If the quantity of cols in the matrix is identical to the quantity of rows in another matrix, then the two matrices can be multiplied. In this case, if M is a matrix with p × k and N is one with k × q , “ the product matrix ” of them is a matrix R with p × q . Each element of “ the product matrix ” R is considered in the way rij = ∑ mik × nkj [5].
“ Scalar multiplication of a matrix ” is defined by multiplying a matrix with a scalar number. If M is a matrix with p × q and β is a scalar number, then R = β × M is a matrix with p × q . In this case, rij = β × mij for each element of the matrix R [5].
Determinant . “ The determinant of an equivalent matrix ” defined as det( M ) for M of size q × q can be designed recursively as given below [5].
• If q = 1, det(M) = m11.
• If q > 1, .
where Mij stands for a matrix M defined by ith row and jth column. The determinant may be found only for an equivalent matrix.
Additive Inverse . If matrix N is “ the additive inverse ” of matrix M , then M + N = 0 because their corresponding elements have the property: nij = − mij for all i ’ s and j ’ s . The symbol – M is generally used to represent the additive inverse of matrix M [5].
Multiplicative Inverse . Only square matrices can be used to compute “ the reciprocal of a matrix ”. Matrix M has a reciprocal of N , resulting in M × N = N × M = I . The symbol M-1 is generally used to represent a reciprocal of M . The matrices have their reciprocals in the case of det( M ) ≠ 0 [5].
4.5 Elliptic Curve Arithmetic
4.5.1 Introduction
The “ elliptic curve ” in a finite field known as E ( GF ) is a curve in cubic-form derived from the Weierstrass equation: y 2+ β 1 xy + β 3 y = x 3+ β 2 x 2+ β 4 x + β 6in GF . In this case, β i∈ GF and GF is a finite field [4].
The curve E ( GF ( p )) has the form: y 2= x 3+ ax + b in which p is a prime greater than 3, a , b ∈ GF ( p ) and 4 a 3+ 27 b 2≠ 0. ( β 1= β 2= β 3= 0; β 4= a and β 6= b on the Weierstrass equation) [4].
4.5.2 Arithmetic Operations on E(GF(p))
Adding points on the curve applies the chord-and-tangent rule and outcomes another point. Adding points on the curve generates an additive group including the point at infinity in symbol O [4]. It is the group of points which are utilized in building cryptosystems using the curve. The description in geometric gives easy understanding. Consider that M = ( x 1, y 1) and N = ( x 2, y 2) are the points existing on the curve. Suppose that adding M and N results P = ( x 3, y 3) on the curve. Adding points is described in Figure 4.2. The tangent line sketching from M to N touches at the point marked by − P . The reflection of − P is P [1, 6]. Consider that doubling a point M results P = ( x 3, y 3) on the curve. Doubling a point is described in Figure 4.3. The tangent line sketching from point M touches at the point marked by − P . The reflection of − P is P as in the case of adding points [1, 6].
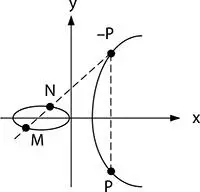
Figure 4.2 Adding points ( P = M + N ).

Figure 4.3 Doubling a point ( P = M + M ).
The algebraic methods for adding points and doubling a point on E ( GF ( p )) are followings [4].
• M + O = O + M = M and M + (−M) = O for any point, M ∈ E(GF(p)). If M = (x, y) ∈ E(GF(p)), then (x, −y) is defined as (−M) which stands for the inverse of M. O is the point at infinity which is known as additive identity.
• (Adding points). Consider that M, N ∈ E(GF(p)), M = (x1, y1), and N = (x2, y2) on the condition: M ≠ ±N. Then, M + N = (x3, y3) in which x3 = λ2 − x1 – x2, y3 = λ(x1 – x3) – y1, and λ(y2 – y1) / (x2 – x1).
• (Doubling a point). Consider that M = (x1, y1) ∈ E(GF(p)) on the condition: M ≠ −M. Then, 2M = (x3, y3) in which x3 = λ2 – 2x1, y3 = λ(x1 – x3) – y1, and λ = (3x12 + a)2y1.
4.6 Cryptographic Applications
4.6.1 Hill Cipher
In standard ciphers, based on matrix transformations, such as Hill cipher, “ residue matrices ” on the plane made of complex numbers may be used to construct non-linear cryptographic transformations. The implementation and the analysis on their mathematical properties are described in the reference [9].
The encryption scheme in Hill Cipher uses a linear matrix transformation to translate plaintext to ciphertext [5]: C = P × K , where P represents “ a plaintext matrix ”, K represents “ a key matrix ”, and C represents “ a ciphertext matrix ”. “ A plaintext matrix ” is opened by transforming: P = C × K −1, satisfying K × K −1= I .
“Affine Hill cipher extends the concept of Hill cipher by integrating it with a nonlinear affine transformation” [10]. The encryption scheme follows the nonlinear transformation of matrices: C = ( P × K ) + E where P represents “ a plain-text matrix ”, K represents “ a key matrix ”, E represents “ an embedded matrix ”, and C represents “ a ciphertext matrix ”. “ A plaintext matrix ” is opened by transforming: P = ( C – E ) × K −1, satisfying K × K −1= I .
On the plane made of complex numbers, a new design of Hill cipher is created. Matrix transformations, affine transformations, and complex transformations are used to create the current concept. As a result, the cipher’s diffusion and confusion properties are greater than those of the standard Hill cipher applied to real numbers. It has the potential to defend against both “ known-plaintext ” and “ chosen-plaintext attacks ”.
The followings are the encryption scheme and the decryption scheme for the new design of Hill cipher applied to the plane made of complex numbers. For practical experiments, the digits “0” to “25” are used to represent the characters “A” to “Z”, respectively, “26” for the space (☐), “27” for the comma, “28” for the question mark, “29” for the apostrophe, and “30” for the full stop. There are 31 elements in total in the field. As a result, the new design is applied to Z(31). The practical experiments resulting in the encryption scheme and the decryption scheme by using the techniques of our system described in the reference [9] are shown in Figures 4.4and 4.5.
Читать дальше














