int bytesRead;
try {
lock (_client.GetStream()) {
//---read from client---
bytesRead = _client.GetStream().EndRead(ar);
}
//---if client has disconnected---
if (bytesRead < 1) return;
else {
//---get the message sent---
string messageReceived =
ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetString(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
Console.WriteLine("Received : " + messageReceived);
//---write back the text to the client---
Console.WriteLine("Sending back : " + messageReceived);
byte[] dataToSend =
ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(messageReceived);
_client.GetStream().Write(dataToSend, 0, dataToSend.Length);
}
//---continue reading from client---
lock (_client.GetStream()) {
_client.GetStream().BeginRead(
buffer, 0, _client.ReceiveBufferSize, receiveMessage, null);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
}
}
}
Here, the constructor of the Clientclass takes in a TcpClientobject and starts to read from it asynchronously using the receiveMessage()method (via the BeginRead()method of the NetworkStreamobject). Once the incoming data is read, the constructor continues to wait for more data.
To ensure that the server supports multiple users, you use a TcpListenerclass to listen for incoming client connections and then use an infinite loop to accept new connections. Once a client is connected, you create a new instance of the Clientobject and continue waiting for the next client. So the Main()function of your application now looks like this:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
namespace Server {
class Program {
const int PORT_NO = 5000;
const string SERVER_IP = "127.0.0.1";
static void Main(string[] args) {
//---listen at the specified IP and port no.---
IPAddress localAddress = IPAddress.Parse(SERVER_IP);
TcpListener listener = new TcpListener(localAddress, PORT_NO);
Console.WriteLine("Listening...");
listener.Start();
while (true) {
//---incoming client connected---
Client user = new Client(listener.AcceptTcpClient());
}
}
}
}
Figure 11-5 shows the server with two clients connected to it.
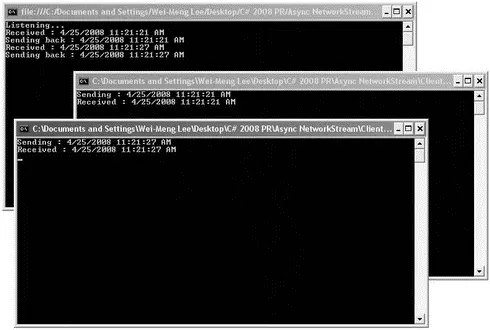
Figure 11-5
The .NET framework contains a number of cryptography services that enable you to incorporate security services into your .NET applications. These libraries are located under the System.Security.Cryptographynamespace and provide various functions such as encryption and decryption of data, as well as other operations such as hashing and random-number generation. One of the core classes that support the cryptographic services is the CryptoStreamclass, which links data streams to cryptographic transformations.
This section explores how to use some of the common security APIs to make your .NET applications more secure.
The most common security function that you will perform is hashing. Consider the situation where you need to build a function to authenticate users before they can use your application. You would require the user to supply a set of login credentials, generally containing a user name and a password. This login information needs to be persisted to a database. Quite commonly, developers store the passwords of users verbatim on a database. That's a big security risk because hackers who get a chance to glance at the users' database would be able to obtain the passwords of your users. A better approach is to store the hash values of the users' passwords instead of the passwords themselves. A hashing algorithm has the following properties:
□ It maps a string of arbitrary length to small binary values of a fixed length, known as a hash value.
□ The hash value of a string is unique, and small changes in the original string will produce a different hash value.
□ It is improbable that you'd find two different strings that produce the same hash value.
□ It is impossible to use the hash value to find the original string.
Then, when the user logs in to your application, the hash value of the password provided is compared with the hash value stored in the database. In this way, even if hackers actually steal the users' database, the actual password is not exposed. One downside to storing the hash values of users' passwords is that in the event that a user loses her password, there is no way to retrieve it. You'd need to generate a new password for the user and request that she change it immediately. But this inconvenience is a small price to pay for the security of your application.
There are many hashing algorithms available in .NET, but the most commonly used are the SHA1 and MD5 implementations. Let's take a look at how they work in .NET.
Using Visual Studio 2008, create a new Console application project. Import the following namespaces:
using System.IO;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
Define the following function:
static void Hashing_SHA1() {
//---ask the user to enter a password---
Console.Write("Please enter a password: ");
string password = Console.ReadLine();
//---hash the password---
byte[] data = ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes(password);
byte[] passwordHash;
SHA1CryptoServiceProvider sha = new SHA1CryptoServiceProvider();
passwordHash = sha.ComputeHash(data);
//---ask the user to enter the same password again---
Console.Write("Please enter password again: ");
password = Console.ReadLine();
//---hash the second password and compare it with the first---
data = System.Text.Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(password);
if (ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetString(passwordHash) ==
ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetString(sha.ComputeHash(data)))
Console.WriteLine("Same password");
else Console.WriteLine("Incorrect password");
}
You first ask the user to enter a password, after which you will hash it using the SHA1 implementation. You then ask the user to enter the same password again. To verify that the second password matches the first, you hash the second password and then compare the two hash values. For the SHA1 implementation, the hash value generated is 160 bits in length (the byte array passwordHashhas 20 members: 8 bits×20=160 bits). In this example, you convert the hash values into strings and perform a comparison. You could also convert them to Base64 encoding and then perform a comparison. Alternatively, you can also evaluate the two hash values by using their byte arrays, comparing them byte by byte. As soon as one byte is different, you can conclude that the two hash values are not the same.
Читать дальше













