//---read the data in ms1 and write to buffer---
ms1.Position = 0;
byte[] buffer = new byte[ms1.Length];
int bytesRead = ms1.Read(buffer, 0, (int)ms1.Length);
With the data in the byte array, you can now proceed to send the data to the Web Service. To verify that the data stored in the byte array is really the image in the PictureBoxcontrol, you can load it back to another MemoryStreamobject and then display it in another PictureBoxcontrol, like this:
//---read the data in buffer and write to ms2---
MemoryStream ms2 = new MemoryStream();
ms2.Write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
//---load it in another PictureBox control---
pictureBox2.Image = new Bitmap(ms2);
The NetworkStreamclass provides methods for sending and receiving data over Streamsockets in blocking mode. Using the NetworkStreamclass is more restrictive than using most other Streamimplementations. For example, the CanSeek()properties of the NetworkStreamclass are not supported and always return false. Similarly, the Length()and Position()properties throw NotSupportedException. It is not possible to perform a Seek()operation, and the SetLength()method also throws NotSupportedException.
Despite these limitations, the NetworkStreamclass has made network programming very easy and encapsulates much of the complexity of socket programming. Developers who are familiar with streams programming can use the NetworkStreamclass with ease.
This section leads you through creating a pair of socket applications to illustrate how the NetworkStreamclass works. The server will listen for incoming TCP clients and send back to the client whatever it receives.
Building a Client-Server Application
The following code is for the server application:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
namespace Server {
class Program {
const int PORT_NO = 5000;
const string SERVER_IP = "127.0.0.1";
static void Main(string[] args) {
//---listen at the specified IP and port no.---
IPAddress localAdd = IPAddress.Parse(SERVER_IP);
TcpListener listener = new TcpListener(localAdd, PORT_NO);
Console.WriteLine("Listening...");
listener.Start();
//---incoming client connected---
TcpClient client = listener.AcceptTcpClient();
//---get the incoming data through a network stream---
NetworkStream nwStream = client.GetStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[client.ReceiveBufferSize;
//---read incoming stream---
int bytesRead = nwStream.Read(buffer, 0, client.ReceiveBufferSize);
//---convert the data received into a string---
string dataReceived = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
Console.WriteLine("Received : " + dataReceived);
//---write back the text to the client---
Console.WriteLine("Sending back : " + dataReceived);
nwStream.Write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
client.Close();
listener.Stop();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
Basically, you use the TcpListenerclass to listen for an incoming TCP connection. Once a connection is made, you use a NetworkStreamobject to read data from the client, using the Read()method as well as write data to the client by using the Write()method.
For the client, you use the TcpClientclass to connect to the server using TCP and, as with the server, you use the NetworkStreamobject to write and read data to and from the client:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
namespace Client {
class Program {
const int PORT_NO = 5000;
const string SERVER_IP = "127.0.0.1";
static void Main(string[] args) {
//---data to send to the server---
string textToSend = DateTime.Now.ToString();
//---create a TCPClient object at the IP and port no.---
TcpClient client = new TcpClient(SERVER_IP, PORT_NO);
NetworkStream nwStream = client.GetStream();
byte[] bytesToSend = ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(textToSend);
//---send the text---
Console.WriteLine("Sending : " + textToSend);
nwStream.Write(bytesToSend, 0, bytesToSend.Length);
//---read back the text---
byte[] bytesToRead = new byte[client.ReceiveBufferSize];
int bytesRead = nwStream.Read(bytesToRead, 0, client.ReceiveBufferSize);
Console.WriteLine("Received : " +
Encoding.ASCII.GetString(bytesToRead, 0, bytesRead));
Console.ReadLine();
client.Close();
}
}
}
Figure 11-4 shows how the server and client look like when you run both applications.
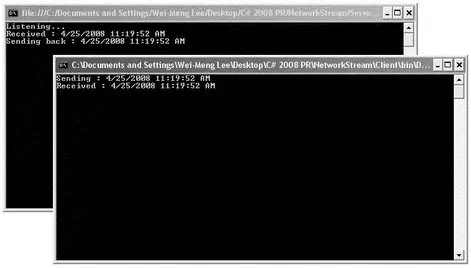
Figure 11-4
Building a Multi-User Server Application
The client-server applications built in the previous section can accept only a single client. A client connects and sends some data to the server; the server receives it, sends the data back to the client, and then exits. While this is a simple demonstration of a client-server application, it isn't a very practical application because typically a server should be able to handle multiple clients simultaneously and runs indefinitely. So let's look at how you can extend the previous server so that it can handle multiple clients simultaneously.
To do so, you can create a class named Clientand code it as follows:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Net.Sockets;
namespace Server {
class Client {
//---create a TCPClient object---
TcpClient _client = null;
//---for sending/receiving data---
byte[] buffer;
//---called when a client has connected---
public Client(TcpClient client) {
_client = client;
//---start reading data asynchronously from the client---
buffer = new byte[_client.ReceiveBufferSize];
_client.GetStream().BeginRead(
buffer, 0, _client.ReceiveBufferSize, receiveMessage, null);
}
public void receiveMessage(IAsyncResult ar) {
Читать дальше













