Computation in BioInformatics
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Computation in BioInformatics» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Computation in BioInformatics
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Computation in BioInformatics: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Computation in BioInformatics»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Computation in BioInformatics — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Computation in BioInformatics», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
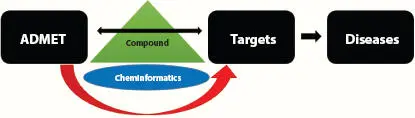
Figure 2.5 Chemoinformatic in drug discovery.
In this way, the way toward making and screening drug-like mixes went under question. As the human genome venture was finished, many new focuses for tranquilize disclosure have been created through genomics and current atomic science [1]. The present truth is that the pharmaceutical drug discovery business is confronting numerous objectives, however with minimal auxiliary data. One currently sees as an excessive number of hits while scanning for lead identification, in this way lead enhancement is obstructed. To get more target auxiliary data, high-throughput protein crystallization has been investigated. Be that as it may, numerous objectives are layer proteins and it is exceptionally hard to acquire auxiliary data for these proteins. Subsequently, lead improvement remains the most genuine bottleneck. Moreover, we realize that, around 40% of all improvement up-and-comers flop because of absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity (“ADMET”) issues. This new Drug discovery technique challenges cheminformatics in the accompanying viewpoints [6]: (1) cheminformatics ought to have the option to separate information from enormous scale crude HTS databases in a shorter timeframes and (2) cheminformatics ought to have the option to give productive in silico devices to anticipate ADMET properties. This is ordinarily exceptionally difficult to do. Cheminformatics has accomplished numerous accomplishments in assorted variety examination, SAR, and virtual screening during the previous decade. It is additionally seen as helpful in the accompanying field from information mining to medicate revelation.
2.6.1 Exploratory Data Analysis
The purposes of this stage are to derive features (descriptors), to select relevant features (bioactivities related descriptors), and to systematically identify the relations among the features.
2.6.2 Example Discovery
This stage utilizes different multivariable arrangement innovations, straight or non-direct relapse advancements, master framework approaches, and AI advances to find the examples, which can clarify the information in incredible detail.
2.6.3 Pattern Explanation
Any outcome ought to be logical to scientific experts or researcher. A few information mining results can be straight forward for physicists, for example, topological data. Nonetheless, the outcomes from measurable methodologies or AI strategies may seem hard for physicists to comprehend. In this manner, de-convolution or information perception advances are required to decipher the dynamic example, for example, neural system designs with the goal that scientific experts can take synthetic activities.
2.6.4 New Technologies
New technologies, such as SVMs, are appearing in recent scientific applications. SVM is one of the discriminant approaches. This method eliminates many problems (such as local minima, un-robust results and too many parameter settings) experienced with other inference methodologies like neural networks and decision trees. However, more investigations are required for applying SVM in cheminformatics.
2.7 Concluding Remarks and Future Prospects
Chemical probes generated through academic programs can provide valuable information on target biology and translatability. The NIH Molecular Libraries Program contributed significantly toward probe discovery and developed 375 probes against a large number of targets. The academic drug discovery consortium (ADCC) lists 149 drug discovery centers across the world. While some of the screening centers focus on specific diseases or capabilities, a vast majority of the screening facilities works on a wide range of targets and diseases. The screening centers differ in the size of screening resources (compound collections, advanced equipments, and platform detection technologies and capabilities) as well as extent of a university’s drug discovery infrastructure support. The extent to which an academic discovery project is taken along the course of mid- to late-stage discovery depends largely on resources and an interest in establishing multidisciplinary collaborations. Obtaining funds for medicinal chemistry optimization, ADME, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, formulations, and toxicology are bottlenecks for majority of the academic programs. The most profitable molecule emerges in the academia if the identified molecule move forward for the late stage drug development at the industry. Around 24% of FDA-endorsed drug discovery programs somewhere in the range of 1998 and 2007 were accounted for to have risen up logically creative college licenses to biotechnology and pharmaceutical organizations. Academic drug discovery programs are not limited to scholarly research but have additionally acquired advanced analytical methodologies into conventional medication revelation forms. Substantial change in the experiment design and computational methodologies with the use of advanced instrumentation leads to major change in academic as well as industrial drug discovery program. Exploiting computational strategies, strong hits can be acquired in only weeks. Looking for new concoction elements has prompted the development of top-notch datasets and libraries that can be streamlined for either sub-atomic assorted variety or likeness with available candidates. What is more, disseminated processing has gotten progressively famous in enormous scale virtual screening, partially on account of progressively ground-breaking innovation.
Although it is apparent that computational drug discovery methods have great potential, one should not rely on computational techniques in a black box manner and should beware of the Garbage In–Garbage Out (GIGO) phenomenon. The in silico segments genererally inquire about virtual screening of the potential candidates followed by use of high-throughput instruments to check the few potential candidates for pharmacological effect however this process is not the substitute for the potential in vivo evaluation. Later on, notwithstanding expanding the precision and adequacy of existing advances, the most significant inclination in computational medication disclosure field will be the incorporation of computational science and science together with chemoinformatics and bioinformatics, which will bring about another field known as pharmacoinformatics. Motivated by the fulfillment of the human genome and various pathogen genomes, incredible endeavors will be made to comprehend the job of quality items so as to misuse their capacities, which could be of extraordinary assistance for finding new medication targets. Computational strategies including objective distinguishing proof will turn out to be more enticing, and planned little atoms will likewise be widely utilized as tests for useful research.
References
1. Augen, J., The evolving role of information technology in the drug discovery process. Drug Discovery Today , 7, 315–323, 2002.
2. Hecht, P., High-throughput screening: beating the odds with informatics-driven chemistry. Curr. Drug Discovery , 7(8), 21–24, 2002 Jan.
3. Xu, J. and Stevenson, J., Drug-like Index: A New Approach To Measure Drug-like Compounds and Their Diversity. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci ., 40, 1177–1187, 2000.
4. Matter, H., Baringhaus, K.-H., Naumann, T., Klabunde, T., Pirard, B., Computational approaches towards the rational design of drug-like compound libraries. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen ., 4, 453–475, 2001.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Computation in BioInformatics»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Computation in BioInformatics» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Computation in BioInformatics» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












