Table 1.13
Some compounds with the NiAs structureTable 1.14
Some compounds with the CsCl structureTable 1.15
Some compounds with the rutile structureTable 1.16
Some compounds with the CdI2 structureTable 1.17
Some compounds with the CdCl2 structureTable 1.18
Some compounds with the perovskite structureTable 1.19
Perovskites: some composition–property correlationsTable 1.20
Some compounds with the ReO3 structureTable 1.21
Some compounds with the tetragonal tungsten bronze, TTB, structu...Table 1.22
Some compounds with the spinel structureTable 1.23
Some compounds with the olivine structureTable 1.24
Some compounds with corundum‐related structuresTable 1.25
Examples of A, B, X combinations in garnetsTable 1.26
Some compounds with the K2NiF4 structureTable 1.27
Relation between chemical formula and silicate anion structureTable 1.28
Point symmetry elementsTable 1.29
The thirty‐two point groupsTable 1.30
Coordinates and labelling of equivalent positions in space group...
2 Chapter 2Table 2.1 Predominant point defects in various ionic crystals
3 Chapter 3Table 3.1 Electrostatic bond strengths of some cationsTable 3.2 Allowed and unallowed combinations of corner‐sharing oxide polyhe...Table 3.3 Minimum radius ratiosTable 3.4 Structures and radius ratios of oxides MO2Table 3.5 Madelung constants for some simple structuresTable 3.6 Some lattice energies in kJ mol−1; all have rock salt structure...Table 3.7 Thermochemical radii (Å) of complex anionsTable 3.8 Lattice energies (kJ mol−1) of silver halidesTable 3.9 Enthalpies of formation (kJ mol−1) of some hypothetical (*) and r...Table 3.10 Non‐polar covalent radiiTable 3.11 Partial charge on oxygen in some solid oxidesTable 3.12 Partial charge and radius of the chlorine atom in some solid chl...Table 3.13 d‐electron configurations in octahedrally coordinated metal atom...Table 3.14 Crystal field stabilisation energies (kJ mol−1) estimated for tr...Table 3.15 Values of the γ parameter of some spinelsTable 3.16 Coordination numbers and geometriesTable 3.17 Orbital hybridisation and resulting shapesTable 3.18 Band gaps of Group IV elementsTable 3.19 Band gaps (eV) of some inorganic solidsa
4 Chapter 4Table 4.1 Different forms of inorganic solids, e.g. alumina, Al2O3Table 4.2 Examples of intercalation compoundsTable 4.3 Synthesis of BiFeO3 by chimie douce methodsTable 4.4 Diamond coatings, their properties and possible areas of applicat...Table 4.5 High‐pressure polymorphism of some simple solids
5 Chapter 5Table 5.1 Comparison of a molecular substance, toluene, C6H5CH3, and a non‐...Table 5.2 X‐ray wavelengths (Å) of commonly used target materials...Table 5.3 X‐ray powder diffraction patterns for potassium halidesTable 5.4 Calculated d‐spacings for an orthorhombic cell, for a = 3.0, b =...Table 5.5 Systematic absences due to lattice typeTable 5.6 Structure–factor calculations for CaF2: powder XRDTable 5.7 Systematic absences associated with space symmetry elements and l...
6 Chapter 6Table 6.1 Strategy and overview for identification, analysis and structure...
7 Chapter 7Table 7.1 Densities of SiO2 polymorphsTable 7.2 Classification of phase transitionsTable 7.3 Characteristics of some first‐order phase transitionsTable 7.4 Some pressure‐induced phase transitionsTable 7.5 Factors that influence kinetics of phase transitions
8 Chapter 8Table 8.1 Typical values of electrical conductivityTable 8.2 Conductivities of some metals at 25 °CTable 8.3 Some superconducting materialsTable 8.4 Typical values of v d and v t for n‐type Si at 25 °C...Table 8.5 Conductivity in NaCl crystals, other ionic solids and characteris...Table 8.6 Some oxygen partial pressures at which andTable 8.7 Electrode potentials of some half‐reactions associated with lithi...Table 8.8 Terminology and units used with dielectricsTable 8.9 Some ferroelectric materials
9 Chapter 9Table 9.1 Magnetic susceptibilitiesTable 9.2 Some Curie and Néel temperaturesTable 9.3 Calculated and observed magnetic moments (BM) for some transition...Table 9.4 Some soft and hard magnetic materialsTable 9.5 Electronic constitution of iron, cobalt and nickel
10 Chapter 10Table 10.1 Activators and their electronic statesTable 10.2 Some lamp phosphor materialsTable 10.3 Some laser systems
11 Chapter 11Table 11.1 Homogeneous and heterogeneous materials, their properties and so...Table 11.2 Capacitance values* and their possible interpretation
12 Chapter 12Table 12.1 Thermoelectric coefficientsTable 12.2 The thermoelectric series; emf values against Pt at 100 °C with...Table 12.3 Some heat capacity, thermal conductivity and thermal expansion d...
13 Chapter 13Table 13.1 Some MAX precursors and their MXene productsTable 13.2 Properties of some single layer TMDs
14 Chapter 14Table 14.1 Glass transition temperatures T g (measured) and T 0 (calculated...Table 14.2 Classification of glass‐forming materials by the type of bonding...Table 14.3 Some differences between spinodal and nucleation and growth text...
15 Chapter 15Table 15.1 Oxide and phase content of a typical Portland cement
16 Appendix GTable G.1 Electrode potentials
1 Chapter 1Figure 1.1 (a) Section through the NaCl structure, showing (b–e) possible re...Figure 1.2 Cubic unit cell of NaCl, a = b = c.Figure 1.3 (a) The seven crystal systems and their unit cell shapes; (b) fiv...Figure 1.4 (a) Threefold and (b) twofold rotation axes; (c) the impossibilit...Figure 1.5 Two‐dimensional Penrose tiling constructed by packing together tw...Figure 1.6 Hypothetical twinned structure showing fivefold symmetry.Figure 1.7 Symmetry elements: (a) mirror plane; (b) centre of symmetry; (c)...Figure 1.8 Arrangement of coins with heads (H) and tails (T) illustrating (a...Figure 1.9 (a) Two‐, three‐ and fourfold axes and (b, c) mirror planes of a...Figure 1.10 (a) Tetragonal unit cell of CaC2: note the cigar‐shaped carbide...Figure 1.11 Representation of (a) the NaCl structure in two dimensions by (b...Figure 1.12 The unit cells of the 14 Bravais lattices: axes refer to the ab...Figure 1.13 (a) Lattice planes (in projection); (b) derivation of Miller ind...Figure 1.14 Miller indices for a hexagonal lattice.Figure 1.15 Examples of Miller indices: (a) (101); (b) (100); (c) (200); (d)...Figure 1.16 (a) A cp layer of equal‐sized spheres; (b) a non‐cp layer with c...Figure 1.17 Two cp layers arranged in A and B positions. The B layer occupie...Figure 1.18 Three close packed layers in ccp sequence.Figure 1.19 Coordination number 12 of shaded sphere in (a) hcp and (b) ccp s...Figure 1.20 Face centred cubic, fcc, unit cell of a ccp arrangement of spher...Figure 1.21 (a, b) Hexagonal unit cell of an hcp arrangement of spheres show...Figure 1.22 (a) Unit cell dimensions for a face centred cubic unit cell with...Figure 1.23 Tetrahedral and octahedral sites between two cp anion layers, se...Figure 1.24 Available cation sites, 1–12, in an fcc anion array.Figure 1.25 (a, b) Tetrahedral sites T+, T– and their relation to a cube. (c...Figure 1.26 (a) hcp arrangement of Br atoms in crystalline Al2Br6; (b) Al at...Figure 1.27 (a) The C60 molecule; one pentagon surrounded by five hexagons i...Figure 1.28 Cation–cation separation in octahedra which share (a) corners an...Figure 1.29 Unit cell of (a, d) NaCl, (b, e) ZnS, sphalerite, and (c, f) Na2...Figure 1.30 Alternative view of the antifluorite structure.Figure 1.31 Unit cell of the rock salt structure showing edge‐sharing octahe...Figure 1.32 The rock salt structure as an array of edge‐sharing octahedra....Figure 1.33 The sphalerite (zinc blende) structure showing (a) the unit cell...Figure 1.34 The antifluorite structure of Na2O showing the unit cell in term...Figure 1.35 The wurtzite and nickel arsenide structures: (a–c) the hexagonal... Figure 1.36 The primitive cubic unit cell of CsCl.Figure 1.37 The rutile structure, TiO2: (a) the unit cell; (b) TiO6 octahedr...Figure 1.38 (a) Octahedral sites in an ideal hcp array; (b) edge‐sharing oct...Figure 1.39 The CdI2 structure: (a) the basal plane of the hexagonal unit ce...Figure 1.40 The CdCl2 structure.Figure 1.41 (a–d) The perovskite structure of SrTiO3. (e) A close packed Sr,...Figure 1.42 (a) Crystal structure of CaCu3Ti4O12. (b) The brownmillerite...Figure 1.43 The structure of (a) ReO3, (b) tungsten bronze NaxWO3, (c, d) br...Figure 1.44 Representative parts of the spinel structure. (a) One octant of...Figure 1.45 Olivine structure of LiFePO4.Figure 1.46 Crystal structures of (a) corundum, (b) ilmenite and (c, d) LiNb...Figure 1.47 Some cation‐ordered fluorites showing cation positions relative...Figure 1.48 The pyrochlore structure, which may be regarded as a distorted,...Figure 1.49 The garnet crystal structure.Figure 1.50 (a) The K2NiF4 structure. (b) The Bi2O2 layers that form part of...Figure 1.51 The crystal structure of MgB2 as (a) an oblique projection showi...Figure 1.52 Silicate anions with (a) bridging and (b) non‐bridging oxygens....Figure 1.53 The point groups (a, b) 2, (c, d) 3, and (e–h) m.Figure 1.54 The point groups (a) 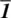 and (b, c)
and (b, c) 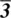 .Figure 1.55 The three orthorhombic point groups 222, mm2, and mmm.Figure 1.56 Equivalent positions in the point group 222. In step 1, a 2‐fold...Figure 1.57 Trigonal point group 32.Figure 1.58 The symmetry of the methylene dichloride molecule, CH2Cl2, point...Figure 1.59 The symmetry of the methyl chloride molecule, CH3Cl, point group...Figure 1.60 (a) The convention used to label axes and origin of space groups...Figure 1.61 Two tetrahedra in a centrosymmetric arrangement.Figure 1.62 Monoclinic space group C2 (No 5); coordinates of equivalent posi...Figure 1.63 Monoclinic space group C2/m (No 12). Coordinates of general equi...Figure 1.64 Orthorhombic space group P2221 (No 17); Coordinates of equivalen...Figure 1.65 Orthorhombic space group F222 (No 22); coordinates of equivalent...Figure 1.66 Tetragonal space group I41 (No 80); coordinates of equivalent po...Figure 1.67 The symmetry elements in space group P42/mnm.
.Figure 1.55 The three orthorhombic point groups 222, mm2, and mmm.Figure 1.56 Equivalent positions in the point group 222. In step 1, a 2‐fold...Figure 1.57 Trigonal point group 32.Figure 1.58 The symmetry of the methylene dichloride molecule, CH2Cl2, point...Figure 1.59 The symmetry of the methyl chloride molecule, CH3Cl, point group...Figure 1.60 (a) The convention used to label axes and origin of space groups...Figure 1.61 Two tetrahedra in a centrosymmetric arrangement.Figure 1.62 Monoclinic space group C2 (No 5); coordinates of equivalent posi...Figure 1.63 Monoclinic space group C2/m (No 12). Coordinates of general equi...Figure 1.64 Orthorhombic space group P2221 (No 17); Coordinates of equivalen...Figure 1.65 Orthorhombic space group F222 (No 22); coordinates of equivalent...Figure 1.66 Tetragonal space group I41 (No 80); coordinates of equivalent po...Figure 1.67 The symmetry elements in space group P42/mnm.
Читать дальше

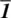 and (b, c)
and (b, c) 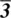 .Figure 1.55 The three orthorhombic point groups 222, mm2, and mmm.Figure 1.56 Equivalent positions in the point group 222. In step 1, a 2‐fold...Figure 1.57 Trigonal point group 32.Figure 1.58 The symmetry of the methylene dichloride molecule, CH2Cl2, point...Figure 1.59 The symmetry of the methyl chloride molecule, CH3Cl, point group...Figure 1.60 (a) The convention used to label axes and origin of space groups...Figure 1.61 Two tetrahedra in a centrosymmetric arrangement.Figure 1.62 Monoclinic space group C2 (No 5); coordinates of equivalent posi...Figure 1.63 Monoclinic space group C2/m (No 12). Coordinates of general equi...Figure 1.64 Orthorhombic space group P2221 (No 17); Coordinates of equivalen...Figure 1.65 Orthorhombic space group F222 (No 22); coordinates of equivalent...Figure 1.66 Tetragonal space group I41 (No 80); coordinates of equivalent po...Figure 1.67 The symmetry elements in space group P42/mnm.
.Figure 1.55 The three orthorhombic point groups 222, mm2, and mmm.Figure 1.56 Equivalent positions in the point group 222. In step 1, a 2‐fold...Figure 1.57 Trigonal point group 32.Figure 1.58 The symmetry of the methylene dichloride molecule, CH2Cl2, point...Figure 1.59 The symmetry of the methyl chloride molecule, CH3Cl, point group...Figure 1.60 (a) The convention used to label axes and origin of space groups...Figure 1.61 Two tetrahedra in a centrosymmetric arrangement.Figure 1.62 Monoclinic space group C2 (No 5); coordinates of equivalent posi...Figure 1.63 Monoclinic space group C2/m (No 12). Coordinates of general equi...Figure 1.64 Orthorhombic space group P2221 (No 17); Coordinates of equivalen...Figure 1.65 Orthorhombic space group F222 (No 22); coordinates of equivalent...Figure 1.66 Tetragonal space group I41 (No 80); coordinates of equivalent po...Figure 1.67 The symmetry elements in space group P42/mnm.










