//---display the creation time---
Console.WriteLine(File.GetCreationTime(newFileName));
//---make the file read-only and hidden---
File.SetAttributes(newFileName, FileAttributes.ReadOnly);
File.SetAttributes(newFileName, FileAttributes.Hidden);
} catch (IOException ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
} catch (Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
This program first checks to see if a file exists by using the Exists()method. If the file exists, the program deletes it using the Delete()method. It then proceeds to create the file by using the Create()method, which returns a FileStreamobject (more on this in subsequent sections). To make a copy of the file, you use the Copy()method. The Move()method moves a file from one location to another. Essentially, you can use the Move()method to rename a file. Finally, the program sets the ReadOnlyand Hiddenattribute to the newly copied file.
In addition to the File class, you have the FileInfoclass that provides instance members for dealing with files. Once you have created an instance of the FileInfoclass, you can use its members to obtain more information about a particular file. Figure 11-1 shows the different methods and properties exposed by an instance of the FileInfoclass, such as the Attributesproperty, which retrieves the attributes of a file, the Delete()method that allows you to delete a file, and so on.
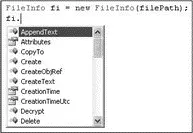
Figure 11-1
Reading and Writing to Files
The Fileclass contains four methods to write content to a file:
□ WriteAllText()— Creates a file, writes a string to it, and closes the file
□ AppendAllText()— Appends a string to an existing file
□ WriteAllLines()— Creates a file, writes an array of string to it, and closes the file
□ WriteAllBytes()— Creates a file, writes an array of byte to it, and closes the file
The following statements show how to use the various methods to write some content to a file:
string filePath = @"C:\temp\textfile.txt";
string strTextToWrite = "This is a string";
string[] strLinesToWrite = new string[] { "Line1", "Line2" };
byte[] bytesToWrite =
ASCIIEncoding.ASCII.GetBytes("This is a string");
File.WriteAllText(filePath, strTextToWrite);
File.AppendAllText(filePath, strTextToWrite);
File.WriteAllLines(filePath, strLinesToWrite);
File.WriteAllBytes(filePath, bytesToWrite);
The Fileclass also contains three methods to read contents from a file:
□ ReadAllText()— Opens a file, reads all text in it into a string, and closes the file
□ ReadAllLines()— Opens a file, reads all the text in it into a string array, and closes the file
□ ReadAllBytes()— Opens a file, reads all the content in it into a byte array, and closes the file
The following statements show how to use the various methods to read contents from a file:
string filePath = @"C:\temp\textfile.txt";
string strTextToRead = (File.ReadAllText(filePath));
string[] strLinestoRead = File.ReadAllLines(filePath);
byte[] bytesToRead = File.ReadAllBytes(filePath);
The beauty of these methods is that you need not worry about opening and closing the file after reading or writing to it; they close the file automatically after they are done.
StreamReader and StreamWriter Classes
When dealing with text files, you may also want to use the StreamReaderand StreamWriterclasses. StreamReaderis derived from the TextReaderclass, an abstract class that represents a reader that can read a sequential series of characters.
You'll see more about streams in the "The Stream Class" section later in this chapter.
The following code snippet uses the StreamReaderclass to read lines from a text file:
try {
using (StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(filePath)) {
string line;
while ((line = sr.ReadLine()) != null) {
Console.WriteLine(line);
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
In addition to the ReadLine()method, the StreamReaderclass supports the following methods:
□ Read()— Reads the next character from the input stream
□ ReadBlock()— Reads a maximum of specified characters
□ ReadToEnd()— Reads from the current position to the end of the stream
The StreamWriterclass is derived from the abstract TextWriterclass and is used for writing characters to a stream. The following code snippet uses the StreamWriterclass to write lines to a text file:
try {
using (StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(filePath)) {
sw.Write("Hello, ");
sw.WriteLine("World!");
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
Console.WriteLine(ex.ToString());
}
BinaryReader and BinaryWriter Classes
If you are dealing with binary files, you can use the BinaryReaderand BinaryWriterclasses. The following example reads binary data from one file and writes it into another, essentially making a copy of the file:
string filePath = @"C:\temp\VS2008Pro.png";
string filePathCopy = @"C:\temp\VS2008Pro_copy.png";
//---open files for reading and writing---
FileStream fs1 = File.OpenRead(filePath);
FileStream fs2 = File.OpenWrite(filePathCopy);
BinaryReader br = new BinaryReader(fs1);
BinaryWriter bw = new BinaryWriter(fs2);
//---read and write individual bytes---
for (int i = 0; i <= br.BaseStream.Length - 1; i++)
bw.Write(br.ReadByte());
//---close the reader and writer---
br.Close();
bw.Close();
This program first uses the Fileclass to open two files — one for reading and one for writing. The BinaryReaderclass is then used to read the binary data from the FileStream, and the BinaryWriteris used to write the binary data to the file.
The BinaryReaderclass contains many different read methods for reading different types of data — Read(), Read7BitEncodedInt(), ReadBoolean(), ReadByte(), ReadBytes(), ReadChar(), ReadChars(), ReadDecimal(), ReadDouble(), ReadInt16(), ReadInt32(), ReadInt64(), ReadSByte(), ReadSingle(), ReadString(), ReadUInt16(), ReadUInt32(), and ReadUInt64().
Читать дальше













