iptables is actually an unusual service. Most other servicessuch as cups , httpd , or gpm have a server process that begins running when the service is started and that is stopped when the service is stopped; iptables , on the other hand, just configures the iptables facility in the kernel when the service is started or stopped, so there's no actual process running when the firewall is active.
8.1.3.1. ...more complex firewall rules?
The firewall interface provided by Fedora's system-config-securitylevel supports only the filtering of inbound (and forwarded) packets and is quite simple. However, the iptables mechanism supports much more complex filtering. Fedora Extras provides several alternate tools for firewall configuration, including firestarter , fwbuilder , and shorewall .
8.1.4. Where Can I Learn More?
The manpages for iptables
The home page for iptables at http://netfilter.org
Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is installed and enabled by default in Fedora Core. SELinux controls what a program is and is not allowed to do, enforcing security policy through the kernel. This prevents an attacker from using a compromised program to do something it was not intended to do.
Although SELinux can at times be challenging to configure, it dramatically improves protection against some common system attacksso a little bit of effort can pay off in a big way.
SELinux is managed using the same graphical tool used to manage the firewall. Click System→Administration→"Security Level and Firewall" to start it, then select the SELinux tab, shown in Figure 8-5.
Figure 8-5. Graphical configuration tool for SELinux
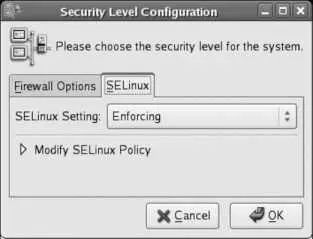
There are three possible values for SELinux Setting:
Enforcing
Fully enables SELinux. Any attempted operation that violates the current security policy is blocked.
Permissive
Enables SELinux security checks but does not enforce the security policy; operations that violate the current security policy are permitted, but an error message is logged to record the event. This is useful if you have previously disabled SELinux and want to evaluate the potential impact before you enable it.
Disabled
Completely disables SELinux.
If you enable SELinux (using Enforcing or Permissive mode), expand the Modify SELinux Policy section by clicking the triangle. The SELinux policy configuration categories will appear, as shown in Figure 8-6 .
Figure 8-6. SELinux policy configuration categories
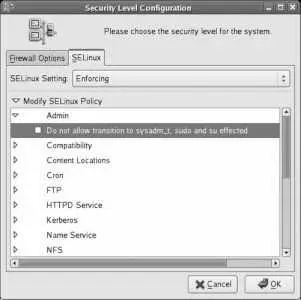
Each of these categories contains a number of options (represented as checkboxes) called booleans . Each boolean may be set on (checked) or off (unchecked).
To expand the options in any category, click on the arrow in front of that category. In Figure 8-6 , the Admin category has been expanded, and the window width has been resized to fully show each option.
After selecting or deselecting booleans as desired, click OK. Changes in boolean values will take effect immediately, but changing the SELinux setting to or from Disabled will take effect only when the system is booted.
8.2.1.1. Configuring SELinux from the command line
SELinux can also be configured very easily from the command line. To enable SELinux, edit the file /etc/selinux/config and set the SELINUX value to enforcing , permissive , or disabled :
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - SELinux is fully disabled.
SELINUX=enforcing
# SELINUXTYPE= type of policy in use. Possible values are:
# targeted - Only targeted network daemons are protected.
# strict - Full SELinux protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
Changes made to this file will take effect when the system is booted. If SELinux is enabled, you can use the getenforce command to view the current mode, and you can use the setenforce command to immediately switch between enforcing and permissive modes:
# getenforce
Enforcing
# setenforce permissive
# getenforce
Permissive
# setenforce enforcing
# getenforce
Enforcing
Boolean valuescorresponding to the checkboxes in the graphical Security Level configuration toolcan be viewed with the getsebool command, using the -a option to see all values:
$ getsebool -a
NetworkManager_disable_trans --> off
allow_cvs_read_shadow --> off
allow_execheap --> off
allow_execmem --> on
...(Lines snipped)...
ypserv_disable_trans --> off
ypxfr_disable_trans --> off
zebra_disable_trans --> off
You can also specify a specific boolean:
$ /usr/sbin/getsebool httpd_enable_cgi
httpd_enable_cgi --> on
To temporarily set a boolean value, use the setsebool command:
# setsebool httpd_enable_cgi 1
# setsebool httpd_enable_homedirs=0
Notice that the on/off state of the boolean is expressed numerically, with 1 representing on and 0 representing off. Also note that the boolean name and value may be specified as two arguments (first example), or they may be specified as a single argument, joined with the = symbol (second example). If you use the second form, you can set multiple booleans with one command:
# setsebool httpd_enable_cgi=1 httpd_enable_homedirs=0
Changes made to boolean values with setsebool take effect immediately but are not permanent; they will reset at the next boot. To make them permanent, add the -P argument:
# setsebool -P httpd_enable_cgi=1
8.2.1.2. Determining which booleans to modify
The default boolean settings for SELinux are reasonable for most systems, but they may need to be changed to relax the security policy for specific applications.
For example, by default, web scripts are not permitted to communicate through the network; this prevents an untrusted script from somehow transferring private data to another host. But if your web scripts need to connect to an IMAP email server or an SQL database such as MySQL or PostgreSQL, you'll need to set the appropriate boolean.
In this case, you can find the boolean in the graphical interface by expanding the HTTPD Service category and looking through the options. Select the checkbox for the boolean labeled "Allow HTTPD scripts and modules to connect to the network."
Читать дальше














