Executing the code within a smart contract also costs some amount of Ether. This feature gives the token added utility. As long as individuals want to use Ethereum for applications and contracts, Ether will hold a value beyond speculation.
The wild growth in the value of Ether has made it a popular token to speculate on. It’s widely traded on exchanges around the world. Some new hedge funds are looking at it as an investment vehicle. However, the volatile nature and low market depth make Ether a risky investment. Find out more about Ether, including how to buy, spend, and trade it, in Book 4, Chapter 1.
Getting Up and Running on Ethereum
This section walks you through how to get started in the Ethereum blockchain ecosystem. Before you can build anything on Ethereum, you need a wallet containing some Ethereum (ETH). Book 2, Chapter 3explains the process of downloading and installing MetaMask for the Brave browser, which you can use for the instructions found in the remainder of this chapter.
Ethereum is kept running by a network of computers all over the world that are processing the contracts and securing the network. These computers are sometimes referred to as nodes, and they’re mining crypto Ether.
In order to reward individuals for the time and cost involved in mining, there is a prize of five Ethers about every 12 seconds. The prize is given to the node that was able to create the latest block in the Ethereum blockchain.
All new blocks have a list of the latest transactions. The proof-of-work consensus algorithm guarantees that prizes are won most often by nodes with the most computational power. Computers that aren’t as powerful can win, too — it just takes longer. If you want to try your hand at mining Ether, you can do it with your home computer, but it will take a very long time to successfully mine a block and win Ether.
Building your first decentralized autonomous organization
DAOs will change how the world does business in the future. They allow anyone in the world to create a new type of company online that is governed by pre-agreed-upon rules that are then enforced through the blockchain network. Creating a DAO is easier than you might think. In this section, you build your first DAO.
 To successfully complete your DAO, you need to have set up a wallet such as MetaMask and have loaded it with some Ethereum ETH.
To successfully complete your DAO, you need to have set up a wallet such as MetaMask and have loaded it with some Ethereum ETH.
Open the browser (such as Brave or Chrome) that you use to access your MetaMask wallet, and follow these steps to create your first DAO:
1 Go to https://alchemy.daostack.io/ .
2 Click the blue Connect Wallet button at the top right of your screen.
3 Click the Create a DAO button at the top right of your screen.
4 Within the Set Description box, name your organization.
5 Under Symbol, type in your ticker name, such as WXYZ, and click Set Description.The name of your ticker symbol should be related to your organization’s actual name. For example, Tesla’s Nasdaq symbol is TSLA, and Apple’s is AAPL.
6 Within Configure, keep all options as they are by default and click Set Configuration.Feel free to manually alter the Configure options if you know what you are doing.
7 Add members to your DAO by adding their ETH addresses.Figure 5-3 shows what the Add Members section looks like.
8 Click the Launch button.Your MetaMask wallet opens as a pop-up window.
9 Confirm the Gas Fee cost, and click Confirm.
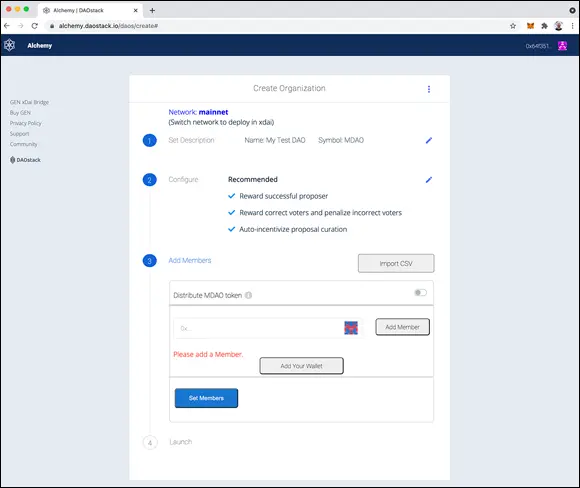
FIGURE 5-3:The Add Members box.
 Important! If you don’t have enough ETH in your wallet to cover the gas fee to create your DAO, just stop at this point. You can always quit this DAO setup and return to these instructions at a later date when your wallet has more ETH. If you have enough ETH to cover the transaction, it takes a few minutes to create your DAO. You are asked to Confirm one more time, and then your DAO is created. Congrats!
Important! If you don’t have enough ETH in your wallet to cover the gas fee to create your DAO, just stop at this point. You can always quit this DAO setup and return to these instructions at a later date when your wallet has more ETH. If you have enough ETH to cover the transaction, it takes a few minutes to create your DAO. You are asked to Confirm one more time, and then your DAO is created. Congrats!
Afterwards, you will have many options to fine-tune your organization within the dashboard. For example, you will be able to establish funding and voting protocols, manage members, and so much more.
Uncovering the Future of DAOs
Smart contracts and decentralized organizations hold a lot of promise. Their pure democratic and hyper-rational nature is very appealing. However, at this point, more possibilities exist than knowns, and each contract that’s created could be groundbreaking or a massive flop.
If you approach Ethereum as the new frontier that it is, you’ll have more success. The Ethereum network has more benefits than drawbacks if you’re careful. But expecting everything to work flawlessly and all the participants to act with integrity will open you up to greater losses. Ethereum has its share of bandits, not to mention those friendly enthusiasts who would like you to succeed.
The smart contract hacks of 2016 have highlighted the importance of security and properly reviewing contracts. They also showed that people with integrity exist, and fight to fix issues.
Reading this book is only the beginning. It will give you a sound basis on which to build your knowledge of Ethereum, but as with all new technologies, Ethereum is quickly evolving. Keep reviewing best practices and security measures.
The following sections touch on a few things to keep in mind as you build your first few DAOs, build smart contracts, and debug your new blockchain systems.
Don’t trust large sums of money to untested contracts and contracts that haven’t been fully vetted. Large contracts are more often targeted by hackers. The DAO hack described earlier in this chapter (see the sidebar, “With great power comes … great power”) showed that even well-thought-out contracts have unexpected weaknesses.
 Although smart contracts and blockchains let you conduct business with anyone around the world, it’s still early days. You can mitigate your risk by working only with known and trusted parties.
Although smart contracts and blockchains let you conduct business with anyone around the world, it’s still early days. You can mitigate your risk by working only with known and trusted parties.
 The security landscape will constantly be evolving with new bugs. Reviewing all new best practices is imperative. Manage the amount of money you’re putting at risk and roll out contracts slowly and in phases. Ethereum is a fairly new technology, and mature solutions are not yet built.
The security landscape will constantly be evolving with new bugs. Reviewing all new best practices is imperative. Manage the amount of money you’re putting at risk and roll out contracts slowly and in phases. Ethereum is a fairly new technology, and mature solutions are not yet built.
Building smarter smart contracts
Smart contract programming requires a different mindset than standard contract writing. There is no third party to make things right if the contract executes in a way that you didn’t expect or intend. The immutable and distributed nature of blockchains makes it tough to change an unwanted outcome.
 Your contract will have flaws and may fail. Build safety valves into your contracts so you can respond to bugs and vulnerabilities as they come up. Smart contracts also need an off switch that lets you pull the plug and pause your contract when things are going wrong.
Your contract will have flaws and may fail. Build safety valves into your contracts so you can respond to bugs and vulnerabilities as they come up. Smart contracts also need an off switch that lets you pull the plug and pause your contract when things are going wrong.
Читать дальше

 To successfully complete your DAO, you need to have set up a wallet such as MetaMask and have loaded it with some Ethereum ETH.
To successfully complete your DAO, you need to have set up a wallet such as MetaMask and have loaded it with some Ethereum ETH.
 The security landscape will constantly be evolving with new bugs. Reviewing all new best practices is imperative. Manage the amount of money you’re putting at risk and roll out contracts slowly and in phases. Ethereum is a fairly new technology, and mature solutions are not yet built.
The security landscape will constantly be evolving with new bugs. Reviewing all new best practices is imperative. Manage the amount of money you’re putting at risk and roll out contracts slowly and in phases. Ethereum is a fairly new technology, and mature solutions are not yet built.










