Amir Sadr - Mathematical Techniques in Finance
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Amir Sadr - Mathematical Techniques in Finance» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Mathematical Techniques in Finance
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Mathematical Techniques in Finance: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Mathematical Techniques in Finance»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Mathematical Techniques in Finance: An Introduction
Mathematical Techniques in Finance: An Introduction
Mathematical Techniques in Finance — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Mathematical Techniques in Finance», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Option Pricing
In Chapter 6, we use the risk‐neutral framework to derive the Black‐Scholes‐Merton (BSM) option pricing formula by modeling asset returns as the continuous‐time limit of a random walk, that is a Brownian motion with risk‐adjusted drift. We recover and investigate the underlying replicating portfolio by considering the option Greeks: delta, gamma, theta. The interplay between these is shown by applying the Ito's lemma to the diffusion process driving an underlying asset and its derivative, leading to the BSM partial differential equation and its solution via methods from the classical boundary value heat equations.
We discuss the Cox‐Ross‐Rubinstein (CRR) model as a popular and practical computational method for pricing options that can also be used to compute the price of options with early exercise features via the backward induction algorithm from dynamic programming. For path‐dependent options such as barrier or averaging options, we present numerical models such as the Monte Carlo simulation models and variance reduction techniques.
Interest Rate Derivatives
Chapter 7introduces interest rate swaps and their derivatives used in structured finance. A plain vanilla swap can be priced via a static replication argument from a bootstrapped discount factor curve. In practice, simple European options on swaps and interest rate products are priced and risk‐managed via the normal version of Black's formula for futures. We introduce this model under the risk‐neutral pricing framework and show the pricing of the mainstream cap/floors, European swaptions, and CMS products. For complex derivatives, one needs a model for the evolution of multiple maturity zero‐coupon bonds in a risk‐neutral framework. We present the popular Hull‐White mean‐reverting model for the short rate and show the typical implementation methods and techniques, such as the forward induction method for yield curve inversion. We show the pricing of Bermudan swaptions via these lattice models. We conclude our discussion by presenting methods for calculating interest rate curve risk and VaR.
Exercises and Python Projects
The end‐of‐chapter exercises are based on real‐world markets and products and delve deeper into some financial products and highlight the details of applying the techniques to them. All exercises can be solved by using a spreadsheet package like Excel. The Python projects are longer problems and can be done by small groups of students as a term project.
It is my hope that by the end of this book, readers have obtained a good toolkit of mathematical techniques, methods, and models used in financial markets and products, and their interest is piqued for a deeper journey into quantitative finance.
—Amir Sadr
New York, New York
December 2021
Acknowledgments
One learns by teaching and I have learned much from my students at NYU. Many thanks to all of my students over the years who have asked good questions and kept me on my toes.
Thanks to my editors at John Wiley & Sons: Bill Falloon, Purvi Patel, Samantha Enders, Julie Kerr, and Selvakumaran Rajendiran for patiently walking me through this project and correcting my many typos. All remaining errors are mine, and I welcome any corrections, suggestions, and comments sent to asadr@panalytix.com.
A.S.
About the Author
Amir Sadrreceived his PhD from Cornell University with his thesis work on the Foundations of Probability Theory. After working at AT&T Bell Laboratories, he started his Wall Street career at Morgan Stanley, initially as a Vice President in quantitative modeling and development of exotic interest rate models, and later as an exotics trader. He founded Panalytix, Inc., to develop financial software for pricing and risk management of interest rate derivatives. He was a Managing Director for proprietary trading at Greenwich Capital, Senior Trader in charge of CAD exotics and USD inflation trading at HSBC, the COO of Brevan Howard U.S. Asset Management in the United States, and co‐founder of Yield Curve Trading, a fixed income proprietary trading firm. He is currently a partner at CorePoint Partners and is focused on crypto and DeFi.
Acronyms
bpbasis points, 1% of 1%, 0.0001 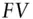 future valueIRRinternal rate of returnPnLprofit and loss
future valueIRRinternal rate of returnPnLprofit and loss 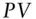 present valueYTMyield to maturityp.a.per annum
present valueYTMyield to maturityp.a.per annum 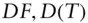 discount factor, today's value unit payment at future date
discount factor, today's value unit payment at future date 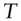
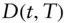 dicount factor at
dicount factor at 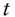 for unit payment at
for unit payment at 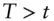
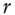 interest rate
interest rate 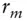 compounding interest rate with
compounding interest rate with 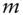 compoundings per year
compoundings per year 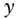 yieldAPRannual percentage rate – stated interest rate without any compoundingsAPYannual pecentage yield – yield of a deposit taking compoundings into consideration:
yieldAPRannual percentage rate – stated interest rate without any compoundingsAPYannual pecentage yield – yield of a deposit taking compoundings into consideration: 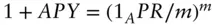 for
for 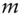 compoundings per yearCFcash flow
compoundings per yearCFcash flow 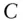 coupon rate
coupon rate 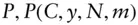 price of an
price of an 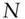 ‐year bond with coupon rate
‐year bond with coupon rate 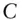 , paid
, paid 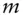 times per year, with yield
times per year, with yield 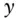
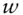 accrual fraction between 2 dates according to some day count basis
accrual fraction between 2 dates according to some day count basis  clean price of a bond = Price
clean price of a bond = Price  accrued interest
accrued interest 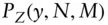 price of an
price of an 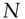 ‐year zero‐coupon bond with yield
‐year zero‐coupon bond with yield 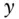 ,
, 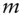 compoundings per year
compoundings per year 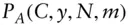 price of an
price of an 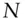 ‐year annuity with annuity rate of
‐year annuity with annuity rate of 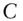 , paid
, paid 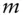 times per year, with yield
times per year, with yield 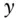
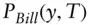 price of
price of 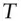 ‐maturity Treasury Bill with discount yield
‐maturity Treasury Bill with discount yield 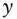 PV01present value change due to an ”01” bp change in yieldPVBPpresent value change due to a 1 bp change in coupon, present value of a 1 bp annuity
PV01present value change due to an ”01” bp change in yieldPVBPpresent value change due to a 1 bp change in coupon, present value of a 1 bp annuity 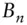 balance of a level pay loan after
balance of a level pay loan after 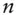 periods
periods 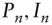 principal and interest payments of a level pay loan in the
principal and interest payments of a level pay loan in the 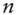 th period
th period 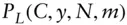 price of
price of 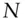 ‐year level pay loan with loan rate of
‐year level pay loan with loan rate of 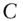 , paid
, paid 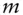 times per year, with yield
times per year, with yield 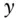 ALaverage life
ALaverage life 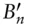 balance of a level pay loan after
balance of a level pay loan after 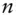 periods with prepayments
periods with prepayments 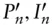 principal and interest payments of a level pay loan within the
principal and interest payments of a level pay loan within the 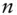 th period with prepaymentsSMMsingle monthly mortality rateCPRconstant prepayment ratio
th period with prepaymentsSMMsingle monthly mortality rateCPRconstant prepayment ratio 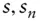 periodic prepayment speed
periodic prepayment speed 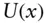 utility of wealth
utility of wealth 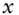
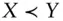 lottery
lottery 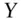 is preferred to
is preferred to 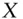
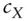 certainty‐equivalent of random payoff
certainty‐equivalent of random payoff 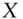 ,
, 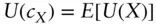
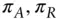 absolute risk premium, relative risk premium
absolute risk premium, relative risk premium 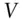 ,
, 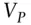 ,
, 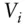 value, value of a portfolio, value of
value, value of a portfolio, value of 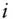 th asset
th asset 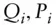 quantity, price
quantity, price 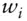 weight of
weight of 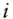 th asset in a portfolio,
th asset in a portfolio, 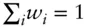
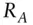 return of an asset over a period
return of an asset over a period 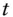 :
: 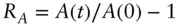 . Can be divided by
. Can be divided by 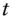 to give rate of return
to give rate of return 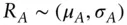 asset
asset 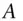 's return, with mean
's return, with mean 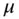 and standard deviation
and standard deviation 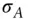
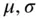 , Cmean vector, standard deviation vector, and covariance matrix of asset returns
, Cmean vector, standard deviation vector, and covariance matrix of asset returns 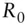 return of a risk‐free asset
return of a risk‐free asset 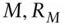 market portfolio, return of the market portfolio
market portfolio, return of the market portfolio 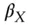 beta of an asset
beta of an asset 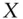 ,
, 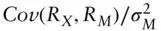
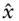 empirical estimate of
empirical estimate of 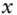
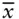 arithmetic average of
arithmetic average of 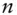 samples of
samples of 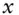 ,
, 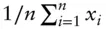
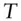 forward date, future date
forward date, future date 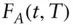 forward value of asset
forward value of asset 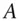 at time
at time 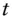 for forward date
for forward date 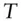
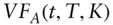
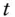 ‐value of a forward agreement on asset
‐value of a forward agreement on asset 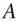 for forward date
for forward date 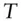 and price
and price 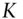
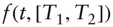 simple (noncompounding) forward rate that can be locked at
simple (noncompounding) forward rate that can be locked at 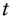 for forward deposit period
for forward deposit period 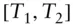 . The first term may be omitted when
. The first term may be omitted when 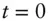 .
. 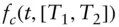 continuously compounding forward rate that can be locked at
continuously compounding forward rate that can be locked at 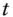 for forward deposit period
for forward deposit period 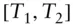 . The first term may be omitted when
. The first term may be omitted when 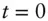 .FXforeign currency exchange rate
.FXforeign currency exchange rate 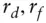 domestic and foreign interest rates for forward exchange rate calculations
domestic and foreign interest rates for forward exchange rate calculations 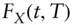 the
the 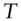 ‐forward exchange rate that can be locked at
‐forward exchange rate that can be locked at 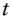
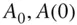 today's value of an asset
today's value of an asset 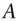
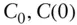 today's value of a contingent claim
today's value of a contingent claim 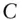
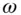 generic random sample path
generic random sample path 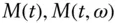 value of a money‐market account at time
value of a money‐market account at time 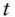 along sample path
along sample path 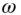
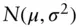 normal or Gaussian random variable with mean
normal or Gaussian random variable with mean 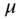 and variance
and variance 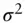
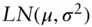 lognormal random variable whose log is
lognormal random variable whose log is 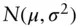 CDFcumulative ditribution functionpdfprobability density functionpmfprobability mass function
CDFcumulative ditribution functionpdfprobability density functionpmfprobability mass function 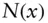 cumulative distribution function of a standard (
cumulative distribution function of a standard ( 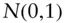 ) normal random variable,
) normal random variable, 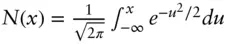
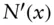 probability density function of a standard normal random variable,
probability density function of a standard normal random variable, 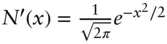 BMBrownian motion
BMBrownian motion 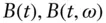 Brownian motion at time
Brownian motion at time 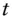 along sample path
along sample path 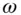
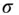 proportional, lognormal volatilityATM, ATMFat‐the‐money spot, at‐the‐money forward
proportional, lognormal volatilityATM, ATMFat‐the‐money spot, at‐the‐money forward 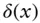 Dirac's delta function,
Dirac's delta function, 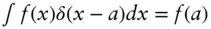
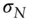 absolute, normalized volatilityCMSconstant maturity swap rateAD,
absolute, normalized volatilityCMSconstant maturity swap rateAD, 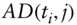 Arrow‐Debreu price, today's price of unit payoff at state
Arrow‐Debreu price, today's price of unit payoff at state 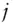 on future date
on future date  i.i.d.independent and identically distributed
i.i.d.independent and identically distributed
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Mathematical Techniques in Finance»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Mathematical Techniques in Finance» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Mathematical Techniques in Finance» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












