This may not strike you as very original, because we all live in a capitalist world that takes Smith’s argument for granted. We hear variations on this theme every day in the news. Yet Smith’s claim that the selfish human urge to increase private profits is the basis for collective wealth is one of the most revolutionary ideas in human history – revolutionary not just from an economic perspective, but even more so from a moral and political perspective. What Smith says is, in fact, that greed is good, and that by becoming richer I benefit everybody, not just myself. Egoism is altruism .
Smith taught people to think about the economy as a ‘win-win situation’, in which my profits are also your profits. Not only can we both enjoy a bigger slice of pie at the same time, but the increase in your slice depends upon the increase in my slice. If I am poor, you too will be poor since I cannot buy your products or services. If I am rich, you too will be enriched since you can now sell me something. Smith denied the traditional contradiction between wealth and morality, and threw open the gates of heaven for the rich. Being rich meant being moral. In Smiths story, people become rich not by despoiling their neighbours, but by increasing the overall size of the pie. And when the pie grows, everyone benefits. The rich are accordingly the most useful and benevolent people in society, because they turn the wheels of growth for everyone’s advantage.
All this depends, however, on the rich using their profits to open new factories and hire new employees, rather than wasting them on non-productive activities. Smith therefore repeated like a mantra the maxim that ‘When profits increase, the landlord or weaver will employ more assistants’ and not ‘When profits increase, Scrooge will hoard his money in a chest and take it out only to count his coins.’ A crucial part of the modern capitalist economy was the emergence of a new ethic, according to which profits ought to be reinvested in production. This brings about more profits, which are again reinvested in production, which brings more profits, et cetera ad infinitum. Investments can be made in many ways: enlarging the factory, conducting scientific research, developing new products. Yet all these investments must somehow increase production and translate into larger profits. In the new capitalist creed, the first and most sacred commandment is: ‘The profits of production must be reinvested in increasing production.’
That’s why capitalism is called ‘capitalism’. Capitalism distinguishes ‘capital’ from mere ‘wealth’. Capital consists of money, goods and resources that are invested in production. Wealth, on the other hand, is buried in the ground or wasted on unproductive activities. A pharaoh who pours resources into a non-productive pyramid is not a capitalist. A pirate who loots a Spanish treasure fleet and buries a chest full of glittering coins on the beach of some Caribbean island is not a capitalist. But a hard-working factory hand who reinvests part of his income in the stock market is.
The idea that ‘The profits of production must be reinvested in increasing production’ sounds trivial. Yet it was alien to most people throughout history. In premodern times, people believed that production was more or less constant. So why reinvest your profits if production won’t increase by much, no matter what you do? Thus medieval noblemen espoused an ethic of generosity and conspicuous consumption. They spent their revenues on tournaments, banquets, palaces and wars, and on charity and monumental cathedrals. Few tried to reinvest profits in increasing their manors’ output, developing better kinds of wheat, or looking for new markets.
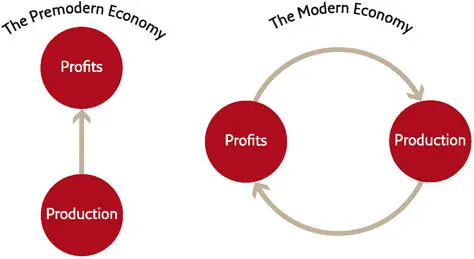
In the modern era, the nobility has been overtaken by a new elite whose members are true believers in the capitalist creed. The new capitalist elite is made up not of dukes and marquises, but of board chairmen, stock traders and industrialists. These magnates are far richer than the medieval nobility, but they are far less interested in extravagant consumption, and they spend a much smaller part of their profits on non-productive activities.
Medieval noblemen wore colourful robes of gold and silk, and devoted much of their time to attending banquets, carnivals and glamorous tournaments. In comparison, modern CEOs don dreary uniforms called suits that afford them all the panache of a flock of crows, and they have little time for festivities. The typical venture capitalist rushes from one business meeting to another, trying to figure out where to invest his capital and following the ups and downs of the stocks and bonds he owns. True, his suits might be Versace and he might get to travel in a private jet, but these expenses are nothing compared to what he invests in increasing human production.
It’s not just Versace-clad business moguls who invest to increase productivity. Ordinary folk and government agencies think along similar lines. How many dinner conversations in modest neighbourhoods sooner or later bog down in interminable debate about whether it is better to invest one’s savings in the stock market, bonds or property? Governments too strive to invest their tax revenues in productive enterprises that will increase future income – for example, building a new port could make it easier for factories to export their products, enabling them to make more taxable income, thereby increasing the government’s future revenues. Another government might prefer to invest in education, on the grounds that educated people form the basis for the lucrative high-tech industries, which pay lots of taxes without needing extensive port facilities.
Capitalism began as a theory about how the economy functions. It was both descriptive and prescriptive – it offered an account of how money worked and promoted the idea that reinvesting profits in production leads to fast economic growth. But capitalism gradually became far more than just an economic doctrine. It now encompasses an ethic – a set of teachings about how people should behave, educate their children and even think. Its principal tenet is that economic growth is the supreme good, or at least a proxy for the supreme good, because justice, freedom and even happiness all depend on economic growth. Ask a capitalist how to bring justice and political freedom to a place like Zimbabwe or Afghanistan, and you are likely to get a lecture on how economic affluence and a thriving middle class are essential for stable democratic institutions, and about the need therefore to inculcate Afghan tribesmen in the values of free enterprise, thrift and self-reliance.
This new religion has had a decisive influence on the development of modern science, too. Scientific research is usually funded by either governments or private businesses. When capitalist governments and businesses consider investing in a particular scientific project, the first questions are usually, ‘Will this project enable us to increase production and profits? Will it produce economic growth?’ A project that can’t clear these hurdles has little chance of finding a sponsor. No history of modern science can leave capitalism out of the picture.
Conversely, the history of capitalism is unintelligible without taking science into account. Capitalisms belief in perpetual economic growth flies in the face of almost everything we know about the universe. A society of wolves would be extremely foolish to believe that the supply of sheep would keep on growing indefinitely. The human economy has nevertheless managed to grow exponentially throughout the modern era, thanks only to the fact that scientists come up with another discovery or gadget every few years – such as the continent of America, the internal combustion engine, or genetically engineered sheep. Banks and governments print money, but ultimately, it is the scientists who foot the bill.
Читать дальше




![Юваль Ной Харари - Sapiens. Краткая история человечества [litres]](/books/34310/yuval-noj-harari-sapiens-kratkaya-istoriya-cheloveche-thumb.webp)





![Юваль Ной Харари - 21 урок для XXI века [Версия с комментированными отличиями перевода]](/books/412481/yuval-noj-harari-21-urok-dlya-xxi-veka-versiya-s-ko-thumb.webp)


