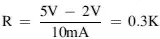Figure 4.12: Passing variable number of arguments to a function
4.1.5 Function Reentrancy
The mikroC compiler supports only a limited function reentrancy. Functions that have no arguments and local variables can be called both from the interrupt service routines and from the main program. Functions that have arguments and/or local variables can only be called from the interrupt service routines or from the main program.
4.1.6 Static Function Variables
Normally, variables declared at the beginning of a program, before the main program, are global, and their values can be accessed and modified by all parts of the program. Declaring a variable used in a function as global ensures that its value is retained from one call of the function to another, but this also undermines the variable’s privacy and reduces the portability of the function to other applications. A better approach is to declare such variables as static . Static variables are mainly used in function definitions. When a variable is declared as static , its value is retained from one call of the function to another. In the example code that follows, variable k is declared as static and initialized to zero. This variable is then incremented before exiting from the function, and the value of k remains in existence and holds its last value on the next call to the function (i.e., on the second call to the function the value of k will be 1):
void Cnt(void) {
static int k = 0; // Declare k as static
..................
..................
k++; // increment k
}
4.2 mikroC Built-in Functions
The mikroC compiler provides a set of built-in functions which can be called from the program. These functions are listed in Table 4.1, along with a brief description of each. Most of these functions can be used in a program without having to include header files.
Table 4.1: mikroC built-in functions
| Function |
Description |
| Lo |
Returns the lowest byte of a number (bits 0 to 7) |
| Hi |
Returns next to the lowest byte of a number (bits 8 to 15) |
| Higher |
Returns next to the highest byte of a number (bits 16 to 23) |
| Highest |
Returns the highest byte of a number (bits 24 to 31) |
| Delay_us |
Creates software delay in microsecond units |
| Delay_ms |
Creates constant software delay in millisecond units |
| Vdelay_ms |
Creates delay in milliseconds using program variables |
| Delay_Cyc |
Creates delay based on microcontroller clock |
| Clock_Khz |
Returns microcontroller clock in KHz |
| Clock_Mhz |
Returns microcontroller clock in MHz |
The exceptions are functions Lo, Hi, Higher , and Highest , which require the header file built_in.h . Further details about using these functions are available in the mikroC manuals.
Functions Delay_us and Delay_ms are frequently used in programs where delays are required (e.g., when flashing an LED). The following example illustrates the use of the Delay_ms function:
Example 4.10
An LED is connected to bit 0 of PORTB (pin RB0) of a PIC18FXXX microcontroller through a current-limiting resistor as shown in Figure 4.13. Choose a suitable value for the resistor and write a program that will flash the LED ON and OFF continuously at one-second intervals.
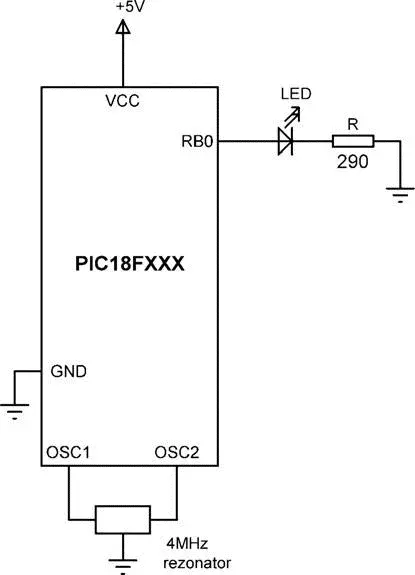
Figure 4.13: LED connected to port RB0 of a PIC microcontroller
Solution 4.10
LEDs can be connected to a microcontroller in two modes: current sinking and current sourcing. In current sinking mode (see Figure 4.14) one leg of the LED is connected to the +5V and the other leg is connected to the microcontroller output port pin through a current limiting resistor R.
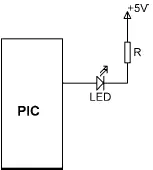
Figure 4.14: Connecting the LED in current sinking mode
Under normal working conditions, the voltage across an LED is about 2V and the current through the LED is about 10mA (some low-power LEDs can operate at as low as 1mA current). The maximum current that can be sourced or sinked at the output port of a PIC microcontroller is 25mA.
The value of the current limiting resistor R can be calculated as follows. In current sinking mode the LED will be turned ON when the output port of the microcontroller is at logic 0 (i.e., at approximately 0V). The required resistor is then:
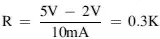
The nearest resistor to choose is 290 Ohm (a slightly higher resistor can be chosen for a lower current and slightly less brightness).
In current sourcing mode (see Figure 4.15) one leg of the LED is connected to the output port of the microcontroller and the other leg is connected to the ground through a current limiting resistor. The LED will be turned ON when the output port of the microcontroller is at logic 1 (i.e., at approximately 5V). The same value of resistor can be used in both current sinking and current sourcing modes.
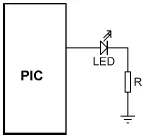
Figure 4.15: Connecting the LED in current sourcing mode
The required program listing is given in Figure 4.16 (program FLASH.C). At the beginning of the program PORTB is configured as output using the TRISB = 0 statement. An endless loop is then formed with the for statement, and inside this loop the LED is turned ON and OFF with one-second delays between outputs.
/*****************************************************************
FLASHING AN LED
===============
This program flashes an LED connected to port RB0 of a microcontroller
with one second intervals. mikroC built-in function Delay_ms is used to
create a 1 second delay between the flashes.
Programmer: Dogan Ibrahim
File: FLASH.C
Date: May, 2007
*******************************************************************/
void main() {
TRISB = 0; // Configure PORTB as output
for(;;) // Endless loop
{
PORTB = 1; // Turn ON LED
Delay_ms(1000); // 1 second delay
PORTB = 0; // Turn OFF LED
Delay_ms(1000); // 1 second delay
}
}

Figure 4.16: Program to flash an LED
The program given in Figure 4.16 can be made more user-friendly and easier to follow by using define statements as shown in Figure 4.17 (program FLASH2.C).
/*******************************************************************
FLASHING AN LED
===============
This program flashes an LED connected to port RB0 of a microcontroller
with one second intervals. mikroC built-in function Delay_ms is used to
Читать дальше