Digital Forensics and Internet of Things
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Digital Forensics and Internet of Things» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Digital Forensics and Internet of Things
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Digital Forensics and Internet of Things: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Digital Forensics and Internet of Things»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
It pays to be ahead of the criminal, and this book helps organizations and people to create a path to achieve this goal.
Digital Forensics and Internet of Things Audience
Digital Forensics and Internet of Things — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Digital Forensics and Internet of Things», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
1.2 Image Processing
Face recognition system is subcategorized in two segments. The primary includes processing of the image, and the secondary includes techniques for recognition.
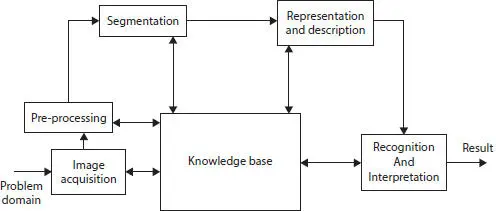
Figure 1.1 Fundamental steps of image processing in face recognition.
The processing of the image segment includes of image accession, image pre-processing, image segmentation, image description, and image recognition. The second part includes the use of artificial intelligence.
Fundamental steps in image processing are (as shown in Figure 1.1):
a. Image accession: to obtain an image digitally.
b. Image pre-processing: intensify the image in processes that increment the probability of advancement of the additional procedures.
c. Image segmentation: divide a given image in its elemental segment of parts.
d. Image representation: transform the given data into a suitable manner for the further procedure.
e. Image description: bring out the attribute which outcomes in some computable intelligence of interest of parts that are primary for distinguishing one class of parts from another.
f. Image recognition: allocate a tag to the parts based on the data delivered from its representation.
1.3 Deep Learning
It is a machine-based program which imitates the function of human intelligence. It can be considered as a subdivision of machine learning. As machine learning uses simpler concepts, and the deep learning makes used artificial neural networks in order to mimic how humans think and learn. This learning is categorized into supervised, semi-supervised, or unsupervised.
Deep learning can be constructed with the help of connected layers:
• The foremost layer is known as the input layer.
• The bottom-most layer is known as the output layer.
• All the in between layers are known as the hidden layers. Here, the word deep indicates the connections between different the neurons.
Figure 1.2depicts a neural network consisting of an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer. The hidden layers consist of neurons. Here, the neurons are interlinked with one another. The neurons help to proceed and transfer the given signal it accepts from the above layer. The stability of signal depends upon the factors of weight, bias, and the activation function.
A deep neural network produces accuracy in numerous tasks and might be from object detection to face recognition. This does not require any kind of predefined knowledge exclusively coded which indicates that it can learn automatically.
The Deep Learning process includes the following:
• Understanding the problem
• Identifying the data
• Selecting the Deep Learning algorithm
• Training the model
• Testing the model
Deep neural network is a very strong tool in order to construct and predict an attainable result. It is an expert in pattern discovery and prediction that is knowledge-based. Deep learning algorithms are keen to provide 41% more accurate results when compared to machine learning algorithm in case classification of image and 27% better fit in case of recognizing of face and 25% in recognizing of voice.
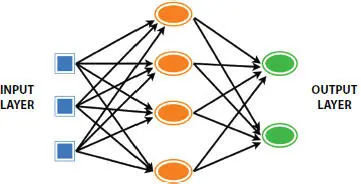
Figure 1.2 Layers of the model.
1.3.1 Neural Network
A neural network is an instrument that is designed to model in the similar way in which the brain responds or executes a task or function; it is usually simulated in digital computer-based software or carried out by using electronic components. It can resemble the brain in the following aspects:
• The knowledge is obtained by the network from its surrounding with the help of a learning procedure.
• Interneuron link strength, known as synaptic weight, is used to accumulate the obtained knowledge.
• The process that is operated to execute the learning procedure is known as the learning algorithm; the purpose of which is to reform the synaptic weights of the network in a well-organized mode to accomplish the desired layout objective.
• It is also possible to improve its own topology.
• Neural network is also mentioned in literature as neurocomputers, connectionist network, and parallel distributed processor.
• Neural network attains its computing power at the beginning from its power of computer at first from the massively side-by-side distributed arrangement and next from its potential to learn and then generalize.
• Generalization leads to the neural network constructing logical outputs for inputs not encountered throughout training (learning).
An ANN is specified by the following:
• Neuron model: Data processing component of the neural network.
• An architecture: A group of neurons along with connections connecting neurons.
• A training algorithm: It is used for instructing the Neural network by changing the weights to model a selected training task correctly on the instructing examples.
1.3.2 Application of Neural Network in Face Recognition
Face recognition implies comparing a face with the saved database of faces to recognize one in the given image. The associated process of face detecting is directly relevant to recognizing the face as the images of the face captured must be at first analyzed and then identified, before they get recognized. Face detection through an illustration assists to focus on the database of the system, improving the systems speed and performance.
Artificial Neural Network is used in face recognition because these models can imitate the neurons of the human brain work. This is one of the foremost reasons for its role in face recognition.
1.4 Methodology
1.4.1 Face Recognition
Face acknowledgment is subject to the numerical features of a face and is probably the most natural approach to manage face affirmation. It is one of the first robotized face affirmation structures. Marker centers (position of eyes, ears, and nose) were used to build a component vector (distance between the centers, point between them). The affirmation was performed by ascertaining the Euclidean distance between included vectors of a test and reference picture. Such a technique is vigorous against changes in enlightenment by its temperament; however, it has an immense disadvantage: The precise enlistment of the marker focuses is confounded, even with cutting edge calculations. Probably, the most recent work on mathematical face recognition was reported by Mulla M.R. [20]. A 22-dimensional component vector was utilized and it was investigated that huge datasets have appeared, that mathematical highlights alone may not convey sufficient data for face Recognition. Figure 1.3depicts the detailed structure of face recognition system.
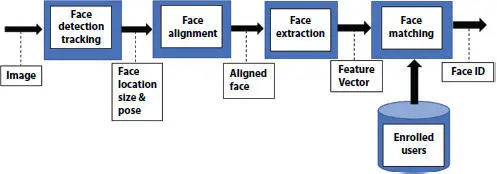
Figure 1.3 Structure of face recognition system.
1.4.2 Open CV
OpenCV (Open-Source Computer Vision) is a famous library developed by Intel in 1999. This platform has various libraries. It helps in real-time image processing and includes various algorithms. It is equipped with programming interface to various languages like C++, C, and Python.
OpenCV 2.4 has a very useful new face recognizer class for face recognition.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Digital Forensics and Internet of Things»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Digital Forensics and Internet of Things» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Digital Forensics and Internet of Things» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












