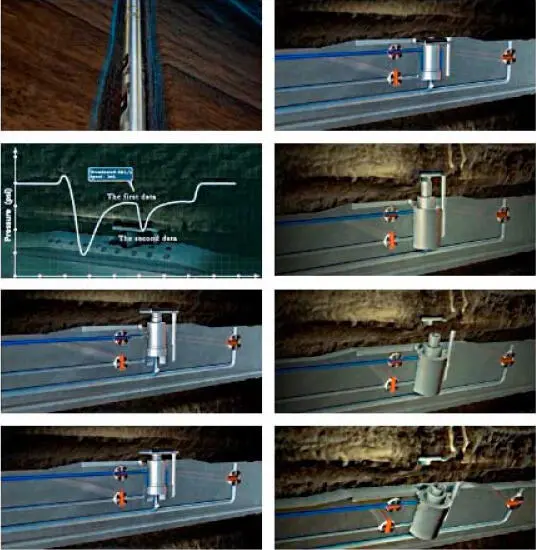
Figure 1.1. Drawdown-buildup pressure response with dynamic pumping action and flowline.
But how are probe arrays configured and placed for optimal effect? Figures 1.1and 1.2illustrate the operation of a single probe tool that withdraws fluid and then stops, creating the expected “drawdown and buildup” shown. If a second probe is desired, should it be placed an axial distance apart but along the same azimuth? Or azimuthally apart, at 180° away along the borehole circumference? What about a “drawdown only” pumpout? Or perhaps, have the pump oscillate sinusoidally in place, thus mimicking the AC transmissions of an electromagnetic logging tool? How many probes are best? What are their flow areas? Do answers to these questions depend on fluid and formation properties?
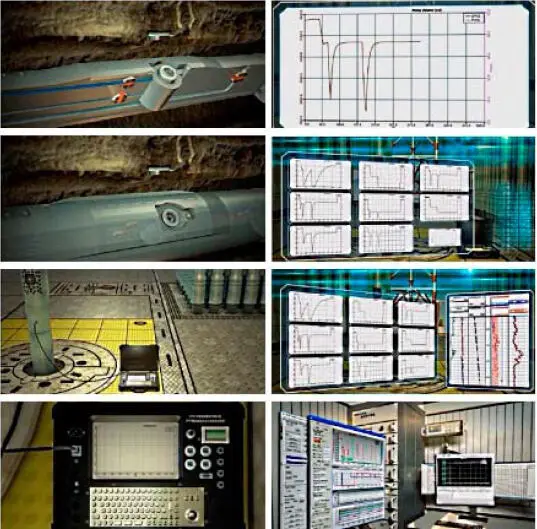

Figure 1.2. Downhole, surface and logging truck operations.
Background development.The present book addresses these questions for “source” or “sink models” of the pumping nozzle, these terms referring to ideal representations of the flow where borehole and pad geometry are described using mathematically small closed surfaces. The recent books due to Chin et al. (2014) or Formation Testing: Pressure Transient and Contamination Analysis , Chin et al. (2015) or Formation Testing: Low Mobility Pressure Transient Analysis, and Chin (2019) or Formation Testing: Supercharge, Pressure Testing and Contamination Models , published by John Wiley & Sons, contain complete math derivations and detailed validations. However, the rapid pace of recent development suggests a separate volume in Wiley’s Handbook of Petroleum Engineering Series , focused on the main ideas behind the recent works. These ideas are essential as they are also used in the design of newer COSL formation testing tools as well as in interpretation software now available to the petroleum industry. What engineers lack, at present, are job planning and PTA tools both useful at the rigsite and at engineers’ desktops. It is our purpose to support this pressing need.

Figure 1.3.Recent formation testing book publications.
1.1 Conventional Formation Testing Concepts.
Formation testing design concepts are rich and varied. A pumping probe, operating as a “sink” or (equivalently) a “source,” or both, also tracks pressure transient responses. Other pressure probes my reside along the tool body, displaced axially, azimuthally or both, which may actively pump or act as passive observers. While the primary formation tester function is fluid sampling, where in-situ reservoir fluids are collected and transported to the surface for analysis, pressure measurements represent critical by-products important to formation evaluation. Examples of testers offered by different manufacturers for wireline and MWD applications are given in Figures 1.4– 1.7.
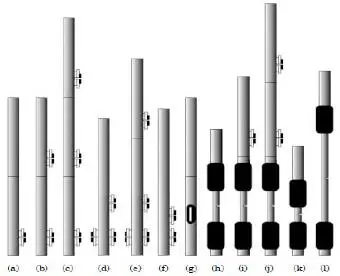
Figure 1.4. Conventional formation tester tool strings.
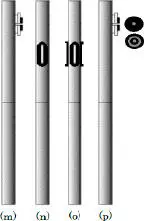
Figure 1.5.Formation testers, additional developments.
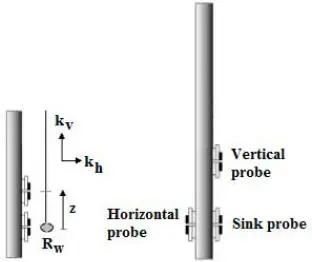
Figure 1.6. Conventional dual and triple probe testers.

Figure 1.7. Dual probe tester with dual packer.
1.2 Prototypes, Tools and Systems.
In a “handbook” such as this, it is important to provide examples of prototypes, commercial tools and systems. The wide ranges in design parameters can be surprising to newcomers in formation testing. For example, the “vertical and sink probes” in Figure 1.6, which are displaced axially but lie along the same azimuth, can range from six or seven inches to as much as 2.3 ft (27.6 in) and 10.3 ft (123.6 in), where the latter two distances are obtained from the manufacturer’s figure in SPE Paper No. 36176. We might, for example, ask, “Just what does the distant observation probe “see” under different mobility backgrounds?” “Will the tool do the job for my formation?” This book attempts to answer the most obvious questions, but it also aims at providing the tools and software for readers to address those pressing questions that invariably arise in any new logging scenario. To provide a flavor of how hardware literature and specifications might appear, we have included discussion of COSL material related to its standard product lines. Note that COSL’s new “triple probe, 120° tool” (as opposed to a conventional 180° tool) is treated separately in our companion 2021 book.
Close-ups of early single and dual probe prototype formation testers are shown in Figure 1.8. These photographs were obtained during field tests. The black pads shown perform an important sealing function, which prevents leakage of fluid through its contact surface with the sandface. However, they are not as “simple” as they appear. For instance, at any given pump rate, the pressure drop, which depends on nozzle diameter, may be excessive and allow the undesired release of dissolved gas – orifice sizes must be chosen judiciously, as suggested by the wide variety of choices shown in Figure 1.9. The shape of the hole or slot is also important; circular or oval shapes may be acceptable for consolidated matrix rock, but slotted models may be required for naturally fractured media or unconsolidated formations. Of course, in supporting PTA interpretation objectives, the size and shape of a formation tester’s pads must be incorporated into the host math model. More often than not, the model must be simple and mathematically tractable in order to obtain useful answers in a reasonable amount of time. This may require the use of idealized source or sink models, or numerical models with limited numbers of grids in the case of finite difference or finite modeling – consequently, questions related to calibration or geometric factors arise, along with test procedures, etc.

Figure 1.8. Early COSL single and dual probe prototype formation testers (details in 2014 and 2015 books).
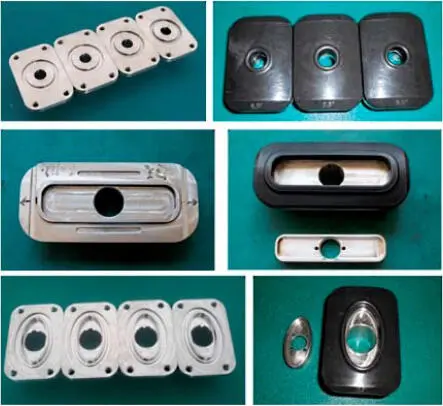

Figure 1.9. COSL pad designs with varied sizes and shapes, for different applications, e.g., firm matrix rock, unconsolidated formations, fractured media, and so on..
Читать дальше



















