Heat was just as debilitating as cold and a great many of the 100 battles recorded here were fought in searing temperatures and dry conditions that quickly turned the battlefield into a fog of churned-up dust or sand. The critical resource in all kinds of weather, more important for soldiers than any weapon, was water. It is what every wounded soldier asks for first. A shrewd commander makes sure that the army is camped near a supply of fresh water or that water can be ferried to the battlefield. Richard the Lionheart only won the battle at Arsuf because Crusader ships plied along the coast leading to Jaffa with barrels of water for the exhausted, sweaty Europeans in his army. Even then, men died of heat exhaustion on the way. It is hard to imagine having to fight amidst all the clamour and gore of the battlefield for hours on end with no prospect of water to assuage the debilitating effects of dehydration. American army recruits in the Second World War did ‘water hikes’ to prepare them for the reality of battle, marching 100 kilometres (60 miles) over two days in warm weather with just a 1-litre (2-pint) canteen to last the whole time. ‘My mouth starts sticking to itself,’ wrote William Wharton, ‘my tongue to the top of my mouth, my teeth to my lips, my lips to each other.’
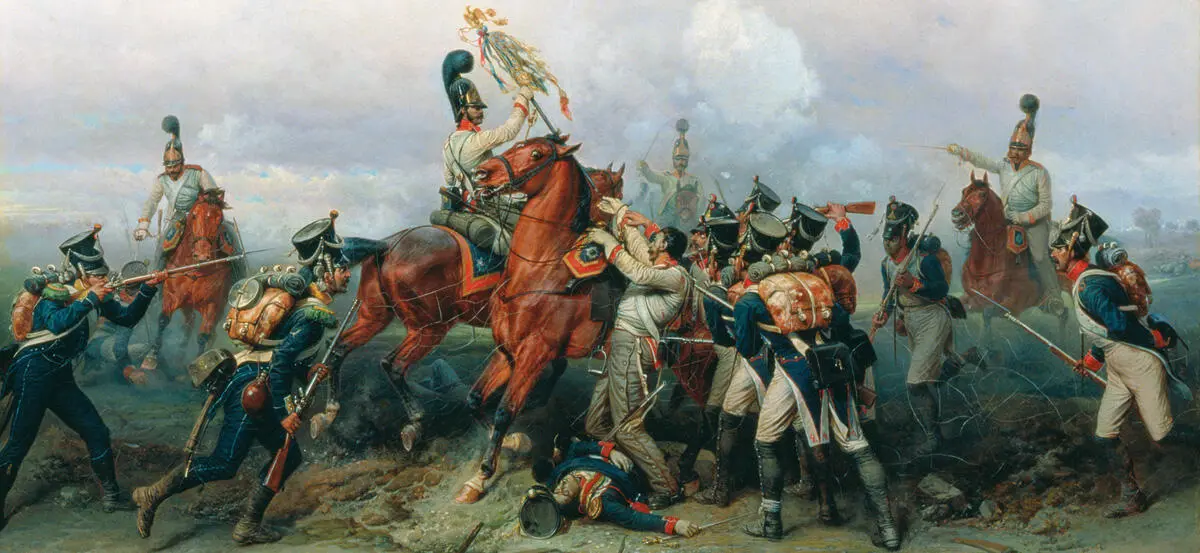

© State Central Military Museum, Moscow, Russia/The Bridgeman Art Library
The Exploit of the Mounted Regiment (1884), by Russian military artist Bogdan Willewalde (1819–1903), depicts an episode during the Battle of Austerlitz in December 1805 between the French armies of Napoleon and the forces of Alexander I of Russia and Francis I, Habsburg ruler of the Austrian Empire. Even battles on this scale became a series of small engagements that merged together into the larger conflict.
There comes a moment in most battles whose outcome is decided in a day or so of combat when one side or the other senses victory and the other senses defeat. Since most soldiers can see little more of the battlefield than what is immediately around them and are given almost no information in the midst of a battle, the way that sense is communicated comes either from the exhortations of commanders if victory seems likely, or the flight of leaders who realize that they have lost. The effect when a commander flees – as at Bannockburn in 1314 when Edward II turned tail – can be immediately damaging. Flight or surrender is a fast-moving infection. Once it is evident, the willingness to continue fighting evaporates with a startling speed. One of the strangest phenomena in battle is the moment when soldiers, who only minutes before are firing muskets or hacking away at the enemy, realize that they have to save themselves. Of course, surrender was often not an option, and there are numerous accounts of battles ancient and modern in which a unit of soldiers or horsemen is annihilated where its stands, surrounded by a sea of enemies. What that moment of certain death means, when men are observed fighting with a frenetic energy against all the odds, self-evidently cannot be known. But where it is possible to flee, at the exact moment when confidence in the outcome collapses, soldiers do so, sometimes in good order, but in a great many battles in complete panic. They are then pursued, hunted down and butchered. Napoleon’s Imperial Guard at Waterloo hurled themselves into the fray with determination, but shortly after, as Wellington’s lines moved forward, they could be seen on their knees weeping and calling for mercy. Soldiers in flight experience a psychological transformation now that their only concern is to save themselves rather than to protect the group.
For ordinary soldiers, the comprehension that they have won a battle can take time to sink in, partly because a large battlefield is a messy and incoherent whole, in which fighting might continue for longer in one small part while overall victory is assured. The Battle of Austerlitz was essentially won by Napoleon by mid-day, but the fighting did not finish at one end of the field for another four hours. Even commanders often have only a hazy view of how a battle is going. They have relied until recently on primitive forms of communication once battle is joined. Very few armies imitated the Mongols, whose commanders would seek high ground in order to signal with coloured flags to their units about their movement on the battlefield. Navies were better adapted to complex signalling, but even here a naval mêlée could easily mask the overall balance of the battle. Otherwise, even with the advent of radio, it could be difficult to direct embattled units or to be confident that plans were being fulfilled. Victory slowly emerged from the literal fog of war only when the enemy abandoned the field, surrendered, or was surrounded and killed.
Victory in battle is clearly likely to be exhilarating and soldiers and sailors indulge that victory in a variety of ways, though time and again they are evidently too exhausted, too damaged and too thirsty to do anything more than occupy the ground. Organized pursuit of a broken enemy, even if strategically sensible, is risky with exhausted men and in many famous cases failed to materialize. The aftermath of battle can be anti-climactic for the winners, particularly the wounded, who die later in droves after battles ancient or modern, their thankless task achieved at an awful cost. Nor is there any guarantee that once the fight is over, there will be food and water available. The Swedish victors at Breitenfeld had to wait until the following morning before they were given anything to eat or drink. The soldiers who survive know what they have done and will use it to weave their own personal narratives, heroic or otherwise. In earlier battles they were often rewarded at once to avert potential disaffection or mutiny and to maintain discipline among men now liberated from the tension of combat.
However exhilarating victory might be, at least for a bittersweet moment, battles seldom decided a war, and victory in one battle could quickly be tarnished by defeat in the next. Beaten soldiers or sailors returned home understanding the nature of their failure, even if glad to have survived. Japanese soldiers were encouraged to kill themselves rather than remain alive and dishonoured. One young conscript in the 1930s recorded in his diary that he was given a knife by his mother so that he could ritually disembowel himself if he was captured. The homecoming could be a mixed blessing even for the victors. The sailors who helped to defeat the Spanish Armada in 1588 were delivered to ports in England a few weeks later with no pay and no means of finding food or shelter save begging. Winning a battle could also be costly for the fortunate commander. The Roman general Flavius Aetius, who defeated Attila the Hun, was battered to death by his jealous emperor in person when he returned to Rome. The victor of Ain Jalut, where the Mongols were finally stopped in their tracks on their way to Egypt, was murdered by jealous officers on his way home. Battle is an event in its own right, with its own history and outcome, but what is made of the battle depends on the wider historical context, political as much as military. Winning in this sense really is only half the battle.
In some cases, battles have been used to serve as symbols or myths to endorse a particular political order or to encourage a shared cultural identity, and have soon assumed a historically abstract character, important for what they might mean for future generations and often surrounded by embellishments that turn the account from historical reality into a comfortable legend. For most ancient and early medieval battles, historians rely on accounts that are literary representations of what might have happened, largely devoid of detail and usually written long after the event. The eleventh-century epic French poem Chanson de Roland was based loosely on a battle that took place at Roncesvalles three centuries before, but its purpose by then was to enshrine notions of Christian nobility in French culture. The famous battle on the ice at Lake Peipus in 1242, where Alexander Nevsky drove back the German invader, was distorted by centuries of myth-making, and in the twentieth century it was adopted as a central motif of Soviet propaganda against the fascist enemy in the Second World War. The Battle of Britain and the Battle of the Somme have become central epic accounts in the search for a British identity, symbols of endurance and courage. Other battles are appropriated as foundation moments – the Battle of the Volturno River in 1860 cemented the unification of Italy; Marengo paved the way for Napoleon’s empire; Actium in 31 BCE became the founding battle of the Augustan age and the triumph of Octavian. There is also a history of how battles have been remembered once they are transformed over time into legend, distinct from the history of the battles themselves.
Читать дальше