A possible reliability strategy for a critical compressor might look like this:
1 Condition monitoringContinuous vibration monitoring with alarms and tripsContinuous temperature monitoring with alarms and tripsContinuous or periodic performance trendingContinuous performance monitoring of compressors if the required instrumentation and analysis software are available
2 Periodic inspectionsDaily operator walkthroughsWeekly inspections by mechanicsQuarterly performance evaluations by engineering if online performance capabilities are not in place
3 Scheduled EventsPeriodic borescope inspections of gas turbinesPeriodic water washing of gas turbinesCleaning (air-cooled electric motors, heat exchangers, fin fan coolers, etc.)Scheduled overhauls based on time in service or fired hours
There is no generic maintenance strategy for all the different types of rotating machinery. Each situation must be evaluated based on the historical failure mode, their consequences, and your maintenance budget. Some trial and error may be needed to identify the right mix of maintenance strategies.
A safeguard is any hardware and procedure designed to directly prevent an equipment failure or mitigate its impact. Typical safeguards include operating procedures, vibration monitoring systems, relief valves, overspeed trip systems, and surge control systems. One of the deliverables of a machinery reliability assessment is to determine if the current set of safeguards are adequate. If they are not considered adequate, then you must explain why they are not and provide detailed recommendations regarding any additions or modifications to the existing safeguards required to reduce risk to acceptable levels.
Compressor Operating Limits
An example of a safeguard is a procedure, alarms, or control system designed to prevent a harmful compressor operating condition. For example, variable speed centrifugal compressors have a maximum rotational speed limit. Above the maximum speed limit there is the potential to permanently damage the compressor rotor due to overstress. Every operating limit typically has a related adverse consequence, i.e., if a certain condition occurs, then something bad could happen. Examples of compressor operating conditions to avoid include:
1 Critical speeds
2 Minimum speed
3 Maximum speed
4 Surge flow
5 Stonewall flow (sonic flow conditions)
6 Maximum discharge temperature limit
7 Maximum vibration (% of bearing clearance) limit
8 Radial and thrust bearing temperature limits
9 Maximum horsepower limit
Centrifugal compressors are designed to operate near their rated flow conditions. Operations away from the design point can result in unstable flow phenomena. Figure 1.4defines some of the operating conditions typically defined by centrifugal compressor manufacturers. Surge and stonewall conditions will be briefly touched on here.
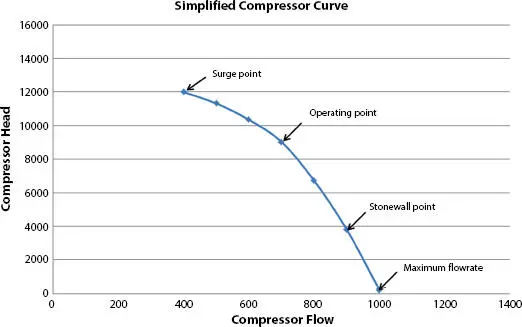
Figure 1.4 Centrifugal compressor operating limits. This compressor curve represents performance at a single speed.
Centrifugal Compressor Surgeis defined as the operating point where the centrifugal compressor peak head capability and minimum flow limits are reached. Surge can be a detrimental condition in compression systems because it causes the compressor to vibrate violently due to rapid internal flow reversals, potentially damaging internal compressor parts. Surge control systems are specifically designed to prevent compressors from operating below the surge flow point or line. Figure 1.5depicts a typical surge control system, which is composed of a flow measurement element, a controller with a surge control algorithm program, and a recycle valve. If, at any time, the inlet flow approaches the surge control line flow programmed into the surge controller, the recycle valve will open to increase the total compressor flow and prevent surge from occurring.
Centrifugal Compressor stonewall or chokedis a flow condition that occurs when the sonic velocity of gas is reached at the exit of a compressor wheel. When stonewall flow is reached, the discharge pressure and flow drop precipitously. Flow through the compressor cannot be increased any further without an increase in the suction pressure. At the stonewall (or choke) flow the pressure versus volume curve becomes essentially vertical, and it is not possible to develop head or pressure at any greater flow. When the required operating flow exceeds the stonewall limit, the only remedy is to reconfigure the compressor with impellers (and matched stationary hardware) designed for larger flow rates.
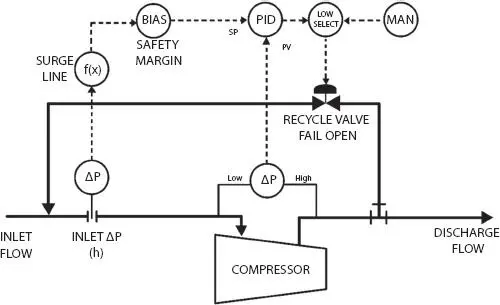
Figure 1.5 Typical centrifugal compressor surge control system.
Note: Axial compressors have been known to fail catastrophically at high flows due to blade vibration and high temperatures generated when operated beyond the stonewall line.
A critical speed is defined as any operating rotational speed that coincide with one of the rotor systems damped, natural frequencies. Operation at the critical speed for extended periods of time can result in internal damage due to excessive lateral vibration levels. It is important for operators to know their compressor critical speeds so they can be avoided. The original equipment manufacturer usually provides a list of critical speeds for users to avoid. Force response plots such as the one shown in Figure 1.6can be used to locate critical speeds once the compressor has been installed in the field. The reader can see by studying the forced response plots in Figure 1.4that rotor vibration increases significantly at about 1350 rpms and 2385 rpms due to the existence of rotor critical speeds.
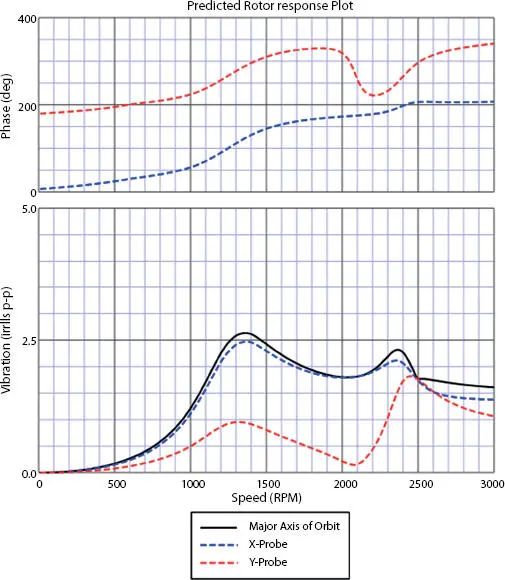
Figure 1.6 Here is a typical predicted forced response plot. The upper plot is the 1x phase versus the rotor speed and the lower plot is lateral vibration versus rotor speed. This analysis was run with mid-span imbalance. Notice: 1) there seems to be a rotor critical at about 1350 rpm where both the X and Y probes will see vibration peaks, which appears to be the rotor first critical, 2) there seems to be a second rotor critical at about 2375 rpm, 3) both critical speeds have major phase shifts associated with them.
The horsepower load on a centrifugal compressor is governed by the flow, gas density, the rotor geometry, and the rotational speed. For a given set of impeller diameters and gas conditions, the fan affinity laws define how flow, pressure, and the required horsepower vary as the compressor’s rotational speed changes as follows:
1 The flow rate varies directly with the speed
2 The differential pressure varies with the square of the speed
3 The power use varies with the cube of the speed
Small operating changes can have significant effects on how a compressor performs, which is why operators should carefully track the compressor’s overall operating characteristics, including the horsepower load, and look for trends indicating process changes. An overload condition may be telling you something is wrong. Overloading may be manifested by high amp loads for compressor with electric motor drivers or a loss of speed for compressors with gas or steam turbine drivers. If amp loads are seen to be rising or dropping, try to determine the cause of the change. Rising amp loads may be caused by changing process conditions or machine degradation, depending on the shape of the compressor performance curves. Falling amp loads may be caused by a decrease in flow due to a flow restriction or a decrease in the suction pressure.
Читать дальше















