Managers rely on mental models that will assure them that they will indeed achieve desired outcomes. Trouble occurs when they use the wrong mental model for the problem at hand. What appears as unfixable or random often looks that way because of a misunderstanding of a process or system . Without underlying principles, it is not possible to explain why a perfectly good solution fails in one instance after tremendous success in another.
A good business model describes the means of fulfilling an organization ’s objective s. However, without a strategy that in some way makes a service provider uniquely valuable to the customer, there is little to prevent alternatives from displacing the organization, degrading its mission or entering its market space . A service strategy therefore defines a unique approach for delivering better value. The need for having a service strategy is not limited to service provider s who are commercial enterprises. Internal service provider s need just as much to have a clear perspective, positioning and plan s to ensure they remain relevant to the business strategies of their enterprises.
Customer s continually seek to improve their business models and strategies. They want solutions that break through performance barriers – and achieve higher quality of outcomes in business process es with little or no increase in cost , as in Figure 3.23. Such solutions are usually made available through innovative products and services. If such solutions are not available within a customer’s existing span of control , service contract s, or value network , they are compelled to look elsewhere.
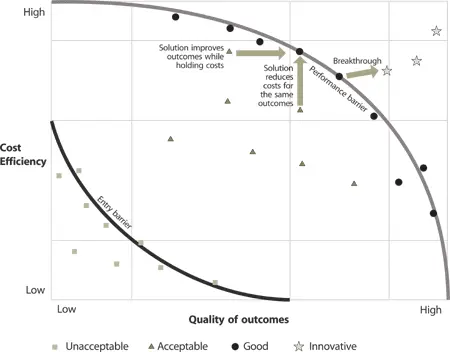
Figure 3.23 Innovative solutions break through performance barriers
Service providers should not take for granted their position and role within their customer’s plan s even though they have the advantage of being incumbents. The value of services from a customer’s perspective may change over time due to conditions, event s, and factors outside a provider’s control. A strategic view of service management means a carefully considered approach to the relationships with customers and a state of readiness in dealing with the uncertainties in the value that defines that relationship .
Imagine you have been given responsibility for an IT organization . This organization could be internal or external, commercial or not-for-profit. How would you go about deciding on a strategy to serve customers? First, acknowledge that there exist other organizations whose aims are to compete with yours. Even government agencies are subject to competitive forces. While the value they create can sometimes be difficult to define and measure, these forces demand that an organization should perform its mission better than the alternatives.
Second, decide on an objective or end-state that differentiates the value of what you do, or how you do it, so that customers believe there is no true alternative. The form of value may be monetary, as in higher profits or lower expenses, or social, as in saving lives or collecting taxes. The differentiation can come in the form of barriers to entry, such as your organization’s know-how of your customer’s business or the broadness of your service offerings. Or it may be in the form of raising switching costs, such as lower cost structures generated through specialization or service sourcing . Either way, it is a means of doing better by being different.
The basic premise of service strategy is that service provider s must meet objectives defined in terms of their customers’ business outcomes while subject to a system of constraints. In a world of constrained resource s and capabilities, they must hold their positions against competing alternatives. By understanding the trade-offs involved in its strategic choices, such as services to offer or markets to serve, an organization can better serve customers and outperform its competitors. The goal of a service strategy can be summed up very simply: superior performance versus competing alternatives.
Case example 8: Internet service provider
Some time in the mid-1990s, a line manager for a leading internet service provider (ISP) noticed a large amount of increased traffic on the bulletin board folders for two satiric stock analysts.
The ISP had adopted the strategic perspective of, ‘Consumer connectivity first – any time, anywhere’.
Rather than caution the subscribers about the abnormal increase in capacity usage, the manager took an alternative path.
What do you think she did?
(Answer at the end of the chapter)
Successful strategies are based on the ability to take advantage of a set of distinct capabilities in offering superior value to customers through services. Such capabilities are viewed as strategic asset s because a service provider can depend on them for success in a market space . Success comes from not only delivering value to customers but also being able to generate returns on investments. Strategic assets are carefully developed bundles of tangibles and intangibles, most notably knowledge, experience, system s, and processes. Service management is a strategic asset because it constitutes the core capabilities for service providers. Service management acts as an operating system for service assets in effectively deploying them to provide services.
A service strategy is sometimes thought of as a future course of action. When senior managers are asked to craft a strategy , the frequent response is a strategic plan detailing how the organization moves from its current state to a desired future state. But there are shortcomings with this definition of service strategy.
The first problem is conditions change. The pace of business change is quickening, no matter how large or small your organization or in what industry you compete. Opportunities arise while others disappear. The world does not hold still waiting for plans to unfold. What was good about a plan today may be rendered a liability tomorrow. A service strategy resolves big issues so that staff can get on with the small details – how best to provide services, for example, rather than debating what services to offer. But focusing on a strategic plan impedes the organization’s ability to respond to changing conditions. Organization s with a high reliance on consistency and formalized procedures, for example, may lose flexibility, the ability to innovate or the ability to quickly adapt to unforeseen conditions. It turns out that a planning approach, while necessary, is insufficient – a service strategy requires more than a plan or direction.
The second problem is the constant focus on improving operational effectiveness. Operational effectiveness is absolutely necessary, but is not enough. A service strategy explains how a service provider will do better – either in what it does or how it does it – not only compared to itself but against competing alternatives. Customers hold government agencies and non-profit organizations to the same standards as service providers in the private sector. Customers must believe there are no reasonable alternatives. The form of value may be monetary, as in higher profits or lower expenses, or social, as in providing healthcare or preventing crime. If a provider’s strategy focuses on operational effectiveness at the expense of distinctiveness, it will not prosper for long. Sooner or later every organization runs into competitors.
Читать дальше

