3. By refocusing staff and budget on service operations, the organization repaired and rebuilt its distinctive quality capabilities for remaining customers. Customer churn was halted.
The solution, while painful in the short term, allowed the provider to break the vicious cycle and pave a long-term strategy for regaining customers. The counter-intuitive breakthrough was based on (a) a big picture view of services and (b) the precept of superior performance versus competing alternatives.
Case example 8 (solution): She used service management as a strategic asset
Rather than caution the subscribers about the marked increase in capacity usage, the manager offered the irreverent analysts the chance to create their own site. The site, now called the Motley Fool, continues to be a heavily trafficked destination for financial advice. The line manager eventually became president of programming.
The manager understood the service provider’s strategic intent: deeper consumer connectivity or broader distribution
4 Service strategy
4.1 Define the market
4.1.1 Services and strategy
Organization s have an interest in strategy within the context of service management in two distinct but related perspectives. There are strategies for services and there are services for strategies (Figure 4.1). From one perspective, strategies are developed for services offered. Providers differentiate their services from competing alternatives available to customers.
From the other perspective, service management is a competence for offering services as part of a business strategy . A software vendor may decide to offer software as a service . It combines its capabilities in software development with new capabilities in service management . It also makes use of its capabilities in maintaining software application s to bundle technical support as part of the core service . By adopting a service-oriented approach supported by service management capabilities, the vendor has transformed itself into a service business. This approach has also been adopted by internal software engineering groups who have changed from being cost centre s to being profit centre s.
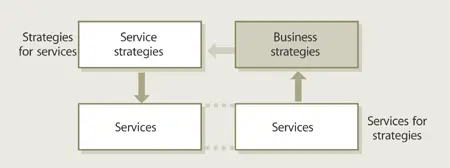
Figure 4.1 Strategies for services and services for strategies
For example, the market leader in airline reservation system s originated from a successful internal computer-based reservation system of a major airline. Such transformations require strong capabilities in marketing, finance, and operations.
4.1.2 Understand the customer
Organization s strive to achieve business objective s using whatever asset s they have at hand, subject to various constraints. Constraints include costs and risk s attributable to complexity, uncertainty and conflicts in the business environment . The value-creating potential of the business depends on the performance of business assets. Asset s must perform well at their full potential. The assets may be owned by the business or available for use from others under various types of financial arrangements.
More often than not such arrangements are agreement s or contract s for services. Business managers are given the responsibility, authority, and resource s necessary to deliver certain outcomes using the best possible means. Service s are a means for managers to enable or enhance the performance of business assets leading to better outcomes. The value of a service is best measured in terms of the improvement in outcomes that can be attributed to the impact of the service on the performance of business assets. Some services increase the performance of customer assets, some services maintain performance, and yet others restore performance following adverse event s. A major aspect of providing value is preventing or reducing the variation in the performance of customer assets.
In a trading system, for example, it is not enough for the service to feed the trading system with real-time market data. To minimize trading losses the data feed must be available without interruption during trading hours, and at as many trading desks necessary with a contingency system in place. An investment bank is therefore willing to pay a premium for a news-feed service providing a higher level of assurance than a service used by a competitor. The difference translates into greater trading gains.
Focus on customer assets
The performance of customer assets should be a primary concern of service management professionals because without customer assets there is no basis for defining the value of a service.
4.1.3 Understand the opportunities
Customer s own and operate configurations of assets to create value for their own customers. The assets are the means of achieving outcomes that enable or enhance value creation. For example, for a lending bank value is created by the outcome of processing a loan application on time (Figure 4.2). Customers receiving the loan will have access to the required financial capital and the lender benefits from the onset and accrual of interest. The lending process is therefore a business asset whose performance leads to specific business outcomes.

Figure 4.2 Analysing an outcome23
It is important for managers to gain deep insight into the businesses they serve or target. This includes identifying all the outcomes for every customer and market space that falls within the scope of the particular strategy . For the sake of clarity, outcomes are classified and codified with reference tag s that can be used in various contexts across the Service Lifecycle (Table 4.1).
Category
Tag
Outcome statement
Enhanced capabilities (EC)
EC1
Decision making and action in response to business events is faster
EC2
Increase in knowledge, skills, and experience for business process es
EC3
Business process es are enhanced with superior logic
EC4
Industry best practice s are available through application updates
EC5
Supply chain is extended
EC6
Availability of specialized knowledge and expertise
Increased performance (IP)
IP1
Increase in throughput of business processes
IP2
Decrease in average collection period (accounts receivables)
IP3
Increase in return on asset s
IP4
Increase in customer satisfaction
Enhanced resource s (ER)
ER1
Resource s are freed up for new opportunities
ER2
Increase in productivity of staff
ER3
Increased flexibility in operations
ER4
Increase in available resources
Reduced costs (RC)
RC1
Decrease in fixed cost s of business process
RC2
Decrease in unit cost s of employee benefits administration
RT3
Lower start-up time for new or expanded operations
Reduced risk s (RR)
RR1
Decrease in operational risks from variation in performance of assets
Читать дальше


