Assistant Professor
Department of Otolaryngology‐Head and Neck Surgery
Medical college of Georgia
Augusta University
Augusta, GA, USA
Jesse Ryan, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Otolaryngology and Communication Sciences
SUNY Upstate Medical University
Syracuse, NY, USA
Zoukaa Sargi, MD, MPH
Professor of Otolaryngology and Neurosurgery
Residency Program Director
Department of Otolaryngology
University of Miami Miller School of Medicine
Miami, FL, USA
Daniel Sharbel, MD
Department of Otolaryngology
Augusta University
Augusta, GA, USA
Lucy Shi, MD
Department of Otolaryngology‐Head and Neck Surgery
Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
Columbus, OH, USA
Andrew G. Shuman, MD, FACS, HEC‐C
Associate Professor, CBSSM
Department of Otolaryngology ‐ Head and Neck Surgery
University of Michigan
Ann Arbor, MI, USA
Dustin A. Silverman, MD
Head & Neck Fellow
Department of Otolaryngology
University of California – Davis
Davis, CA, USA
Carl H. Snyderman, MD, MBA
Professor, Departments of Otolaryngology and Neurological Surgery
University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
Co‐Director, Center for Cranial Base Surgery
University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Bharat Yarlagadda, MD
Division of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery
Lahey Hospital and Medical Center
Assistant Professor
Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck SurgeryBoston University School of Medicine
Boston, MA, USA
Charles Yates, MD
Associate Professor
Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery
University of Indiana
Bloomington, IN, USA
Jessica Yesensky, MD
Assistant Professor
Department of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery
University of Indiana
Bloomington, IN, USA
Chad Zender, MD, FACS
Associate Chief Medical Officer, UC Health
Center of Excellence Leader, Head and Neck, UC Cancer Institute
Professor Department of Otolaryngology – Head & Neck Surgery
University of Cincinnati College of Medicine
Cincinnati, OH, USA
Chase Heaton
Babak Givi
History of Present Illness
A 53‐year‐old man presents with a 1‐month history of tongue soreness and pain. He has not noticed any change in voice, difficulty swallowing, or a neck mass. However, the tongue pain is persistent and has not gone away with over‐the‐counter medications. His past medical history includes type II diabetes, controlled with oral agents, and hypertension. He does not smoke and has no history of tobacco or alcohol abuse. No other past medical history was identified.
No palpable neck mass was identified. Oral cavity exam shows a slightly raised lesion on the right lateral tongue, which is soft and tender to palpation, measuring 1 cm in diameter (see Figure 1.1). There is no mass noted deep to the lesion. The rest of the exam, including fiberoptic laryngoscopy, is within normal limits.
Question: What would you recommend next?
Answer:Tissue sampling with a punch or incisional biopsy of the lesion, preferably from the corner of the lesion.
Question: The biopsy shows squamous cell carcinoma (SCC ), moderately differentiated, with a depth of invasion of at least 4 mm (punch biopsy specimen with tumor transected at the base). What would you recommend next in the workup?
Answer:Imaging of the neck is usually recommended to assess lymph node involvement. A computed tomography (CT) scan with contrast or an ultrasound of the neck (which can be performed in the clinic) are both reasonable first options. The risk of distant metastases in early (T1 and T2) oral cavity SCC is extremely low. Therefore, extensive metastatic workup is not necessary. While positron emission tomography (PET)/CT has become more common, the evidence for its added benefit does not exist. Obtaining a chest CT to rule out lung metastases is considered adequate.
Question: A CT scan of the head and neck does not show any evidence of regional metastases. How would you clinically stage this disease?
Answer:Based on the AJCC staging manual, 8th Edition, the clinical stage is cT1N0Mx, stage I.
Question: What treatment would you recommend?
Answer: Early stage tongue cancer treatment is wide local excision of the primary tumor and addressing the regional lymph nodes. If the risk of regional lymph node metastases is presumed to be higher than 20%, an elective, selective neck dissection should be performed. Depth of invasion is a prognostic marker for the presence of occult nodal metastases in the cN0 neck. With a depth of invasion >3 mm, it is believed that the risk of occult nodal metastases is >20%, and therefore an elective neck dissection should be performed. In this scenario, the recommended treatment is wide local excision of the primary tumor with 1 cm margins and elective neck dissection (ipsilateral levels I–III, i.e., supra‐omohyoid neck dissection). Alternatively, sentinel node biopsy could be offered if adequate expertise in the treating facility exists.
Question: Patient undergoes sentinel node mapping followed by wide local excision and sentinel node biopsy. The tongue defect is repaired with biologic dressing and secondary intention closure. On lymphoscintigraphy, the sentinel node is located in an ipsilateral level II lymph node (Figure 1.2). Excisional biopsy and frozen section assessment shows metastatic SCC in the level II node. How would you proceed?
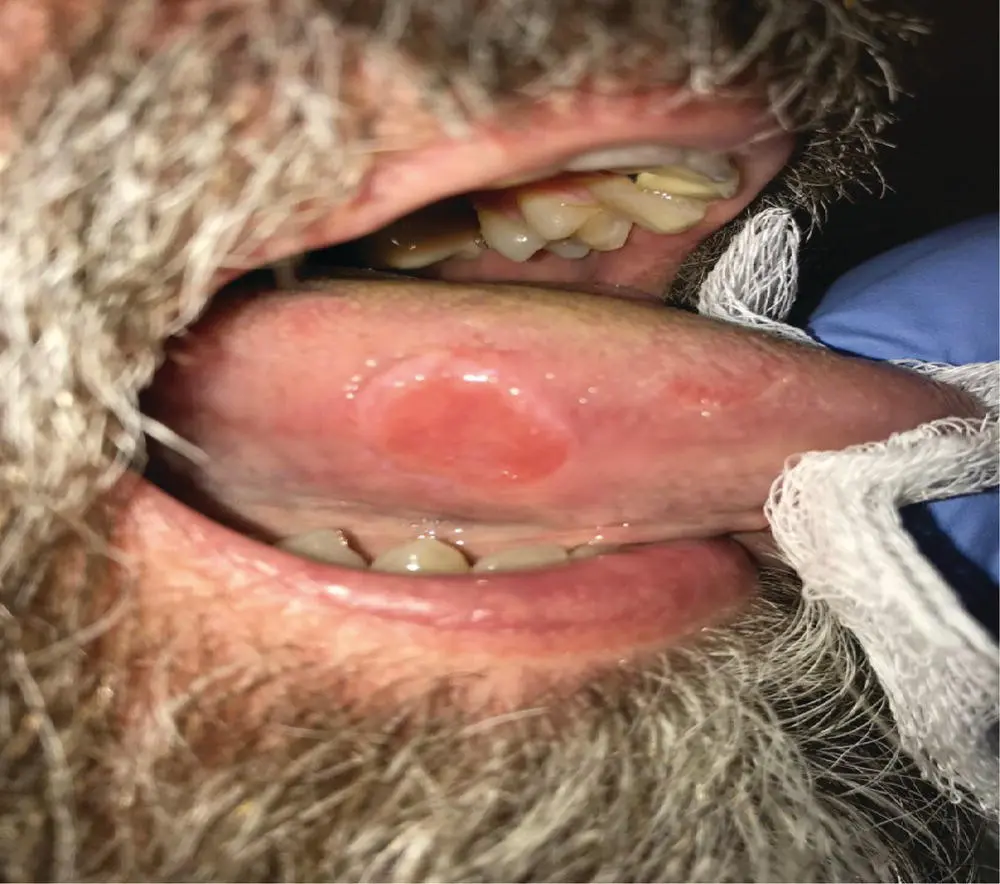
FIGURE 1.1 This photo demonstrates the patient's right lateral tongue ulceration.
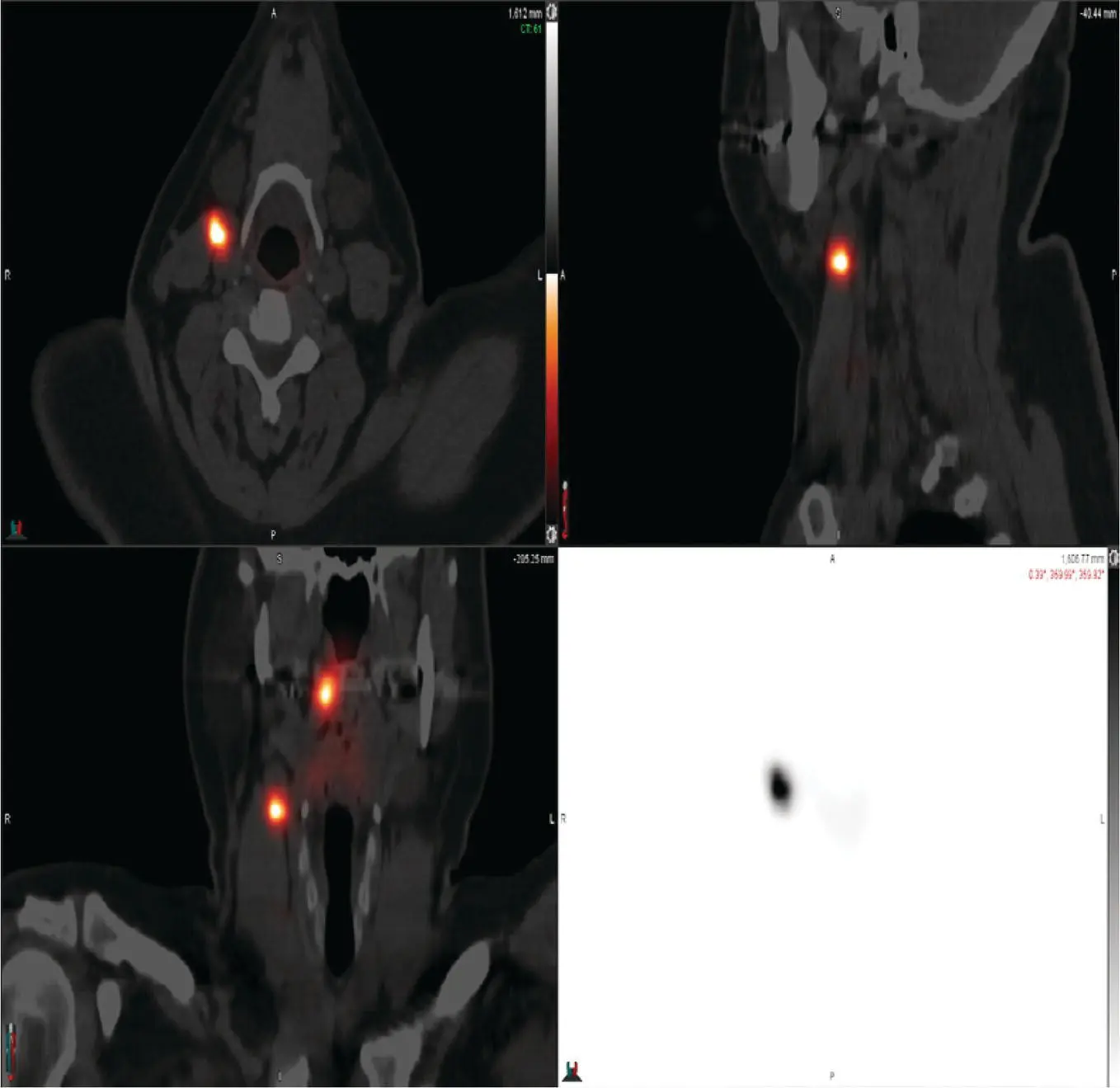
FIGURE 1.2 This image shows the patient's fused CT‐ lymphoscintigraphy image. Note the uptake at the injection site and a right level II lymph node.
Answer:If the sentinel node is positive, completion lymphadenectomy (selective neck dissection, level I–IV) is recommended.
The patient recovers well from the operation. The final pathology report shows a 1.5 cm moderately differentiated SCC with a depth of invasion of 7 mm. All margins are free of tumor, with the closest margin being 8 mm from tumor. No lymphovascular or perineural invasion is identified. One out of 30 lymph nodes is positive for metastatic SCC without extranodal extension, measuring 1.9 cm (sentinel node).
Question: Based on these pathologic findings, what is the appropriate stage for this patient?
Answer:According to AJCC 8th Edition, tumors of the oral cavity with a depth of invasion of more than 5 mm are considered T2, even if the diameter is less than 2 cm. Therefore, the pathologic stage is pT2N1M0, stage III.
Question: What adjuvant treatment regimen, if any, would you recommend to this patient?
Читать дальше