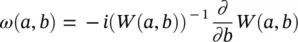and for 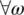 and
and 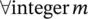 :
:
(4.50) 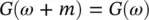
The frequency band is also reduced by a factor of two at each step. These relationships are also valid for DWT following Section 4.5.1.4.
The reconstruction of the data from its wavelet coefficients can be performed step‐by‐step, starting from the lowest resolution. At each scale, we compute:
(4.51) 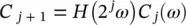
(4.52) 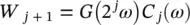
we look for C jknowing C j + 1, W j + 1, h , and g . Then 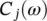 is restored by minimizing:
is restored by minimizing:
(4.53) 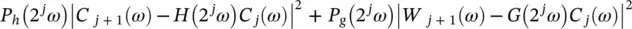
using a least minimum squares estimator. 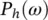 and
and 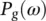 are weight functions which permit a general solution to the restoration of
are weight functions which permit a general solution to the restoration of 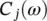 . The relationship from of
. The relationship from of 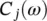 is in the form of:
is in the form of:
(4.54) 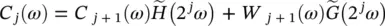
where the conjugate filters have the expressions:
(4.55) 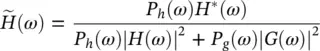
(4.56) 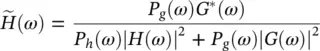
It is straightforward to see that these filters satisfy the exact reconstruction condition given in Eq. (4.35). In fact, Eqs. (4.55)and (4.56)give the general solutions to this equation. In this analysis, the Shannon sampling condition is always respected. No aliasing exists, so that the anti‐aliasing condition (4.76)is not necessary.
The denominator is reduced if we choose:
(4.57) 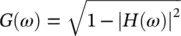
This corresponds to the case where the wavelet is the difference between the squares of two resolutions:
(4.58) 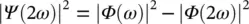
The reconstruction algorithm then carries out the following steps:
1 Compute the fast Fourier transform (FFT) of the signal at the low resolution.
2 Set j to np (number of WT resolutions); perform the following iteration steps:
3 Compute the FFT of the wavelet coefficients at the scale j.
4 Multiply the wavelet coefficients Wj by .
5 Multiply the signal coefficients at the lower resolution Cj by .
6 The inverse Fourier transform of gives the coefficients Cj‐1.
7 j = j − 1 and return to step 3.
The use of a band‐limited scaling function allows a reduction of sampling at each scale and limits the computation complexity.
The WT has been widely used in EEG signal analysis. Its application to seizure detection, especially for neonates, modelling of the neuron potentials, and the detection of EP and ERPs will be discussed in the corresponding chapters of this book.
4.5.2 Synchro‐Squeezed Wavelet Transform
The synchro‐squeezing wavelet transform (SSWT) has been introduced as a post‐processing technique to enhance the TF spectrum obtained by applying the WT [23]. Assuming that the input f ( t ) is a pure harmonic signal ( f ( t ) = Acos ( ωt )), using Plancherel's theorem, the following equations are derived from (4.20)[23]:
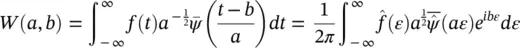
(4.59) 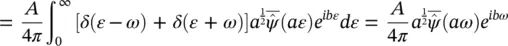
One assumption in the above equation ( Eq. 4.59) is that the selected mother wavelet is concentrated within the positive energy range, which means 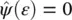 , for ε < 0. If
, for ε < 0. If 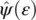 is concentrated around ε = ω 0, then, W ( a , b ) is concentrated around a = ω 0/ ω . This is spread out over a region of the horizontal line (e.g. a = ω 0/ ω ). In the situation where ω is almost but not exactly similar to the actual instantaneous frequency (IF) of the input signal, then, W ( a , b ) has non‐zero energy. By synchro‐squeezing, the idea is to move this energy away from ω . The proposed method in the SSWT aims to reassign the frequency locations which are closer to the actual IF to obtain an enhanced spectrum. To do that, first, the candidate IFs are calculated. For these IFs, W ( a , b ) ≠ 0:
is concentrated around ε = ω 0, then, W ( a , b ) is concentrated around a = ω 0/ ω . This is spread out over a region of the horizontal line (e.g. a = ω 0/ ω ). In the situation where ω is almost but not exactly similar to the actual instantaneous frequency (IF) of the input signal, then, W ( a , b ) has non‐zero energy. By synchro‐squeezing, the idea is to move this energy away from ω . The proposed method in the SSWT aims to reassign the frequency locations which are closer to the actual IF to obtain an enhanced spectrum. To do that, first, the candidate IFs are calculated. For these IFs, W ( a , b ) ≠ 0:
(4.60) 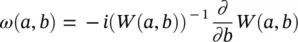
Considering the selected pure harmonic signal f ( t ) = Acos ( ωt ), it is simple to observe that ω ( a , b ) = ω . The candidate IFs are exploited to recover the actual frequencies. Therefore, a reallocation technique has been used to map the time domain into TF domain using ( b , a ) ⇒ ( b , ω ( a , b )). Based on this, each value of W ( a , b ) (computed at discrete values of a k) is re‐allocated into T f( ω l, b ) as provided in the following equation ( Eq. 4.61):
Читать дальше

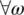 and
and 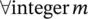 :
: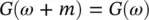
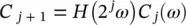
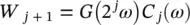
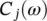 is restored by minimizing:
is restored by minimizing: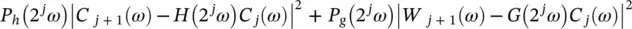
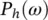 and
and 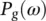 are weight functions which permit a general solution to the restoration of
are weight functions which permit a general solution to the restoration of 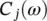 . The relationship from of
. The relationship from of 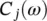 is in the form of:
is in the form of: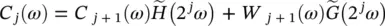
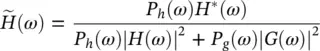
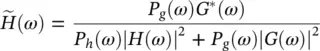
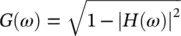
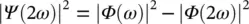
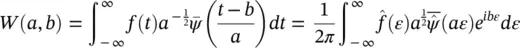
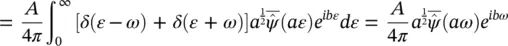
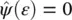 , for ε < 0. If
, for ε < 0. If 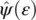 is concentrated around ε = ω 0, then, W ( a , b ) is concentrated around a = ω 0/ ω . This is spread out over a region of the horizontal line (e.g. a = ω 0/ ω ). In the situation where ω is almost but not exactly similar to the actual instantaneous frequency (IF) of the input signal, then, W ( a , b ) has non‐zero energy. By synchro‐squeezing, the idea is to move this energy away from ω . The proposed method in the SSWT aims to reassign the frequency locations which are closer to the actual IF to obtain an enhanced spectrum. To do that, first, the candidate IFs are calculated. For these IFs, W ( a , b ) ≠ 0:
is concentrated around ε = ω 0, then, W ( a , b ) is concentrated around a = ω 0/ ω . This is spread out over a region of the horizontal line (e.g. a = ω 0/ ω ). In the situation where ω is almost but not exactly similar to the actual instantaneous frequency (IF) of the input signal, then, W ( a , b ) has non‐zero energy. By synchro‐squeezing, the idea is to move this energy away from ω . The proposed method in the SSWT aims to reassign the frequency locations which are closer to the actual IF to obtain an enhanced spectrum. To do that, first, the candidate IFs are calculated. For these IFs, W ( a , b ) ≠ 0: