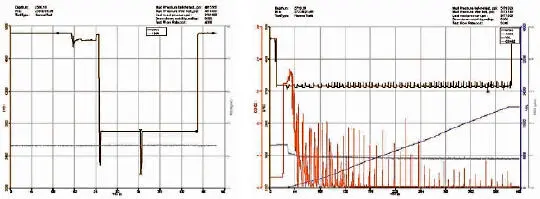
Figure 1.13. Pressure measurement chart (left) and real-time fluid monitoring chart (right).
1.2.2 Basic Reservoir Characteristic Tester (BASIC-RCT™).
COSL’s “Basic Reservoir Characteristic Tester” or “BASIC-RCT” is a third generation product of the formation tester family, characterized by its pump through function. BASIC RCT is a compact, convenient, safe and efficient tool. It can replace in part Drill Stem Testing (DST) operations in order to save rig time. BASIC RCT provides economical and reliable solutions to formation evaluation for oilfield exploration and engineering, representing a good means to reduce cost while solving difficult technical problems. BASIC RCT can be run on any service company logging unit, requiring only winch, cable head and depth measurement. All services, telemetry, gamma ray recording, test recording (digital, numerical listing, screen and printer graphics) are provided in real time. Tool configurations are shown in Figure 1.14. For latest specifications, the reader should refer to the manufacturer’s updates.
Functions
Measuring formation pressure accurately
Taking multi-samples of formation fluids
Taking large samples
Pumping through contaminated formation fluids
Monitoring formation fluid properties in real time.
Flowing formation fluids at controlled rates
Pumping through in reverse
Making quick well site sampler transfer
Providing real time and reliable data for analyzing permeability and formation damage
Structure
The BASIC RCT is a combination of surface system and downhole tools. The surface system includes the Acquisition and Data Process software, PC and DC control panel, and AC power supply. The downhole tools include the upper electronics section, mechanical/hydraulic section, sensor section, lower electronics section with a standard configuration, and also include the 2 × 520 cc large sampler with optional configuration (see Figures 1.15and 1.16).

Читать дальше















