Christopher Whall - Stained Glass Work - A text-book for students and workers in glass
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Christopher Whall - Stained Glass Work - A text-book for students and workers in glass» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_antique, foreign_home, visual_arts, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Stained Glass Work: A text-book for students and workers in glass
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:3 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 60
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Stained Glass Work: A text-book for students and workers in glass: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Stained Glass Work: A text-book for students and workers in glass»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Stained Glass Work: A text-book for students and workers in glass — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Stained Glass Work: A text-book for students and workers in glass», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Fig. 31.
It requires a good deal of patience and practice to lay matt successfully over unfired outline. It is a question of the amount and quality of the gum, the condition of your brush, even the dryness or dampness of the air. You must try what degree of gum suits you best, both in the outline and in the matt which you are to pass over it. Try it a good many times on a slab of plain glass or on the plate of your easel first, before you try on your painting. Of course it's a much easier thing to matt successfully over a small piece than over a large. A head as big as the palm of your hand is not a very severe test of your powers; but in one as large as the whole of your hand, say a head seven inches from crown to chin, the problem is increased quite immeasurably in difficulty. The real test is being able to produce in glass a real facsimile of a head by Botticelli or Holbein, and when you can do that satisfactorily you can do anything in glass-painting.
Do not aim to get too much in the first painting, at any rate not till you have had long practice. Be content if you get enough modelling on a head to turn the outline into a more sensitive and artistic drawing than it could be if planted down, raw and hard, upon the bare, cold glass. After all it is a common practice to fire the outline separately, and anything beyond this that you get upon the glass for first fire is so much to the good.
But besides the quality of the gum you will find sometimes differences in the quality or condition of the pigment . It may be insufficiently ground; in which case the matt, in passing over, will rasp away every vestige of the outline, so delicate a matter it is.
You can tell when colour is not ground sufficiently by the way it acts when laid as a vertical wash. Lay a wash, moist enough to "run," on a bit of your easel-slab; it will run down, making a sort of seaweed-looking pattern—clear lanes of light on the glass with a black grain at the lower end. Those are the bits of unground material: under a 100-diameter microscope they look like chunks of ironstone or road metal, or of rusty iron, and you'll soon understand why they have scratched away your tender outline.
You must grind such colour till it is smooth, and an old-fashioned granite muller is the thing, not a glass one.
Now, after all this, how am I to excuse the paradox that it is possible to have the colour ground too fine! All one can say is that you "find it so." It can be so fine that it seems to slip about in a thin, oily kind of way.
It's all as you find it; the differences of a craft are endless; there is no forecasting of everything, and you must buy your experience, like everybody else, and find what suits you, learning your skill and your materials side by side.
Now these are the chief processes of painting, as far as laying on colour goes; but you still have much of your work before you, for the way in which light and shade is got on glass is almost more in "taking off" than in "putting on." You have laid your dark "matt" all over the glass evenly; now the next thing is to remove it wherever you want light or half-tone.
Fig. 32.
How to Finish a Shaded Painting out of the Even Matt. —This is done in many ways, but chiefly with those tools which painters call "scrubs," which are oil-colour hog-hair brushes, either worn down by use, or rubbed down on fine sandpaper till they are as stiff as you like them to be. You want them different in this: some harder, some softer; some round, some square, and of various sizes (figs. 32 and 33), and with these you brush the matt away gently and by degrees, and so make a light and shade drawing of it. It is exactly like the process of mezzotint, where, after a surface like that of a file has been laboriously produced over the whole copper-plate, the engraver removes it in various degrees, leaving the original to stand entirely only for the darkest of all shadows, and removing it all entirely only in the highest lights.
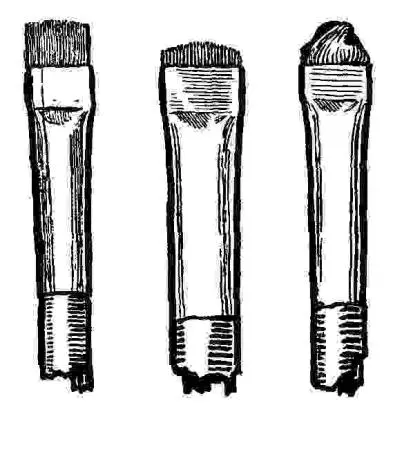
Fig. 33.
There is nothing for this but practice; there is nothing more to tell about it; as the conjurers say, "That's how it's done." You will find difficulties, and as these occur you will think this a most defective book. "Why on earth," you will say, "didn't he tell us about this, about that, about the other?" Ah, yes! it is a most defective book; if it were not, I would have taken good care not to write it. For the worst thing that could happen to you would be to suppose that any book can possibly teach you any craft, and take the place of a master on the one hand, and of years of practice on the other.
This book is not intended to do so; it is written to give as much information and to arouse as much interest as a book can; with the hope that if any are in a position to wish to learn this craft, and have not been brought up to it, they may learn, in general, what its conditions are, and then be able to decide whether to carry it further by seeking good teaching, and by laying themselves out for a patient course of study and practice and many failures and experiments. While, with regard to those already engaged in glass-painting, it is of course intended to arouse their interest in, and to give them information upon, those other branches of their craft which are not generally taught to those brought up as glass-painters.
CHAPTER V
Cutting (advanced)—The Ideal Cartoon—The Cut-line—Setting the Cartoon—Transferring the Cut-line to the Glass—Another Way—Some Principles of Taste—Countercharging.
We have only as yet spoken of the processes of cutting and painting in themselves, and as they can be practised on a single bit of glass; but now we must consider them as applied to a subject in glass where many pieces must be used. This is a different matter indeed, and brings in all the questions of taste and judgment which make the difference between a good window and an inferior one. Now, first, you must know that every differently coloured piece must be cut out by itself, and therefore must have a strip of lead round it to join it to the others.
Draw a cartoon of a figure, bearing this well in mind : you must draw it in such a simple and severe way that you do not set impossible or needlessly difficult tasks to the cutter. Look now, for example, at the picture in Plate V. Конец ознакомительного фрагмента. Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес». Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес. Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.
by Mr. Selwyn Image—how simple the cutting!
You think it, perhaps, too "severe"? You do not like to see the leads so plainly. You would like better something more after the "Munich" school, where the lead line is disguised or circumvented. If so, my lesson has gone wrong; but we must try and get it right.
You would like it better because it is "more of a picture"; exactly, but you ought to like the other better because it is "more of a window." Yes, even if all else were equal, you ought to like it better, because the lead lines cut it up. Keep your pictures for the walls and your windows for the holes in them.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Stained Glass Work: A text-book for students and workers in glass»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Stained Glass Work: A text-book for students and workers in glass» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Stained Glass Work: A text-book for students and workers in glass» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.