CAN_CONFIG_LINE_FILTER_OFF;
send_flag = CAN_TX_PRIORITY_0 &
CAN_TX_XTD_FRAME &
CAN_TX_NO_RTR_FRAME;
read_flag = 0;
//
// Initialise CAN module
//
CANInitialize(SJW, BRP, Phase_Seg1, Phase_Seg2, Prop_Seg, init_flag);
//
// Set CAN CONFIG mode
//
CANSetOperationMode(CAN_MODE_CONFIG, 0xFF);
mask = -1;
//
// Set all MASK1 bits to 1's
//
CANSetMask(CAN_MASK_B1, mask, CAN_CONFIG_XTD_MSG);
//
// Set all MASK2 bits to 1's
//
CANSetMask(CAN_MASK_B2, mask, CAN_CONFIG_XTD_MSG);
//
// Set id of filter B1_F1 to 3
//
CANSetFilter(CAN_FILTER_B2_F3,500,CAN_CONFIG_XTD_MSG);
//
// Set CAN module to NORMAL mode
//
CANSetOperationMode(CAN_MODE_NORMAL, 0xFF);
//
// Program loop. Read the temperature from analog temperature
// sensor
//
for(;;) // Endless loop
{
//
// Wait until a request is received
//
dt = 0;
while(!dt) dt = CANRead(&id, data, &len, &read_flag);
if (id == 500 && data[0] == 'T') {
//
// Now read the temperature
//
temp = Adc_Read(0); // Read temp
mV = (unsigned long)temp * 5000 / 1024; // in mV
temperature = mV/10; // in degrees C
//
// send the temperature to Node:Display
//
data[0] = temperature;
id = 3; // Identifier
CANWrite(id, data, 1, send_flag); // send temperature
}
}
}

Figure 9.18: COLLECTOR program listing
Inside the program loop, the program waits until it receives a request to send the temperature. Here the request is identified by the reception of character “T”. Once a valid request is received, the temperature is read and converted into °C (stored in variable temperature ) and then sent to the CAN bus as a byte with an identifier value equal to 3. This process repeats forever.
Figure 9.19 summarizes the operation of both nodes.
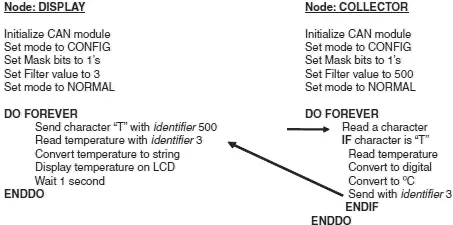
Figure 9.19: Operation of both nodes
CHAPTER 10
Multi-Tasking and Real-Time Operating Systems
Nearly all microcontroller-based systems perform more than one activity. For example, a temperature monitoring system is made up of three tasks that normally repeat after a short delay, namely:
• Task 1 Reads the temperature
• Task 2 Formats the temperature
• Task 3 Displays the temperature
More complex systems may have many complex tasks. In a multi-tasking system, numerous tasks require CPU time, and since there is only one CPU, some form of organization and coordination is needed so each task has the CPU time it needs. In practice, each task takes a very brief amount of time, so it seems as if all the tasks are executing in parallel and simultaneously.
Almost all microcontroller-based systems work in real time. A real-time system is a time responsive system that can respond to its environment in the shortest possible time. Real time does not necessarily mean the microcontroller should operate at high speed. What is important in a real-time system is a fast response time, although high speed can help. For example, a real-time microcontroller-based system with various external switches is expected to respond immediately when a switch is activated or some other event occurs.
A real-time operating system (RTOS) is a piece of code (usually called the kernel) that controls task allocation when the microcontroller is operating in a multi-tasking environment. RTOS decides, for instance, which task to run next, how to coordinate the task priorities, and how to pass data and messages among tasks.
This chapter explores the basic principles of multi-tasking embedded systems and gives examples of an RTOS used in simple projects. Multi-tasking code and RTOS are complex and wide topics, and this chapter describes the concepts pertaining to these tools only briefly. Interested readers should refer to the many books and papers available on operating systems, multi-tasking systems, and RTOS.
There are several commercially available RTOS systems for PIC microcontrollers. At the time of writing, mikroC language did not provide a built-in RTOS. Two popular high-level RTOS systems for PIC microcontrollers are Salvo (www.pumpkin.com), which can be used from a Hi-Tech PIC C compiler, and the CCS (Customer Computer Services) built-in RTOS system. In this chapter, the example RTOS projects are based on the CCS (www.ccsinfo.com) compiler, one of the popular PIC C compilers developed for the PIC16 and PIC18 series of microcontrollers.
State machines are simple constructs used to perform several activities, usually in a sequence. Many real-life systems fall into this category. For example, the operation of a washing machine or a dishwasher is easily described with a state machine construct.
Perhaps the simplest method of implementing a state machine construct in C is to use a switch-case statement. For example, our temperature monitoring system has three tasks, named Task 1, Task 2, and Task 3 as shown in Figure 10.1. The state machine implementation of the three tasks using switch-case statements is shown in Figure 10.2. The starting state is 1, and each task increments the state number by one to select the next state to be executed. The last state selects state 1, and there is a delay at the end of the switch-case statement. The state machine construct is executed continuously inside an endless for loop.
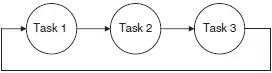
Figure 10.1: State machine implementation
for (;;) {
state = 1;
switch (state) {
CASE 1:
implement TASK 1
state++;
break;
CASE 2:
implement TASK 2
state++;
break;
CASE 3:
implement TASK 3
state = 1;
break;
}
Delay_ms(n);
}

Figure 10.2: State machine implementation in C
In many applications, the states need not be executed in sequence. Rather, the next state is selected by the present state either directly or based on some condition. This is shown in Figure 10.3.
for (;;) {
state = 1;
switch (state) {
CASE 1:
implement TASK 1
state = 2;
break;
CASE 2:
implement TASK 2
Читать дальше















