Samuel Forman - Stories of Useful Inventions
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Samuel Forman - Stories of Useful Inventions» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_prose, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Stories of Useful Inventions
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Stories of Useful Inventions: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Stories of Useful Inventions»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Stories of Useful Inventions — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Stories of Useful Inventions», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:

FIG. 6. – TINDER BOX, FLINT, STEEL, AND SULPHUR-TIPPED SPLINTERS.
The strike-a-light method was discovered many thousands of years ago, and it has been used by nearly all the civilized nations of the world. 4 4 The ancient Greeks used a burning-glass or – lens for kindling fire. The lens focused the sun's rays upon a substance that would burn easily and set it afire. The burning-glass was not connected in any way with the development of the match.
And it has not been so very long since this method was laid aside. There are many people now living who remember when the flint and steel and tinder-box were in use in almost every household.
About three hundred years ago a third method of producing fire was discovered. If you should drop a small quantity of sulphuric acid into a mixture of chlorate of potash and sugar, you would produce a bright flame. Here was a hint for a new way of making a fire; and a thoughtful man in Vienna, in the seventeenth century, profited by the hint. He took one of the sulphur-tipped splinters which he was accustomed to use with his tinder-box, and dipped it into sulphuric acid, and then applied it to a mixture of chlorate of potash and sugar. The splinter caught fire and burned with a blaze. Here was neither friction nor percussion. The chemical substances were simply brought together, and they caught fire of themselves; that is to say, they caught fire by chemical action.
The discovery made by the Vienna man led to a new kind of match – the chemical match. A practical outfit for fire-making now consisted of a bottle of sulphuric acid (vitriol) and a bundle of splints tipped with sulphur, chlorate of potash, and sugar. Matches of this kind were very expensive, costing as much as five dollars a hundred; besides, they were very unsatisfactory. Often when the match was dipped into the acid it would not catch fire, but would smolder and sputter and throw the acid about and spoil both the clothes and the temper. These dip-splint matches were used in the eighteenth century by those who liked them and could afford to buy them. They did not, however, drive out the old strike-a-light and tinder-box.
In the nineteenth century – the century in which so many wonderful things were done – the fourth step in the development of the match was taken. In 1827, John Walker, a druggist in a small English town, tipped a splint with sulphur, chlorate of potash, and sulphid of antimony, and rubbed it on sandpaper, and it burst into flame. The druggist had discovered the first friction-chemical match, the kind we use to-day. It is called friction-chemical because it is made by mixing certain chemicals together and rubbing them. Although Walker's match did not require the bottle of acid, nevertheless it was not a good one. It could be lighted only by hard rubbing, and it sputtered and threw fire in all directions. In a few years, however, phosphorus was substituted on the tip for antimony, and the change worked wonders. The match could now be lighted with very little rubbing, and it was no longer necessary to have sandpaper upon which to rub it. It would ignite when rubbed on any dry surface, and there was no longer any sputtering. This was the phosphorus match, the match with which we are so familiar.

FIG. 7. – A "BLOCK" OF MATCHES.
After the invention of the easily-lighted phosphorus match there was no longer use for the dip-splint or the strike-a-light. The old methods of getting a blaze were gradually laid aside and forgotten. The first phosphorus matches were sold at twenty-five cents a block – a block (Fig. 7) containing a hundred and forty-four matches. They were used by few. Now a hundred matches can be bought for a cent. It is said that in the United States we use about 150,000,000,000 matches a year. This, on an average, is about five matches a day for each person.
There is one thing against the phosphorus match: it ignites too easily. If one is left on the floor, it may be ignited by stepping upon it, or by something falling upon it. We may step on a phosphorus match unawares, light it, leave it burning, and thus set the house on fire. Mice often have caused fires by gnawing the phosphorus matches and igniting them. In one city thirty destructive fires were caused in one year by mice lighting matches.
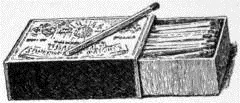
FIG. 8. – A BOX OF MODERN SAFETY MATCHES.
To avoid accident by matches, the safety match (Fig. 8) has recently been invented. The safety match does not contain phosphorus. The phosphorus is mixed with fine sand and glued to the side of the box in which the matches are sold. The safety match, therefore, cannot be lighted unless it is rubbed on the phosphorus on the outside of the box. It is so much better than the old kind of phosphorus match that it is driving the latter out of the market. Indeed, in some places it is forbidden by law to sell any kind of match but the safety match.
The invention of the safety match is the last step in the long history of fire-making. The first match was lighted by rubbing, and the match of our own time is lighted by rubbing; yet what a difference there is between the two! With the plowing-stick or fire-drill it took strength and time and skill to get a blaze; with the safety match an awkward little child can kindle a fire in a second.
And how long it has taken to make the match as good as it is! The steam-engine, the telegraph, the telephone, and the electric light were all in use before the simple little safety match.
THE STOVE
From the story of the match you have learned how man through long ages of experience gradually mastered the art of making a fire easily and quickly. In this chapter, and in several which are to follow, we shall have the history of those inventions which have enabled man to make the best use of fire. Since the first and greatest use of fire is to cook food and keep the body warm, our account of the inventions connected with the use of fire may best begin with the story of the stove.

FIG. 1. – THE PRIMITIVE STOVE.
The most important uses of fire were taught by fire itself. As the primitive man stood near the flames of the burning tree and felt their pleasant glow, he learned that fire may add to bodily comfort; and when the flames swept through a forest and overtook a deer and baked it, he learned that fire might be used to improve the quality of his food. The hint was not lost. He took a burning torch to his cave or hut and kindled a fire on his floor of earth. His dwelling filled with smoke, but he could endure the discomfort for the sake of the fire's warmth, and for the sake of the toothsomeness of the cooked meats. After a time a hole was made in the roof of the hut, and through this hole the smoke passed out. Here was the first stove. The primitive stove was the entire house; the floor was the fireplace and the hole in the roof was the chimney (Fig. 1). The word "stove" originally meant "a heated room." So that if we should say that at first people lived in their stoves, we should say that which is literally true.

FIG. 2. – PRIMITIVE COOKING.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Stories of Useful Inventions»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Stories of Useful Inventions» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Stories of Useful Inventions» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












