Android 1.5 introduces some new widgets, notably SlidingDrawerand HorizontalScrollView.
SlidingDrawerintroduces a container akin to the one on the home screen used to hold the application icons. You control the image to use for the drawer “handle” and the contents to go in the drawer. You can also control the orientation, to determine if the drawer opens from the bottom or the side. Then, you can add listeners to monitor the state of the drawer, or toggle the state yourself, if desired.
As the name suggests, HorizontalScrollViewworks just like the original ScrollViewexcept that it scrolls horizontally, not vertically.
With the May 2009 debut of the HTC Magic, we now have Android phones lacking hardware keyboards. This makes text entry rather difficult… except that Android 1.5 added in support for soft keyboards. Soft keyboards also help for internationalization, as the user is not limited to the particulars of whatever hardware keyboard their device may actually have.
Soft keyboards take effect automatically, for basic functionality. The EditText widgets in your layout will cause the soft keyboard to spring up, assuming the device either does not have a QWERTY keyboard (e.g., HTC Magic) or is being held with the keyboard closed (e.g., T-Mobile G1 in portrait mode) as seen in Figure A-1.

Figure A-1. Android 1.5’s Input Method Editor (a.k.a., soft keyboard)
You can tailor the behavior of the soft keyboard in your layouts or via Java code. For example, in the screenshot shown previously, you will see a “Next” button in the lower-right corner. By default, Android will take a guess as what to use this “action button” for — in this case, it moves you to the next field. You can add attributes to your layout to control what the caption is for this button, and what actually occurs when the action button is tapped. So, for example, if you are allowing people to enter a URL to visit in a Web browser, you might rename the action button to “Go” and have it launch the Browser application upon the typed-in URL.
You can also provide light control over what sort of keyboard is displayed by indicating what sort of text entry is supposed to occur in the EditText. For example, you can indicate that the android:inputTypeis textEmailAddress, which will ensure an @ key is available without having to use a soft shift key.
You can also control what happens to your activity layout when the soft keyboard is displayed. Your activity can either scroll out of the way to support the keyboard, or it can be resized to accommodate the keyboard, or have the keyboard appear full-screen, eclipsing your activity until the text entry is complete. Android will attempt to determine the best answer automatically, but via the android:windowSoftInputModeon your element in your manifest, you can override the default behavior.
This Input Method Framework (IMF) is extensible, should you wish to create your own customized soft keyboard (a.k.a., input method editor, or IME) for use in your application or by other applications. A sample IME is provided with the SDK to serve as a basis for your own custom keyboards.
Android 1.5 lets you do more with the built-in home screen application, notably by adding “app widgets” and “live folders”. As an application developer, you can choose to offer app widgets and/or live folders from your own applications for users to add to their home screens.
App widgets are simply user interface elements added to the home screen. Previous Android editions had some of these (the analog clock, the Google search bar), but they were fixed in type and number. Now, not only does Android add in a couple of more app widgets (e.g., media player, picture frame), but users can add and remove app widgets, and developers can create their own (see Figure A-2).
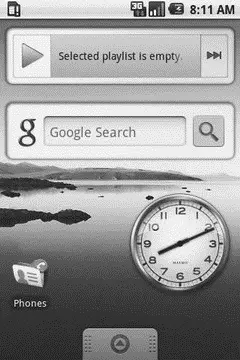
Figure A-2. Some stock Android 1.5 app widgets
App widgets are built not using ordinary layouts, but rather with a layout subset known as RemoteViews. You cannot use arbitrary widgets with RemoteViews, though it supports many common ones. The term “remote views” comes from the fact that while the UI is defined by your application, the UI (in the form of the “app widget”) runs in the context of another application, in this case the home screen.
Implementing an app widget involves creating some XML metadata, associating that metadata with a element in your manifest, and implementing that receiver as an AppWidgetProvider. Most likely in conjunction with a service that will handle any time-consuming work (e.g., network lookups), your provider will create and push out RemoteViewswhen requested by the home screen. Note that app widgets are designed for infrequent update, since frequent polling for new widget contents can rapidly drain the device battery.
Live folders are, in essence, a simplified home-screen-launched look into the contents published by a ContentProvider. In the screenshot shown previously, you see a “Phones” icon. Tapping that brings up a dialog over the home screen containing a list of all contacts containing phone numbers as you can see in Figure A-3.
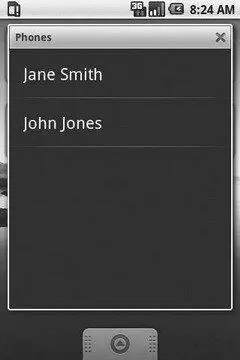
Figure A-3. A Live Folder in Android 1.5
Tapping an individual contact, of course, brings up the detail screen for that contact.
To create your own live folders for your users to offer, you can add an intent filter watching for a CREATE_LIVE_FOLDER Intenton an activity in your application. That activity, in turn, simply calls setResult()with another Intentobject, this one describing the live folder, such as its icon, name, and display mode (e.g., LiveFolders.DISPLAY_MODE_LIST). This Intentalso contains the Uripointing to the ContentProviderwhose information you are trying to display. That ContentProvidershould be updated to recognize the live folder Uriand, on query(), return an ID, title, and description of each piece of content in the provider (or a subset if appropriate). Android will take care of the rest, in terms of formatting the data in the live folder convention (large font title, small font description), pouring the query results into a list, etc.
A common pattern in Android is to perform some work on a background thread, then update something on the UI thread when the background work is complete. A simple way to handle this is to fork a background thread and use a Handleror runOnUiThread()to accomplish the UI thread work. However, the danger here is in forking too many threads — the user might do something that causes you to fork many threads in short order, bogging down the device at best. And while there are classes that can help you manage a work pool (e.g., LinkedBlockingQueue), their use can be mildly tedious.
Читать дальше














