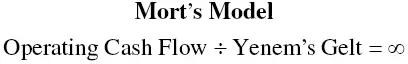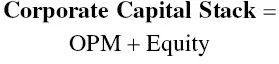Accountants like to include within company liabilities non-interest-costing obligations, such as trade payables, deposits (deferred income), and accrued liabilities. As a finance guy, I ignore such liabilities within the corporate capital stack. Since they cost nothing to me, I subtract them from the amount I would otherwise have to make to determine business investment, the first of the Six Variables, which was discussed in the preceding chapter.
Borrowings at cost are generally visible on a corporate financial statement, while the cost of leased assets is nowhere to be seen. Accountants have always been obsessed with lease accounting, which embodies why accounting is always going to be an imperfect reflection of financial reality. For most of my career, real estate leases were not included on a balance sheet at all. They just showed up in the form of rent expense, and required a detailed financial statement footnote disclosure explaining how much in lease payments the company was obligated to pay over time. All of this changed with new accounting rules imposed in 2019.
GAAP Lease Accounting
|
Old Rules |
2019 Rules |
| Show an Asset? |
No |
Yes |
| Show a Liability? |
No |
Yes |
| Show OPM Proceeds? |
No |
No |
In 2019, new lease accounting standards set by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) were enacted, resulting in the creation of non-cash “right to use” assets and liabilities, representing the estimated present values of lease payment obligations. 1 Since a lease is generally not a debt substitute, but instead a debt and equity substitute, the amount of the “right to use” liability and asset created will typically not approximate the actual amount of the OPM represented by your decision to lease.
Variables #2 and #3: Amount and Cost of OPM
A company's capital stack provides numbers two and three of the Six Variables at the hands of corporate leadership to deliver investor returns.
The second of the Six Variables is the OPM/equity mix.
The third variable is the cost of OPM.
In starting a company, business owners understand fully the cost of assets they choose to rent instead of buy. Business owners also understand the amount of money they borrow from banks and other sources. Add the two together and you get the second variable, the amount of OPM used in a business.

In determining current investor returns, the cost of OPM is paired with the amount of OPM used to arrive at the third equation variable. The simple formula is as follows:

If you were computing the cost of OPM for a year, you would take the total amount of interest and lease payments shown above and then divide them into the average of the loan principal outstanding and the cost of the leased assets deployed. When it comes to determining the cost of OPM, my treatment of leases can seem simplistic, because leases often have escalators built into them and sometimes allow for an accumulation of equity with a future known purchase option. But, as you will see as we go on, I am most interested in computing a current investor rate of return, and not a theoretical total rate of return. To do this requires that I simply compute a current cost of OPM.
Cost of Capital vs. Cost of Equity
A corporate capital stack is comprised solely of interest-costing OPM, together with equity that is likewise demanding of a return. If you can take the total annual OPM interest and lease cost, together with the desired current annual rate of return for equity investors, and then divide that cost by the amount of your capital stack, you can determine your current annual corporate cost of capital. Then, if you can realize current corporate returns that exceed that cost of capital, you have market value added (MVA), creating a business worth more than its cost. The whole is now worth more than the sum of the cost of its parts.
In golfing terms, you have broken par, which is a feat few can accomplish.
Corporate cost of capital is a frequent topic of conversation in business schools. However, I decided some time ago that the only thing that really mattered from a mathematical point of view was the cost of equity. After all, entrepreneurs are not trying to make their lenders, equipment owners, or landlords rich. They are trying to make their equity owners rich.
So, to keep it simple, the important metric to know is not corporate market value added. It's equity market value added, which is the amount by which the value of corporate equity exceeds its historic cost .
When it comes to your capital stack, you want to strike a balance between OPM and equity having the potential to deliver the highest equity rate of return. Hence, in the order of operations to determining a capital stack, you start with the amount of OPM you can attain and then back into the amount of equity you require. When it comes to equity, less tends to be more.
During my business career, I gained something of a reputation for creating financial models. Not to be outdone, Mort Fleischer—my mentor and business partner for most of those years—created “Mort's Model,” which he had framed, and then freely passed around, and which I will immortalize here. Mort's Model embodies the notion of less equity is more, and goes like this:
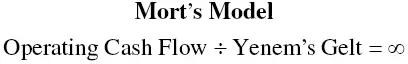
“Yenem's Gelt” is Yiddish for OPM, and “∞,” otherwise called a “lazy eight,” is the mathematical notation for infinity, which is supposed to be the resultant equity return. The formula is intended to convey that a business generating cash flow and funded entirely with OPM will yield an infinite rate of return to the owners of the business. Of course, equity rates of return would not be computed this way. Instead, operating cash flow would be divided into the equity investment of zero to arrive at an effective infinite rate of return. Mort simply wanted to make the point of the importance of OPM. Saying it in Yiddish elevated the amusement level. In my years in business, I have seen a number of people successfully start or buy businesses with no equity. It is possible, but not easy.
Consistent with Mort's Model, forming a capital stack begins with a determination of the maximum amount of OPM you can get. In the end, you may not want to maximize your use of OPM, but it is good to know the art of the possible. As I noted in the conclusion to the last chapter, companies go out of business because they run out of cash. So, understanding where liquidity can be accessed outside of business operating cash flow is important. Plus, understanding how to maximize OPM will give you the best shot of minimizing equity and achieve something close to Mort's Model.
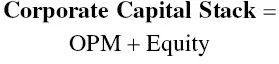
At a high level, when it comes to the puzzle of how to assemble an equity stack, there are just three simple steps:
Step 1: Start with money that has the longest repayment requirements. Hard assets like real estate and equipment can be financed for a long time and may even be leased.
Читать дальше